PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
Will Russia Sanctions Accelerate Inflation, Devalue US Dollar and Strengthen Chinese Yuan?
Russia is a commodities superpower. The nation's Eurasian landmass is rich in all kinds of natural resources from food to fuel to metals. To punish Moscow for invading Ukraine, the US and G-7 nations have imposed sanctions on Russia. These sanctions have effectively removed Russian commodities from the global supply chain, triggering double digit price increases for food, fuels and metals. Will the G-7 actions leave the US dollar much weaker? Will the Chinese currency, backed by commodities, gain strength at the expense of the US dollar and Euro? Will the era of commodity-backed money return? In a note to clients, Credit Suisse investment strategist Zoltan Pozsar has answered some of these questions. He says "this (Russia) crisis is not anything we have seen since President Nixon took the U.S. dollar off gold in 1971". "After this war is over, "money" will never be the same again.....and bitcoin (if it still exists then) will probably benefit from all this,” he adds.
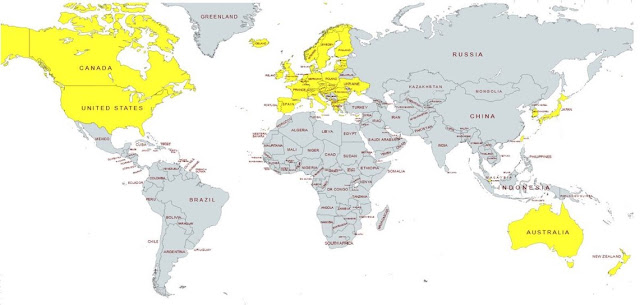 |
| Map of "International Community" Sanctioning Russia |
Post World War II History:
The current global financial system was created in Bretton Woods located in the US State of New Hampshire. Over 700 delegates representing 44 countries met in Bretton Woods in July 1944. The Bretton Woods System, now referred to as Bretton Woods I, required a currency peg to the U.S. dollar which was in turn pegged to the price of gold. This system collapsed in the 1970s but created a lasting influence on international currency exchange and trade through its development of the IMF and World Bank. Zoltan Pozsar believes it is now time for Bretton Woods III. What is Bretton Woods III? Here's how Zoltan Pozsar explains it:
"From the Bretton Woods era backed by gold bullion, to Bretton Woods II backed by inside money (Treasuries with un-hedgeable confiscation risks), to Bretton Woods III backed by outside money (gold bullion and other commodities)".
 |
| Russia's Commodity Exports. Source: Bloomberg |
Commodity Superpower:
Russia is a vast country. Russian landmass extends from Europe to East Asia. It is one of the largest suppliers of oil, gas, metals and wheat. Russia is also a major exporter of fertilizer. China will likely take advantage of the western sanctions to buy up Russian commodities at lower prices.
Pozsar argues that while Western central banks cannot close the gap between Russian and non-Russian commodity prices as sanctions lead them in opposite directions, the People’s Bank of China can “as it banks for a sovereign who can dance to its own tune.”
“If you believe that the West can craft sanctions that maximize pain for Russia while minimizing financial stability risks and price stability risks in the West, you could also believe in unicorns,” Pozsar wrote.
 |
| Pre-Ukraine War Inflation in US. Source: Wall Street Journal |
Bretton Woods III:
Pozsar argues that the Bretton Woods II collapsed when the G7 countries seized Russia’s foreign exchange (FX) reserves, leading to a rise of outside money – reserves kept as commodities – over inside money – reserves kept as liabilities of global financial institutions.
 |
| East vs West Economic Output. Source: Wall Street Journal |
"We are witnessing the birth of Bretton Woods III – a new world (monetary) order centered around commodity-based currencies in the East (Chinese Yuan) that will likely weaken the Eurodollar system and also contribute to inflationary forces in the West,” Zoltan wrote.
Related Links:
Pakistani-American Banker Heads SWIFT, the World's Largest Interban...
Pakistani-Ukrainian Billionaire Zahoor Sees "Ukraine as Russia's Af...
Ukraine Resists Russia Alone: A Tale of West's Broken Promises
Ukraine's Lesson For Pakistan: Never Give Up Nuclear Weapons
Can the Chinese Yuan Replace the US Dollar?
Ukraine's Muslim Billionaire Akhmetov Holds Balance of Power
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 5, 2022 at 8:32pm
-
#India's #payment giant #NPCI has #SWIFT alternative for 32 million #NRIs. UPI (Unified Payment Infrastructure) linkage with other nations will anchor #trade, #travel, #remittance flows between countries & lower the cost of cross-border transactions https://www.livemint.com/news/india/payment-giant-npci-has-swift-al...
The company that built India’s digital payments backbone plans to make it cheaper and easier for the nation’s 32 million expatriates to bring their money home.
Indians overseas remitted $87 billion last year, the biggest inflow for any country tracked by the World Bank. The remittances market, where it costs $13 on average to send $200 across borders, is ripe for disruption, according to Ritesh Shukla, chief executive officer of NPCI International Payments Ltd.
“We have displaced cash in India to a large extent and are now looking to repeat the success in cross-border corridors," said Shukla. “Overseas Indians can use our rails to remit money inwards straightway into their bank accounts, and for the markets where Indians travel frequently, we will build acceptance for our instruments."
Successful overseas forays by NCPI would give India a home-grown alternative to SWIFT, the Belgium-based cross-border payment system operator, though Shukla stressed that the objective was not to displace existing platforms. About 330 banks and 25 apps -- including Alphabet Inc.’s Google Pay and Meta Platform Inc.’s WhatsApp -- share NCPI’s unified payment interface, which has helped make instantaneous digital transactions a $3 trillion market in India.
NPCI is in the process of connecting the UPI platform to systems in other countries to replicate its domestic success. It is negotiating collaborations with governments, fintech companies and service providers around the world, aiming to reduce transaction costs and enable more small-ticket transactions, Shukla said.
Cutting Costs
“This is going to take the payments world by storm," said Mayank Goyal, CEO of moneyHop, a cross-border banking app that lets users make international remittances through the SWIFT network. The company will seek to integrate UPI rails into the app as it makes cross-border payments easier, Goyal said.
UPI’s linkage with overseas nations will further anchor trade, travel and remittance flows between the countries and lower the cost of cross-border remittances, the Reserve Bank of India said in a report.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 13, 2022 at 7:43am
-
#US #inflation soars to record high of 9.1% in 4 decades. Prices were up broadly across the #economy as inflation reached its highest rate in nearly 41 years in June
https://www.wsj.com/articles/us-inflation-june-2022-consumer-price-...
U.S. consumer inflation rose to a new four-decade high at an annual rate of 9.1% in June, extending a year and a half stretch of persistently higher prices.
The consumer-price index’s rate of increase last month was the highest since December 1981, the Labor Department said Wednesday. It also eclipsed May’s annual rate of 8.6% that led Federal Reserve officials to shift to a faster pace of benchmark interest-rate increases in its campaign to bring down inflation.
The report likely keeps the Fed on track to raise its benchmark interest rate by 0.75 percentage point at its meeting later this month. Stocks dropped and bond yields jumped following the inflation report.
Core prices, which exclude volatile food and energy components, increased by 5.9% in June from a year earlier, slightly less than May’s 6.0% gain, the Labor Department said.
On a month-to-month basis, core prices rose 0.7% in June, a bit more than their 0.6% increase in May—a sign of inflationary pressures throughout the economy.
The report showed few signs of relief from higher prices. Costs were up broadly across the economy, with gasoline far outpacing other categories with an 11.2% gain over the prior month. Gasoline prices have been on a downward path in recent weeks. Shelter and food price increases were also major contributors to inflation, the Labor Department said.
“This report will make for very uncomfortable reading at the Fed,” said Ian Shepherdson, chief economist at Pantheon Macroeconomics.
Despite June’s inflation reading, economists point to recent developments that could subdue price pressures in the coming months.
Investor expectations of slowing economic growth world-wide have led to a decline in commodity prices in recent weeks, including for oil, copper, wheat and corn, after those prices rose sharply following the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Retailers have warned of the need to discount goods, especially apparel and home goods, that are out of sync with customer preferences as spending shifts to services and away from goods, and consumers spend down elevated savings.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 18, 2022 at 11:10am
-
#Russia seeking #oil payments from #India in #UAE dirhams as #Moscow moves away from the #US #dollar to insulate itself from the effects of Western #sanctions. #Ukraine #energy #EU
https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/exclusive-russia-seeking-oi...
Russia is seeking payment in United Arab Emirates dirhams for oil exports to some Indian customers, three sources said and a document showed, as Moscow moves away from the U.S. dollar to insulate itself from the effects of Western sanctions.
Russia has been hit by a slew of sanctions from the United States and its allies over its invasion of Ukraine in late February, which it terms a "special military operation".
An invoice seen by Reuters shows the bill for supplying oil to one refiner is calculated in dollars while payment is requested in dirhams.
Russian oil major Rosneft is pushing crude through trading firms including Everest Energy and Coral Energy into India, now its second biggest oil buyer after China.
Western sanctions have prompted many oil importers to shun Moscow, pushing spot prices for Russian crude to record discounts against other grades.
That provided Indian refiners, which rarely bought Russian oil due to high freight costs, an opportunity to snap up exports at hefty discounts to Brent and Middle East staples.
Moscow replaced Saudi Arabia as the second biggest oil supplier to India after Iraq for the second month in a row in June.
At least two Indian refiners have already settled some payments in dirhams, the sources said, adding more would make such payments in coming days.
The invoice showed payments to be made to Gazprombank via Mashreq Bank, its correspondent bank in Dubai.
The United Arab Emirates, seeking to maintain what it says is a neutral position, has not imposed sanctions on Moscow, and the payments could add to the frustration of some in the West, who privately say the UAE's position is untenable and siding with Russia..
The trading firms used by Rosneft have started asking for the dollar equivalent payment in dirhams from this month, the sources said.
Rosneft, Coral Energy and Everest Energy did not respond to Reuters emails seeking comment.
Russia wants to increase its use of non-Western currencies for trade with countries such as India, its foreign minister Sergi Lavrov said in April.
The country's finance minister last month also said Moscow may start buying currencies of "friendly" countries, using such holdings to influence the exchange rate of the dollar and euro as a means of countering sharp gains in the rouble.
The Moscow currency exchange is preparing to launch trading in the Uzbek sum and the dirham.
Dubai, the Gulf's financial and business centre, has emerged as a refuge for Russian wealth.
India, also maintaining a neutral position, recongnises insurance cover by Russian companies and has offered classification to ships managed by a Dubai-based subsidiary of Moscow's top shipping group to enable trade.
India's central bank last week introduced a new mechanism for international trade settlements in rupees, which many experts see as a way to promote trade with countries that are under Western sanctions, such as Russia and Iran.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 19, 2022 at 4:27pm
-
The dollar sits atop a global monetary order shaken by sanctions
Countries tend to hold certain currencies as reserve assets mostly for economic, not geopolitical, reasons
ISABELLE MATEOS Y LAGO
https://www.ft.com/content/e2a69a2b-8eb1-4164-97ab-7a532cf743a2
"But ultimately, international reserves are held for specific economic reasons, not geopolitical ones: pegging or managing the exchange rate to another currency; paying for imports and international debt service; providing foreign exchange liquidity of last resort to domestic banks. So what will determine the extent of any shift in global reserve allocations is not the portfolio preferences of central bankers or the intrinsic properties of US dollar alternatives. It is whether new currencies come to play an important role in international trade and financial relations. The recent news of China negotiating with Saudi Arabia to pay for oil in renminbi is not, in itself, game-changing. If it finally happens and more of China’s inbound and outbound trade partners follow, it might well be"
-----
Days after Russian troops invaded Ukraine, the G7 and a host of allies in Europe and Asia declared a freeze on the assets of the Central Bank of Russia. The move, unprecedented in its swiftness and scale, instantly incapacitated roughly half of its $630bn in international reserves. Up to this point, central bank reserves had only been frozen multilaterally after abrupt regime change — think of the Bolshevik and Chinese revolutions, or more recently Hugo Chávez’s Venezuela.
Immediately, warnings were uttered about unintended consequences, in particular the stability of the US dollar in the international monetary system. As many have convincingly argued, the Russian reserves freeze alone is unlikely to end the dominant role of the US dollar. But it might, over time, induce major shifts in global monetary relations alongside a broader rewiring of globalisation, making the last 30 years look like a lost golden age.
Prudence and deliberation are in central banks’ DNA. They do not make rash decisions. So while many central bankers privately felt shock or dismay at the reserves freeze, they do not appear to have significantly reallocated assets away from the dollar or euro.
Yet there is consensus among central bank reserve managers that something fundamental has changed: geopolitical considerations now need to be taken into account when assessing the safety and liquidity of a reserve asset. For most, this is an argument in favour of currency diversification, a trend under way already over the past 20 years at the expense of the US dollar and to the benefit of smaller advanced economy currencies such as the Canadian dollar or the Korean won. This might now accelerate, and possibly extend to additional currencies.
Might the renminbi be one of the beneficiaries, as suggested by a recent survey? In fact, when it comes to the attractiveness of Chinese bonds in reserve portfolios after the sanctions on Russia, geopolitics is a clear dividing line. By and large, central bankers I talk to in countries in or close to the sanctioning coalition are reviewing — but not yet retreating from — whatever exposure or planned exposure they had to the renminbi. Others seem more inclined to stick to their holdings and plans to ramp them up further over time.
In the near term there is little practical scope to overhaul trade and financing patterns, even if some countries want to. But other forms of rewiring may develop. Countries that see themselves as politically aligned may try to create a mutual aid system, separate from the sanctioning coalition. China’s recent creation of a renminbi liquidity facility at the Bank for International Settlements can be seen in this light. Discussions could also resurface between large reserve holders from the global south about swap arrangements, like those between the Fed, European Central Bank, Bank of England and a few others in the 2008 financial crisis. Cross-border payment systems to rival Swift will probably continue to grow.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 30, 2022 at 6:30pm
-
JPMorgan says #Russia has had no problem rerouting its #oil #exports from #Europe. Expects Russian production in Q3 to be higher than a year ago. Better-than-expected global production amid signs of a drop in #demand pushing oil #prices lower. #Ukraine https://africa.businessinsider.com/markets/jpmorgan-says-russia-has...
Russia has been able to reroute its oil exports away from Europe without serious disruptions, JPMorgan has said, adding that the expected drop in output "never happened."
Better-than-expected Russian production, along with the release of oil from global strategic reserves, helps explain the recent drop in crude prices, the bank's head of commodities research Natasha Kaneva said in a note to clients.
Russia's oil exports to Europe its biggest market have fallen relatively sharply in 2022, as companies have "self-sanctioned" in the wake of Vladimir Putin's invasion of Ukraine in late February.
However, Russia has been able to shift its exports towards Asia, with India and China in particular stepping up their purchases. More recently, a jump in domestic demand has caused Russian oil production to rise back to prewar levels.
"The market consensus was too pessimistic about Russia's capability to re-route volumes to other buyers," Kaneva and her colleagues said in the note Wednesday. "Russia's exports adjusted towards other buyers without a serious disruption to its production."
"At its peak, the oil market was pricing in the worst-case scenario a 3 million barrel a day loss of Russian production combined with record-high summer demand while, in reality, it never happened."
JPMorgan expects Russia production to produce 9.95 million barrels a day of oil in the third quarter, above the 9.76 million barrels a day produced in the same quarter a year earlier.
It thinks production will slip to 9.5 million barrels a day in 2023, staying relatively strong despite the European Union's ban on most oil imports from the country.
Oil prices have fallen in recent weeks, with global supply stronger than expected and demand likely to weaken in the coming months as the world economy slows. WTI crude, the US benchmark price, was down around 10% over the last month to trade at $98 a barrel Friday.
Russia's oil and gas revenues have helped Putin's government prop up the local currency, the ruble, alleviating some of the pressure on the economy.
However, the economy is still expected to shrink sharply this year. Imports have cratered in a sign of domestic stress.
Yale academics, led by Jeffrey Sonnenfeld, said in a study this week that Western sanctions are "catastrophically crippling" the economy, with domestic production slowing dramatically.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on August 10, 2022 at 4:55pm
-
The (Chinese) yuan accounted for 31% of the non-US dollar payments for Russian coal in June and the Hong Kong dollar for 28%. The euro made up under a quarter and the Emirati dirham around one-sixth, the data from the trade source showed.
In June, Indian buyers paid for at least 742,000 tonnes of Russian coal using currencies other than the US dollar, according to a summary of deals compiled by a trade source based in India using customs documents and shared with Reuters, equal to 44% of the 1.7 million of tonnes of Russian imports that month.
https://thewire.in/business/indian-companies-are-swapping-dollar-fo....
Indian companies are using Asian currencies more often to pay for Russian coal imports, according to customs documents and industry sources, avoiding the US dollar and cutting the risk of breaching Western sanctions against Moscow.
Reuters previously reported on a large Indian coal deal involving the Chinese yuan, but the customs data underline how non-dollar settlements are becoming commonplace.
India has aggressively stepped up purchases of Russian oil and coal since the war in Ukraine began, helping to cushion Moscow from the effects of sanctions and allowing New Delhi to secure raw materials at discounts compared to supplies from other countries.
Russia became India’s third-largest coal supplier in July, with imports rising by over a fifth compared with June to a record 2.06 million tonnes.
In June, Indian buyers paid for at least 742,000 tonnes of Russian coal using currencies other than the US dollar, according to a summary of deals compiled by a trade source based in India using customs documents and shared with Reuters, equal to 44% of the 1.7 million of tonnes of Russian imports that month.
Indian steelmakers and cement manufacturers have bought Russian coal using the United Arab Emirates dirham, Hong Kong dollar, yuan and euro in recent weeks, according to customs documents separately reviewed by Reuters.
The yuan accounted for 31% of the non-US dollar payments for Russian coal in June and the Hong Kong dollar for 28%. The euro made up under a quarter and the Emirati dirham around one-sixth, the data from the trade source showed.
The Ministry of Finance, which administers the customs board, did not respond to emails seeking comment confirming the documents. The Ministry of Commerce and Industry declined to comment.
The Reserve Bank of India also did not respond to requests for comment.
The RBI has approved payments for commodities in the Indian rupee, a move it expects to boost bilateral trade with Russia in its own currency.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on August 24, 2022 at 2:21pm
-
What's driving inflation?
https://www.wsj.com/articles/inflation-jackson-hole-fed-powell-1166...
Force 1: Globalization. Increased flows of trade, money, people and ideas flourished with the Cold War’s end and China’s entry into the international trading system in the 1990s. Multinational companies using new technologies constructed global supply chains focused on driving down costs by finding the cheapest place and workers to produce products. Worldwide competition drove prices lower for many goods.
This helped keep U.S. inflation stable. Over the 20 years that ended in 2019, U.S. goods prices rose an average of 0.4% a year, while services prices grew 2.6% annually, leaving “core inflation”—which excludes volatile food and energy prices—around 1.7%.
After the pandemic and the Ukraine war disrupted supply chains, many business leaders adopted new processes to increase reliability even if they cost more, such as by moving production closer to home or buying from multiple suppliers. And tensions between Western democracies and Russia and China raise concerns about a possible further retreat from globalization and rise of protectionism, which would raise production costs.
“If you had all of your supply chain in just one country, you have to question why take that risk in a world where pandemics could hit or country relations could deteriorate or wars could happen between countries,” said Richmond Fed President Tom Barkin, a former McKinsey & Co. executive. It is difficult to predict just how durable such changes will be, he added.
Force 2: Labor markets. In an August 2020 book, “The Great Demographic Reversal,” former British central banker Charles Goodhart and economist Manoj Pradhan argued that the low inflation since the 1990s had less to do with central-bank policies and more with the addition of hundreds of millions of low-wage Asian and Eastern European workers, which held down labor costs and prices of manufactured goods exported to richer countries.
Mr. Goodhart wrote that global labor glut was giving way to an era of worker shortages, and hence higher inflation.
Meanwhile, the U.S. labor force has roughly 2.5 million fewer workers since the pandemic began, compared with what it would have if the prepandemic trend in workforce participation had continued and after accounting for the aging of the population, according to an analysis by Didem Tüzemen, an economist at the Kansas City Fed. Its growth had already slowed before Covid-19, reflecting an aging population, declining birthrates and less immigration. The slower growth rate of the U.S. workforce could force wages higher, feeding inflation.
Wages rose about 3% annually before the pandemic. Average hourly earnings grew 5.2% in the year ended in July.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 21, 2022 at 8:37am
-
Bangladesh could be a test case for end of dollar dominance
By Abhishek G Bhaya
https://news.cgtn.com/news/2022-09-20/Bangladesh-could-be-a-test-ca...
Bangladesh is moving to trade in local currencies with two of its largest trading partners – China and India – in a decision that could well prove to be a test case for the end of the U.S. dollar's dominance in global trade.
Last week, Bangladesh allowed its banks to maintain accounts in Chinese yuan for overseas transactions to reduce dependency on the U.S. dollar as the South Asian country grapples to contain its dwindling foreign reserves.
And according to media reports on Monday, India's top lender, State Bank of India, has asked exporters to trade with Bangladesh in rupee and taka warning against settling deals in the U.S. dollar to avoid exposure to Dhaka's falling reserves.
The developments come amid calls from the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) – which has both China and India as its members – for increasing the use of national currencies for trade among the member countries at its leadership summit in the Uzbek city of Samarkand last week. Bangladesh is not yet an SCO member but has applied for observer status in the Eurasian organization.
The South Asian country's $416-billion economy is facing severe stress due to rapidly increasing food and energy prices with the prolonged Russia-Ukraine conflict further widening its current account deficit. Bangladesh is facing a shortage of foreign currency due to higher import bills and a steep fall in the Bangladeshi taka's value against the U.S. dollar in recent months.
The country's foreign exchange reserves fell from $48 billion last year to $37 billion as of last Friday, which is sufficient for import cover for only five months, according to data from Bangladesh's central bank.
No wonder, Bangladesh wants to lower trade dependency on the U.S. dollar and it does not see a problem in dealing in local currencies, as the country's Commerce Minister Tipu Munshi asserted last week. Responding to a query at an event in Dhaka, Munshi said that Bangladesh's finance ministry is studying the issue and working on ways to implement local currency trade with its key trading partners.
Last week, the Bangladesh central bank allowed local banks to carry out overseas transactions in Chinese yuan. It is important to note that China-Bangladesh bilateral currency cooperation dates back to 2018 when Dhaka had authorized dealers to maintain a foreign currency clearing account with the central bank in the Chinese yuan.
The Bangladesh Bank's latest decision followed demands from major business chambers such as the Metropolitan Chamber of Commerce and Industries (MCCI) of introducing a second currency besides the U.S. dollar for international trading amid the surging taka-dollar exchange rate.
The MCCI proposed the Chinese yuan as Beijing happens to be Dhaka's largest trade partner and also the largest source of imports. The fact that China already has a Cross-Border Inter-Bank Payments System (CIPS) with the Chinese yuan as the trading currency was also a factor in Bangladesh's decision.
If Bangladesh creates a mechanism for bilateral trade in local currency with India – its second largest trade partner – as well, as recent reports indicate, it will go a long way in reducing the country's dependence on the U.S. dollar for international trade.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 23, 2022 at 9:39am
-
#Japan's #Toyota to stop #automobile #production in #Russia due to #supplychain disruption amid #UkraineWar & western #sanctions. "After 6 months, we have not been able to resume normal activities and see no indication that we can restart in the future". https://asia.nikkei.com/Politics/Ukraine-war/Toyota-to-terminate-au...
NAGOYA, Japan -- Toyota Motor said Friday it will exit from automobile production in Russia, citing difficulties supplying key materials and parts in the country amid the war in Ukraine.
The automaker suspended operations at its plant in St. Petersburg on March 4, after the Russian invasion began.
"After six months, we have not been able to resume normal activities and see no indication that we can restart in the future," Japan's top automaker said.
A protracted disruption would hurt Toyota's ability to support its employees, leaving it no choice but to end production in the country, it said. Mounting geopolitical risks in the region are believed to have contributed to the decision as well.
Toyota had continued to pay its factory workers after suspending production, reassigning them to maintenance and other tasks instead. Details regarding the termination process and treatment of employees at the St. Petersburg plant will be ironed out at a later time.
Toyota holds a larger market share in Russia than any other Japanese automaker. It produced 80,000 vehicles and sold 110,000 in the country in 2021.
It began locally producing vehicles in 2007 at St. Petersburg. The plant's lineup included the RAV4 sport utility vehicle and the Camry sedan in 2021.
Nissan Motor, another Japanese automaker, has extended its production freeze at its St. Petersburg plant to the end of December from the end of September.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 3, 2022 at 11:04am
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Pakistani Student Enrollment in US Universities Hits All Time High
Pakistani student enrollment in America's institutions of higher learning rose 16% last year, outpacing the record 12% growth in the number of international students hosted by the country. This puts Pakistan among eight sources in the top 20 countries with the largest increases in US enrollment. India saw the biggest increase at 35%, followed by Ghana 32%, Bangladesh and…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on April 1, 2024 at 5:00pm
Agriculture, Caste, Religion and Happiness in South Asia
Pakistan's agriculture sector GDP grew at a rate of 5.2% in the October-December 2023 quarter, according to the government figures. This is a rare bright spot in the overall national economy that showed just 1% growth during the quarter. Strong performance of the farm sector gives the much needed boost for about …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on March 29, 2024 at 8:00pm
© 2024 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network