PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
“So where will the children of the future come from? Increasingly they will come from people who are at odds with the modern world. Such a trend, if sustained, could drive human culture off its current market-driven, individualistic, modernist course, gradually creating an anti-market culture dominated by fundamentalism - a new dark ages.” ― Philip Longman, The Empty Cradle: How Falling Birthrates Threaten World Prosperity & What to Do About It
Fear of Population Bomb:
The above quote captures the true essence of the West's racist fears about what some of them call the "population bomb": East will dominate the West economically and politically for centuries if the growing colored populations of developing Asia and Africa turn the West's former colonies into younger and more dynamic nations with rising education and better living standards.
Much of the developed world has already fallen below the "replacement" fertility rate of 2.1. Fertility rates impact economic dynamism, cultural stability and political and military power in the long run.
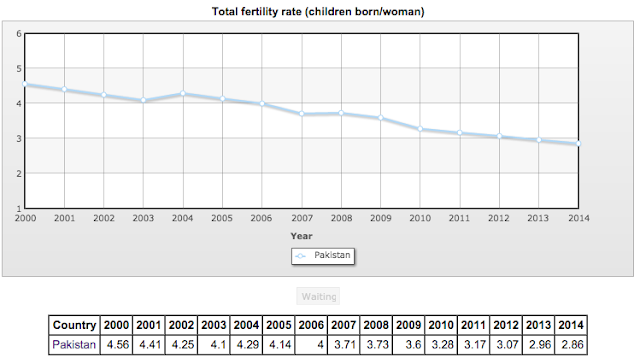
Pakistan Population Growth:
Pakistani women's fertility rates have declined significantly from about 4.56 in 2000 to 2.86 babies per woman in 2014, a drop of 37% in 14 years. In percentage terms, Pakistan population growth rate has come down from 2.3% in 2000 to 1.6% in 2014, a decline of about 30%. It is being driven drown by the same forces that have worked in the developed world in the last century: increasing urbanization, growing incomes, greater participation in the workforce and rising education. Pakistan now ranks 65 among 108 countries with TFR of 2.1 (replacement rate) or higher.
Total Fertility Rate Per Pakistani Woman. Source: CIA World FactBook |
Pakistan is already the most urbanized country in South Asia and its urbanization is accelerating. Pakistan has also continued to offer much greater upward economic and social mobility to its citizens than neighboring India over the last two decades. Since 1990, Pakistan's middle class had expanded by 36.5% and India's by only 12.8%, according to an ADB report titled "Asia's Emerging Middle Class: Past, Present And Future.
Pakistan Population Growth in Percentage Terms. Source: World Bank |
Pakistan has the world’s sixth largest population, seventh largest diaspora and the ninth largest labor force with growing human capital. With rapidly declining fertility and aging populations in the industrialized world, Pakistan's growing talent pool is likely to play a much bigger role to satisfy global demand for workers in the 21st century and contribute to the well-being of Pakistan as well as other parts of the world.
With half the population below 20 years and 60 per cent below 30 years, Pakistan is well-positioned to reap what is often described as "demographic dividend", with its workforce growing at a faster rate than total population. This trend is estimated to accelerate over several decades. Contrary to the oft-repeated talk of doom and gloom, average Pakistanis are now taking education more seriously than ever. Youth literacy is about 70% and growing, and young people are spending more time in schools and colleges to graduate at higher rates than their Indian counterparts in 15+ age group, according to a report on educational achievement by Harvard University researchers Robert Barro and Jong-Wha Lee. Vocational training is also getting increased focus since 2006 under National Vocational Training Commission (NAVTEC) with help from Germany, Japan, South Korea and the Netherlands.
Pakistan's work force is over 60 million strong, according to the Federal Bureau of Statistics. With increasing female participation, the country's labor pool is rising at a rate of 3.5% a year, according to International Labor Organization.
With rising urban middle class, there is substantial and growing demand in Pakistan from students, parents and employers for private quality higher education along with a willingness and capacity to pay relatively high tuition and fees, according to the findings of Austrade, an Australian govt agency promoting trade. Private institutions are seeking affiliations with universities abroad to ensure they offer information and training that is of international standards.
 Trans-national education (TNE) is a growing market in Pakistan and recent data shows evidence of over 40 such programs running successfully in affiliation with British universities at undergraduate and graduate level, according to The British Council. Overall, the UK takes about 65 per cent of the TNE market in Pakistan.
Trans-national education (TNE) is a growing market in Pakistan and recent data shows evidence of over 40 such programs running successfully in affiliation with British universities at undergraduate and graduate level, according to The British Council. Overall, the UK takes about 65 per cent of the TNE market in Pakistan.
It is extremely important for Pakistan's public policy makers and the nation's private sector to fully appreciate the expected demographic dividend as a great opportunity. The best way for them to demonstrate it is to push a pro-youth agenda of education, skills development, health and fitness to take full advantage of this tremendous opportunity. Failure to do so would be a missed opportunity that could be extremely costly for Pakistan and the rest of the world.
In the high fertility countries of Africa and Asia family sizes are continuing to decline. And in low fertility countries family sizes will continue to remain below replacement levels. Why? Because the same juggernaut forces are operating: increasing urbanization, smaller and costly housing, expanding higher education and career opportunities for women, high financial costs and time pressures for childrearing and changing attitudes and life styles.
Countries With Declining Populations:
115 countries, including China (1.55), Hong Kong (1.17), Taiwan (1.11) and Singapore (0.8) are well below the replacement level of 2.1 TFR. Their populations will sharply decline in later part of the 21st century.
United States is currently at 2.01 TFR, slightly below the replacement rate. "We don't take a stance one way or the other on whether it's good or bad," said Mark Mather, demographer with the Population Reference Bureau. Small year-to-year changes like those experienced by the United States don't make much difference, he noted. But a sharp or sustained drop over a decade or more "will certainly have long-term consequences for society," he told Utah-based Desert News National.
Japan (1.4 TFR) and Russia (1.6 TFR) are experiencing among the sharpest population declines in the world. One manifestation in Japan is the data on diaper sales: Unicharm Corp., a major diaper maker, has seen sales of adult diapers outpace infant diapers since 2013, according to New York Times.
Median Age Map: Africa in teens, Pakistan in 20s, China, South America and US in 30s, Europe, Canada and Japan in 40s. |
The Russian population grew from about 100 million in 1950 to almost149 million by the early 1990s. Since then, the Russian population has declined, and official reports put it at around 144 million, according to Yale Global Online.
Reversing Trends:
Countries, most recently China, are finding that it is far more difficult to raise low fertility than it is reduce high fertility. The countries in the European Union are offering a variety of incentives, including birth starter kits to assist new parents in Finland, cheap childcare centers and liberal parental leave in France and a year of paid maternity leave in Germany, according to Desert News. But the fertility rates in these countries remain below replacement levels.
Summary:
Overzealous Pakistani birth control advocates need to understand what countries with sub-replacement fertility rates are now seeing: Low birth rates lead to diminished economic growth. "Fewer kids mean fewer tax-paying workers to support public pension programs. An "older society", noted the late Nobel laureate economist Gary Becker, is "less dynamic, creative and entrepreneurial."
Related Links:
Pakistan's Expected Demographic Dividend
Pakistan's Growing Human Capital
Pakistan Most Urbanized in South Asia
Hindu Population Growth Rate in Pakistan
Do South Asian Slums Offer Hope?
How "Illiterate" Are Pakistan's "Illiterate" Cell Phone Users?






Riaz Haq
There are over 3 million students enrolled in grades 13 through 16 in Pakistan's 1,086 degree colleges and 161 universities, according to Pakistan Higher Education Commission report for 2013-14. The 3 million enrollment is 15% of the 20 million Pakistanis in the eligible age group of 18-24 years. In addition, there are over 255,000 Pakistanis enrolled in vocational training schools, according to Technical Education and Vocational Training Authority (TEVTA).
Pakistani universities have been producing over half a million graduates every year since 2010, according to HEC data. The number of university graduates in Pakistan increased from 380,773 in 2005-6 to 493,993 in 2008-09. This figure is growing with rising enrollment and contributing to Pakistan's growing human capital.
http://www.riazhaq.com/2015/07/pakistans-rising-college-enrollment-...
Jul 24, 2015
Riaz Haq
In 2014, 37 per cent Pakistanis hoped for a better economic future. In 2015, it increased to 47pc, registering a 10pc improvement, according to the latest Pew survey.
Other nations on this list include Nigeria, Argentina, India and Spain.
In 2014, 64pc people in India saw their future as bright, which increased to 74pc in 2015.
The survey by the Washington-based Pew Research Centre, however, shows that most Pakistanis (51pc) are unhappy with the current economic situation while 47pc say it is good. Others declined to comment.
Forty-eight pc see economic situation in Pakistan improving over the next 12 months, 23pc say it will remain the same and 13pc say it will worsen.
Fifty-one pc Pakistanis believe that when today’s children grow up, they will be financially better off than their parent but 22pc say they will be worse off.
The report also includes a World Bank economic categorisation, which places Pakistan in the lower middle group with a gross domestic product of $241 billion, GDP per capita based on purchasing power parity at $4,886, and average GDP growth of 4.4pc between 2005 and 2014.
The survey of 40 nations finds that publics in fewer than half of those countries have a positive view of their nation’s economy.
But there are signs of growing public faith in economic recoveries in some of the world’s largest economies.
Roughly four-in-ten Americans, Europeans and Japanese say economic conditions are good in their countries. Such sentiment is up 30 percentage points in Japan from a low point in 2012; up 23 points from the 2009 low in the United States; and up 23 points from the 2013 low for the median of five European Union nations surveyed.
Overall, people in emerging economies and developing countries are more likely than those in advanced economies to believe that economic conditions will improve over the next 12 months.
The IMF expects global growth in 2015 will be marginally slower than that in 2014. Only in developing nations does a majority (58pc) expect conditions to get better.
http://www.dawn.com/news/1196015
http://www.pewglobal.org/2015/07/23/global-publics-economic-conditi...
Jul 25, 2015
Riaz Haq
CNN on Hans Rosling's "Ignorance Project":
The world is spinning so fast that it can be hard to keep track of everything that is going on. Yet despite the fact that we can feel like we are being increasingly overloaded with information, it's not clear that we're doing a very good job of making sense of all that data we're receiving.
Don't believe me? Well, try answering these three questions on major global trends:
1) What percent of 1-year-olds in the world are vaccinated against measles? Is it 20, 50 or 80%?
2) Young adult men today have, on average, eight years of schooling, globally. How many years of school do you think the world's women of the same age have attended? Is it 3 years, 5 years or 7 years?
3) How has the proportion of people living in extreme poverty around the world changed over the past 25 years? Has it doubled, stayed about the same, or been halved?
So, here are the answers: Around 83 percent of the world's 1-year-olds are vaccinated against measles; 25-year-old women have, on average, been to school almost as long as males the same age, having attended for about seven years; and extreme poverty has been more than halved since 1990.
Did you get those right? You probably didn't. And you're very far from alone. In fact, when the Gapminder Foundation partnered with polling firms around the world to ask members of the public in Europe and the United States these and similar questions, what we found was a depressing lack of awareness about some of the most basic facts about our world. In fact, less than a fifth of Americans, Swedes, Germans and Britons answered these three questions correctly.
One of the biggest misconceptions about the world we live in is about global population growth. The number of children in the world has actually stopped increasing, because 80 percent of us live in societies where the two-child family is the norm. And how many people would have guessed that women in Brazil, Iran and Vietnam today have fewer babies, on average, than women in the United States?
In a way, this lack of knowledge shouldn't come as much of a surprise because there is something that actively skews our thought process: Preconceived ideas.
We all have them. Even those of us who think we keep abreast of what is going on in the world have personal biases because we have been taught a mountain of facts that are now outdated, whether we learned them in school or at work. And then there is our news media, which is built upon conflict and a black-and-white model of explanation (hence our susceptibility to negative headlines).
All this means that if you went to the zoo with the questions posed earlier written down on piece of cardboard, placed a banana beside each of the three alternatives and let some chimps have a go at picking the answers, they could be expected to get one in three questions correct, beating most humans in the process.
Does our ignorance of strong positive trends, which makes us believe that the world is a sicker, worse place than it is, really matter?
Yes, because as a result we are more likely to make the wrong decisions. Indeed, a world view based on outdated facts can have severe consequences -- from not investing where we will get the best returns, to allocating aid where it might have little impact.
With this in mind, the director of Gapminder, Ola Rosling, has launched The Ignorance Project in an effort to identify where our collective knowledge is weakest, and therefore where we might be likely to make the biggest mistakes. We will be formulating 250 questions on major aspects of global development and the state of the world and, over five years, will gradually identify the 25 least known but important global facts through surveys across 130 countries.
With luck, by highlighting just how little we know about the world, we will be able to encourage fact-based teaching of the world in our schools.
http://www.cnn.com/2015/03/07/opinions/rosling-global-knowledge/
Jul 25, 2015
Riaz Haq
A new UN study of global population trends predicts that India will overtake China to become the world's most populous nation by 2022.
The report also says that Nigeria will replace the US as the world's third most populous country by around 2050.
Africa is expected to account for more than half of the world's population growth over the next 35 years.
The current world population of 7.3 billion will reach 9.7 billion in 2050 and 11.2 billion in 2100, it predicts.
The new projection has India overtaking China's population six years earlier than previously predicted.
The reports says half of the world's population growth between 2015 and 2050 is expected to be concentrated in nine countries: India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Ethiopia, Tanzania, the United States, Indonesia and Uganda.
The populations of 28 African countries are projected to more than double, and by 2100, 10 African countries are projected to have increased by at least a factor of five.
"The concentration of population growth in the poorest countries presents its own set of challenges, making it more difficult to eradicate poverty and inequality, to combat hunger and malnutrition," said John Wilmoth, Director of the UN's Population Division.
http://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-33720723
Jul 30, 2015
Riaz Haq
#Pakistan teenage student wins second prize at #NASA contest http://tribune.com.pk/story/943287/pakistani-boy-wins-second-prize-... … A Pakistani boy secured second prize at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Ames Space Settlement Design Contest 2015.
Shah Mir Aizaz, a student of O’ Levels, participated in the annual design competition for students from grade 7 to grade 12, sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center and the National Space Society NSS. He won second prize for his design titled, ‘Beyond Infinity – Eros Outer Atmosphere Settlement’.
Aug 23, 2015
Riaz Haq
Sixteen-year-old Raffay Ansari is a self-taught programmer. He’s been an iOS developer for over three years and has now graduated into full-stack, meaning he’s comfortable working with a number of different languages as well as both back-end and front-end technologies. The teenage prodigy from Pakistan has earned several thousand dollars freelancing online, coded games that have attracted about 8 million cumulative downloads, and is now on the brink of launching his own start-up....Raffay has Ataxia, which means he has difficulty walking, speaking clearly, writing, reading, and other activities that require fine motor control. Raffay tells Tech in Asia that his muscles continue to weaken, even after his diagnosis over two years ago.
“The disease is more of a gift to me. As I can’t sleep much at night, I utilise the time learning new things instead. People treat me differently and are always willing to help. It’s a huge advantage,” he beams.
------------
The internet became Raffay’s teacher. He taught himself how to code through free online courses, primarily from Code Academy. His parents were initially reluctant to encourage his sudden interest in programming, but warmed up to the idea once they saw his passion for it. By the age of 13, he had successfully bid for and completed his first freelance assignment – coding the iOS game Mr Flap.
Raffay is now on the brink of launching his own start-up, Odyssy, which he describes as a data-driven content management system (CMS) targeted at bloggers and publishers who aren’t very technologically savvy and who don’t want to spend time coding in HTML. He reveals Odyssy is on the brink of closing its seed funding round – $20,000 from an angel investor based out of Islamabad.
http://www.business-standard.com/article/companies/meet-the-16-year...
https://www.techinasia.com/this-self-taught-coder-probably-has-more...
Aug 31, 2015
Riaz Haq
NPR on the development of the birth control pill:
The Great Bluff That Led To A 'Magical' Pill And A Sexual Revolution
She (Margaret Sanger) went to work in the slums of New York City where women were having eight, nine, 10 children with no idea how to stop it, other than having abortions, which were often poorly performed and very dangerous. So she saw this stuff very up close. ...
But by the time you get to Sanger and she's a young woman working in New York City, it's very hard for women to get any kind of education even about birth control, much less birth control products. She has this plan to improve education for women. But her dream, and it's really just a dream, is that there should be some kind of magical pill — something that would allow women to turn on and off their reproductive systems.
Eig tells the history in his new book The Birth of the Pill: How Four Crusaders Reinvented Sex and Launched a Revolution.
The four people who created this revolution were: Margaret Sanger, who believed that women could not enjoy sex or freedom until they could control when and whether they got pregnant; scientist Gregory Pincus, who was fired from Harvard for experimenting with in-vitro fertilization and bragging about it to the mainstream press; John Rock, who was a Catholic OB-GYN and worked with Pincus to conduct tests of the pill on women; and Katharine McCormick, who funded much of the research.
In the '50s, selling contraception was still officially illegal in many states.
But Sanger and McCormick, a feminist who had been active in the suffrage movement, wanted women to enjoy sex — without fear of getting pregnant.
After McCormick's husband died, McCormick got in touch with Sanger.
According to Eig, McCormick said, "What's the most important thing we could possibly work on?"
"Sanger said, 'The best thing we could possibly do is work on this pill, this miracle tablet ... something that would give women the right to control their bodies for the first time.' And McCormick said, 'I'm in: Whatever you need.' "
http://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2014/10/07/354103536/the-g...
Oct 2, 2015
Riaz Haq
#China to End One-Child Policy, Allowing Families Two Children http://nyti.ms/1kVju7L
Driven by fears that an aging population could jeopardize China’s economic ascent, the Communist Party leadership ended its decades-old “one child” policy on Thursday, announcing that all married couples would be allowed to have two children
The decision was a dramatic step away from a core Communist Party position that Deng Xiaoping, the Chinese leader who imposed the policy in the late 1970s, once said was needed to ensure that “the fruits of economic growth are not devoured by population growth.”
For China’s leaders, the controls were a triumphant demonstration of the party’s capacity to reshape even the most intimate dimensions of citizens’ lives. But they bred intense resentment over the brutal intrusions involved, including forced abortions and crippling fines, especially in the countryside.
Parents gathered at a “marriage market” at the Temple of Heaven in Beijing to seek spouses for their children. Xie Zuoshi, an economics professor, supports more flexible marital arrangements to address the surplus of bachelors.Sinosphere Blog: A Chinese Economist Responds to Critics of His Proposal to Let Men Share a WifeOCT. 27, 2015
The Chinese limit of one child for most families, which was enacted to slow population growth, has led to criticism.China to Ease
The efforts to limit family size also led to a skewed sex ratio of males to females, because traditional rural families favor boys over girls, sometimes even resorting to infanticide to ensure they have a son.
Thursday’s announcement was the highlight of a party meeting at which President Xi Jinping sought to display his control over a flagging economy after a jittery summer of tepid indicators, deepening skepticism about official data and a tumultuous slide in the stock market.
Yet while the decision surprised many experts and ordinary Chinese, some said it was unlikely to ignite either a baby boom or an economic one.
“Anything demographic, we always have to think in terms of decades in terms of long-term impact,” said Tao Wang, the chief China economist at UBS.
“It’s not about stimulating growth or consumption of baby powder next quarter or next year,” she said. “Will the birthrate go up? Yes. Will it somehow increase significantly? We don’t know.”
China eased some restrictions in the one-child policy in 2013, allowing couples to have two children if one of the spouses was an only child. But many eligible couples declined to have a second child, citing the expense and pressures of raising children in a highly competitive society.
The initial public reaction to the party leaders’ decision was restrained, and many citizens in Beijing who were asked whether they would grasp the chance to have two children expressed reluctance or outright indifference. Some, however, were pleased.
“Really, can you show me the news on your phone?” said Sun Bing, 34, the owner of a small technology store in Beijing, who had his 2-year-old son by his side.
“This is a good thing, and I’m very supportive,” he said. “I want to have a second kid in two years. But, of course, it’s not cheap to raise children.”
------------
Liang Zhongtang, a retired demographer who has advised Chinese officials on population policy since the 1980s and has long argued that they should relax the one-child policy, said the change had come too late to make a big difference in the country’s population trajectory. He said he had pushed for such a change since the 1980s.
“It’s not just a problem of whether you permit ordinary people to have one or two kids. It’s about returning their reproductive rights to them,” Mr. Liang said in a telephone interview from Shanghai. “In over 200 countries and regions around the world, which of them nowadays controls people’s reproduction like this?”
Michael Forsythe contributed reporting from Hong Kong. Owen Guo, Vanessa Piao and Kiki Zhao contributed research.
Oct 29, 2015
Riaz Haq
Here (in Stuttgart, Germany), migration has long been an engine of growth, and integration the bedrock of civic pride. The problems Stuttgart faces are ones that prosperous cities around the globe now share, American ones included: a dearth of affordable housing and the kind of apartments that suit the evolving demographics of the people who occupy them.
A screenshot from the website of Norbert Baksa, a Hungarian photographer, showing a model playing a migrant taking a selfie.Open Source: Hungarian Fashion Photographer Defends ‘Migrant Chic’ SpreadOCT. 7, 2015
President Recep Tayyip Erdogan of Turkey on Monday in Brussels, where he said that the key to resolving the migration crisis was for Europe to do more to contain the war in Syria.Turkish Leader Says E.U. Should Do More About SyriaOCT. 5, 2015
A security officer near a fence on Saturday in Coquelles, France, that was damaged as migrants tried to enter the Channel Tunnel.Migrants Evade Security to Enter Tunnel in France OCT. 3, 2015
Open Source: Young Refugee Who Fled Syria in Wheelchair Thanks ‘Days of Our Lives’ Stars Who Reunited for HerOCT. 1, 2015
A family of migrants from Macedonia at a processing center on a former American military base in Bamberg, Germany.Defining Refugees Versus Migrants in GermanySEPT. 29, 2015
“Boomtowns are integration cities,” said Gari Pavkovic, the son of a Croatian guest worker who arrived here decades ago. Mr. Pavkovic now manages immigration for the city government.
He ticked off numbers. Forty percent of Stuttgart’s 600,000 residents (or 60 percent of people under the age of 18) come from abroad, twice the national average. After World War II, foreign laborers rebuilt local industry: first Italians, then Greeks, Spaniards, Yugoslavians, Turks. And they’re still coming. Some 20,000 newcomers arrive annually, not counting the current wave of Syrians and others. Immigrants account for one of every three start-ups.
The other day, Levent Gunes, who works for the city planning office, provided a tour of a disused tank engine factory, an industrial relic being converted into an arts complex. The man who bought it was born in Turkey and owns a bakery across the street, Mr. Gunes said, next to a big Turkish supermarket and mosque.
“The percentage of entrepreneurs in Stuttgart with migrant backgrounds is the highest in Germany,” Mr. Gunes, who teaches at Stuttgart University and is the son of Turkish migrants himself, elaborated over börek and yogurt at the bakery.
“We’re talking I.T. people, engineers, architects, artists,” he said. “You only see the greengrocer and the butcher at street level, not all the doctors and lawyers upstairs.”
Stuttgart’s big move was to avoid pushing migrants into poor, isolated suburbs as in Rome or Paris, he emphasized.
“The layout of the city has reinforced integration,” he said.
One can see what he means by what’s not here. Stuttgart doesn’t have ethnic enclaves. After World War II, Mercedes and Bosch erected hostels for guest workers. But by the 1970s, when Manfred Rommel became mayor, political and business leaders adopted a different tack, integrating migrants into existing communities in the city center. Stuttgart embraced a melting pot urbanism.
Wilfried Porth, a member of the Daimler board and director of the company’s labor relations, recalls Stuttgart as a dour place years ago.
http://www.nytimes.com/2015/10/07/world/europe/stuttgart-embraces-m...
Nov 3, 2015
Riaz Haq
How plunging birth rates spell disaster for economic growth? #China #Europe #US http://on.wsj.com/1MqBH5Z via @WSJ
By RUCHIR SHARMA
Sept. 23, 2015 6:27 p.m. ET
News reports suggest that the world is overflowing with people. Politicians in the U.S. and Europe talk about migrants—whether from Latin America or the Middle East—as a threat: They’ll steal jobs, depress wages and upend local ways of life. The backlash plays on deep-seated fears about a “population bomb.” The latest United Nations forecasts suggest that the global population will rise to 9.7 billion over the next 35 years, an increase of 2.4 billion. Where will they live, and what will they eat?
This narrative is sorely out of date. For much of the post-World War II era the world’s population grew at an average annual rate of almost 2%. But growth started to plummet in 1990 and is now running at about 1%—the lowest level in the postwar era—according to U.N. data.
This collapse is seriously undermining potential economic growth—roughly calculated as the rate of growth in the working-age population added to the rate of growth in productivity, or output per worker—and goes a long way toward explaining the sluggish recovery from the crisis of 2008.
Global GDP growth has been trending lower this decade and now stands at just under 2.5% a year, a full percentage point below its long-term precrisis average of 3.5%. It is no coincidence that since 2005 the growth in the working-age population, ages 15 to 64, has slowed from about 1.8% to 1%.
Thanks to rising prosperity and increased urbanization, women around the world are having fewer children. Since 1960 the average number of births per woman has fallen to 2.5 from nearly 5. Yet the global fertility rate continues to slip toward 2.1—the figure required to keep the population from shrinking.
In 83 countries, which contain almost half the world’s population, the typical woman has fewer than two children, including the U.S., China, Russia, Brazil, South Korea and every major country in Europe.
Falling fertility rates typically affect the economy after a lag of 15 years, as babies grow into working-age adults. But oddly, anti-immigrant sentiment has erupted precisely as the economic fallout of the birthrate implosion has become clearly visible. This year, for the first time in the postwar era, China’s working-age population is expected to decline—and it is likely to continue falling in coming years. The emerging world is going to have many fewer people to export than the anti-immigrant populists in the developed world imagine.
The negative economic effect of falling birthrates is magnified by another trend: Since 1960 the average lifespan world-wide has climbed to 69 from 50. The overall global population is still rising, slowly, but a greater share of it is people over 50. As previous generations retire they will impose a larger burden, in health care and pensions, on working-age sons and daughters.
The aging squeeze will be felt much more sharply in the emerging world where life expectancy has risen, and fertility rates have fallen, faster. In India the fertility rate has plunged from more than 6 in 1960 to 2.5. Though India is still on track to become the world’s most populous country in 2022, the annual growth in its working-age population will fall from an average of 2.2% last decade to 1.1% next decade.
Many countries see the threat posed by an imbalance between workers and retirees. Some have offered women “baby bonuses” to have more children, but with spotty results so far. Others have focused on boosting the size of the active labor force by bringing mothers or elderly people back to work. Most European countries are raising their “retirement age”—a 20th-century concept—to prevent energetic 50-somethings from quitting work.
---
Only the countries that adapt early to the population implosion will thrive in the baby-bust era. Meanwhile, the controversies over immigrants “stealing jobs” are likely to fade in the coming years, and give way to a new war for talent.
Nov 3, 2015
Riaz Haq
India will be the world’s most populous country, Nigeria will be third and Indonesia fifth, according to the U.N. China will slip from first to second-most populous place on the planet.
Most, though, will still be poor. Indeed, low-income countries will make up 14% of the world’s population in 2050, compared with 9% now. These are, therefore, the countries that are likeliest to provide immigrants.
Next year, the world’s advanced economies will reach a critical milestone. For the first time since 1950, their combined working-age population will decline, according to United Nations projections, and by 2050 it will shrink 5%. The ranks of workers will also fall in key emerging markets, such as China and Russia. At the same time the share of these countries’ population over 65 will skyrocket.
By 2050, the world’s population will have grown 32%, but the working-age population (15 to 64 years old) will expand just 26%.
Among advanced countries, the working-age population will shrink 26% in South Korea, 28% in Japan, and 23% in both Germany and Italy, according to the U.N. For middle-income countries it will rise 23%, led by India at 33%. But Brazil’s will edge up just 3% while Russia’s and China’s will contract 21%.
http://blogs.wsj.com/indiarealtime/2015/11/24/what-indias-growing-p...
Note: Pakistan will remain the world's 6th most populous nation with 310 million people in 2050.
Nov 27, 2015
Riaz Haq
India will be the world’s most populous country, Nigeria will be third and Indonesia fifth, according to the U.N. China will slip from first to second-most populous place on the planet.
Most, though, will still be poor. Indeed, low-income countries will make up 14% of the world’s population in 2050, compared with 9% now. These are, therefore, the countries that are likeliest to provide immigrants.
Next year, the world’s advanced economies will reach a critical milestone. For the first time since 1950, their combined working-age population will decline, according to United Nations projections, and by 2050 it will shrink 5%. The ranks of workers will also fall in key emerging markets, such as China and Russia. At the same time the share of these countries’ population over 65 will skyrocket.
By 2050, the world’s population will have grown 32%, but the working-age population (15 to 64 years old) will expand just 26%.
Among advanced countries, the working-age population will shrink 26% in South Korea, 28% in Japan, and 23% in both Germany and Italy, according to the U.N. For middle-income countries it will rise 23%, led by India at 33%. But Brazil’s will edge up just 3% while Russia’s and China’s will contract 21%.
http://blogs.wsj.com/indiarealtime/2015/11/24/what-indias-growing-p...
Note: Pakistan will remain the world's 6th most populous nation with 310 million people in 2050.
Ever since the global financial crisis, economists have groped for reasons to explain why growth in the U.S. and abroad has repeatedly disappointed, citing everything from fiscal austerity to the euro meltdown. They are now coming to realize that one of the stiffest headwinds is also one of the hardest to overcome: demographics.
Next year, the world’s advanced economies will reach a critical milestone. For the first time since 1950, their combined working-age population will decline, according to United Nations projections, and by 2050 it will shrink 5%. The ranks of workers will also fall in key emerging markets, such as China and Russia. At the same time the share of these countries’ population over 65 will skyrocket.
Previous generations fretted about the world having too many people. Today’s problem is too few.
This reflects two long-established trends: lengthening lifespans and declining fertility. Yet many of the economic consequences are only now apparent. Simply put, companies are running out of workers, customers or both. In either case, economic growth suffers. As a population ages, what people buy also changes, shifting more demand toward services such as health care and away from durable goods such as cars.
Demographic forces are assumed to be slow-moving and predictable. By historical standards, though, these aren’t, says Amlan Roy, a demographics expert at Credit Suisse. They are “dramatic and unprecedented,” he says, noting it took 80 years for the U.S. median age to rise seven years, to 30, by 1980, and just 34 more to climb another eight, to 38.
There is no simple answer for how business and government should cope with these changes, since each country is aging at different rates, for different reasons and with different degrees of preparedness.
Automation can boost workers’ productivity and support the burgeoning ranks of the elderly. Assumptions about aging also need to change. The typical 65-year-old today is roughly as healthy as a 58-year-old was four decades ago and can thus work longer.
Older, richer countries can boost their immigrant intake from low-income economies primarily in Africa and Asia, which will make up a growing share of the world’s working-age population—if they can overcome political opposition.
http://www.wsj.com/articles/how-demographics-rule-the-global-econom...
Nov 27, 2015
Riaz Haq
Via @nprbooks: How #China's One-Child Policy Led To Forced Abortions, 30 Million Bachelors. http://n.pr/1m87hwk
"Right now China has a dependency ratio of about 5 working adults to support one retiree. That's a very healthy ratio. In about 20 years that's going to jump to about 1.6 working adults to support one retiree."
...Not so good.
Last October, China ended its 35-year-old policy of restricting most urban families to one child. Commonly referred to as the "one-child" policy, the restrictions were actually a collection of rules that governed how many children married couples could have.
"The basic idea was to encourage everybody, by coercion if necessary, to keep to ... one child," journalist Mei Fong tells Fresh Air's Terry Gross.
Fong explores the wide-ranging impact of what she calls the world's "most radical experiment" in her new book, One Child. She says that among the policy's unintended consequences is an acute gender imbalance.
"When you create a system where you would shrink the size of a family and people would have to choose, then people would ... choose sons," Fong says. "Now China has 30 million more men than women, 30 million bachelors who cannot find brides. ... They call them guang guan, 'broken branches,' that's the name in Chinese. They are the biological dead ends of their family."
Fong says the policy also led to forced abortions and the confiscation of children by the authorities. Looking ahead, China is also facing a shortage of workers who can support its aging population.
"Right now China has a dependency ratio of about five working adults to support one retiree. That's pretty good, that's a very healthy ratio. In about 20 years that's going to jump to about 1.6 working adults to support one retiree," Fong says. "The one-child policy drastically reshaped the composition of China's people. So now they have a population that's basically too old and too male and, down the line, maybe too few."
Feb 3, 2016
Riaz Haq
#US #Demographics Milestone: #Millennials (born 1980 to 2000) Outnumber Baby #Boomers (born between 1946 and 1964)
http://philadelphia.cbslocal.com/2016/04/26/millennials-outnumber-b...
Millennials have now officially surpassed the aging baby boomer population in America according to a report published by the US Census Bureau.
Acoording to the report, the 18 to 35-year-olds living in the United States currently top the seniors by 500,000. That gap is expected to widen as baby boomers between the ages of 51 and 69 tend to deal with more health issues as they approach their 70s and 80s.
The Pew Research Center who analyzed the report projects millennials will peak at just over 81 million in 2036, beating the baby boomer’s peak population of 78.8 million in 1999.
Gen Xers, born between 1965 and 1980 are also on track to outnumber baby boomers but not until 2028.
In the future it may not be as easy for younger generations to outnumber older ones because the numbers show that all people in general are living longer. A prime example are the centenarians, those 100 or older. In 2015 there were nearly half a million of them living throughout the world which was four times as many in 1990 according to estimates from the United Nations. They project 3.7 million centenarians will be alive in 2050.
With new medicines and therapies being developed it’s only a matter of time before the world reaches its next billion.
Apr 27, 2016
Riaz Haq
#Pakistan to start #University of #Technology & Skills Development with #Japan's help in 2017 http://www.pakistantoday.com.pk/2016/11/24/city/islamabad/pak-japan... … via @epakistantoday
The first National University of Technology and Skills Development to be established at a cost of Rs 700 million would start functioning by next year.
“The draft law for the establishment of the university would soon be tabled after approval,” Construction Technology Training Institute’s (CTTI) Director, Jamil Ahmed told participants of “Japan Official Development Assistance (ODA) press tour, organised by Embassy of Japan in collaboration with Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) on Thursday.
He said the draft law was pending with ministry of science and technology after approval from the ministry of law.
Jamil Ahmed informed that the syllabus of the university has already been approved by the Higher Education Commission (HEC). He said, five degree courses in five disciplines would be taught to the students.
He said that CTTI is strictly following the quota, and 45 percent seats are reserved for Punjab, 20 percent for Sindh, 15 percent for KP, 10 percent for Baluchistan and 10 percent for AJK, FANA and FATA. However he said that people from Baluchistan and Sindh are not coming according to their quota, while Punjab and KP is utilizing their 100 percent quota.
Giving the briefing regarding CTTI established with financial assistance of JICA, he said, more than 28,000 students from across the country had been imparted training of different short and long-terms courses since 1986.
He informed that 265 students from 28 countries had also completed their training from this institute.
The Director said a large number of the students of this institute were working with domestic and international companies after completing their training.
Jamil Ahmed said, spreading over 53.36 acres, the institute offers diplomas in mechanical, civil, automobile and diesel, quantity surveyor to the students of all provinces.
So far, 1,910 students are being imparted training on the equipment provided by the Japanese government.
He said the institute has 86 different types of machinery including dozers, graders, wheel loaders, excavators, truck crane etc which were donated by Japan.
He said, three hostels accommodate around 600 students on nominal charges while a new hostel for 200 students is under construction, however, there is no female stundent in CTTI.
Rebate in fee is offered to the students of backward areas, he added.
He informed that Japan has assisted in expansion and enhancement of this centre in 1995 and 2006, which is worth US$ 50 million.
“It has also extended technical cooperation under which it has assisted with the modification of curriculum and textbook and with provision of latest equipment in order to match modern technology and requirement of the industrial sector,” he added.
He said CTTI has played a leading role among these kinds of institutes by training people, by producing useful engineers, and also by providing third country training program through inviting students from Asian and African countries.
Later, the participants of the tour were taken to different class rooms to meet with the teachers and students.
Nov 26, 2016
Riaz Haq
Excerpts of ADB Asia Economic Integration Report (AEIR) 2016 report:
In Asia and the Pacific, many economies could expand
their role as the source or host economy for migrant
workers. Labor supply is still growing in developing
economies—such as Cambodia, Indonesia, the Lao
People’s Democratic Republic, Mongolia, Myanmar, India,
Pakistan, and the Philippines—and they could export
labor across the region. In contrast, developed but aging
economies such as Hong Kong, China; the Republic of
Korea; Japan; and Singapore are unable to meet labor
demand with their dwindling workforce. Hence, these
economies would benefit from immigrant labor. Kang
and Magoncia (2016) further discuss the potential for
migration to reallocate labor from surplus to deficit
economies and offer a glimpse of how the demographic
shift will frame Asia’s future population structure,
particularly the future working age population. Among the
issues explored is the magnitude of labor force surpluses
and deficits within different economies in Asia
------
World populations are aging—with the speed and extent of the
demographic shift varying across developed and developing
economies. Asia and the Pacific is at the heart of this demographic
shift with the world’s largest share of people aged 60 or over—
estimated to reach 62% by 2050. With the high and growing
share of economically inactive retirees and declining fertility
rates, labor supply will suffer, ultimately undermining the region’s
economic output.
How will the demographic shift frame Asia’s future population
structure, particularly working-age population? Using population
accounting methodology, Kang and Magoncia (2016) show how
effective certain policies could address the challenges associated
with the demographic change of population aging. One of the
policies explored is the increase in regional migration to augment
labor force deficits in aging economies in the region.
https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/214136/aeir-201...
Dec 8, 2016
Riaz Haq
http://www.geoba.se/country.php?cc=PK&year=2016
Selected Rankings - 2016
#4
in the world
Population - Age 15-19
22,097,116 people
#29
in the world
Infant Mortality Rate
53.86 per 1,000 births
Birth Rates - 2016
· Gross Reproduction Rate 1.31 Per 1,000 Rank: 66
· Ratio at Birth - Male to Female 1.05 Ratio Rank: 88
· Total Fertility Rate 2.68 Births Per Woman Rank: 67
· Fertility Rate
· 15-19 31.20 Per 1,000 Women Rank: 97
· 20-24 113.80 Per 1,000 Women Rank: 80
· 25-29 163.00 Per 1,000 Women Rank: 59
· 30-34 129.40 Per 1,000 Women Rank: 61
· 35-39 64.70 Per 1,000 Women Rank: 75
· 40-44 26.90 Per 1,000 Women Rank: 64
· 45-49 7.80 Per 1,000 Women Rank: 55
Growth Rates - 2016
· Growth Rate 1.45 Percent Rank: 78
· Natural Growth 1.59 Percent Rank: 69
· Births Per 1000 22.28 Per 1,000 Rank: 69
· Net Migrants per 1000 -1.41 Per 1,000 Rank: 165
Mortality Rates - 2016
· Life Expectancy 67.73 Years Rank: 169
· Female 69.77 Years Rank: 171
· Male 65.79 Years Rank: 166
· Deaths Per 1000 6.40 Per 1,000 Rank: 153
· Infant Mortality Rate 53.86 Per 1,000 Births Rank: 29
· Female 50.55 Per 1,000 Births Rank: 28
· Male 57.01 Per 1,000 Births Rank: 31
· Mortality Rate - Age 1-4 17.71 Per 1,000 Births Rank: 48
· Female 17.42 Per 1,000 Births Rank: 49
· Male 18.00 Per 1,000 Births Rank: 47
· Mortality Rate - Under Age 5 70.62 Per 1,000 Births Rank: 36
· Female 67.09 Per 1,000 Births Rank: 35
· Male 73.98 Per 1,000 Births Rank: 38
Land Area
· Area
· Square Miles 310,403
· Square Kilometers 803,940
· Area Rank
· Asia Rank: 8
· Worldwide Rank: 36
Apr 23, 2017
Riaz Haq
#India's #fertility rate declines to 2.2 children, just above replacement level 1.1. Population 1.7 billion by 2050
http://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/indias-population-story/artic...
Evidence from India’s last Census in 2011, confirmed by data from the recent National Family Health Survey 2017 (NFHS-4), shows that fertility in India is fast approaching replacement levels. This means that couples will have children who will essentially replace their number, to stabilise population growth. The NFHS-4 shows that in the past decade, the average number of children per family has come down from 2.7 to 2.2. With replacement fertility being 2.1 children per woman, this is good news for the land and the people.
Even after fertility rates drop to replacement levels, the total population will still grow, and is likely to reach 1.7 billion by 2050. The thrust of this growth will come from the youth bulge, with 365 million (10-24 years old) already in, or soon to enter, their reproductive ages. Even if they have children only in numbers that replace themselves, the resultant growth due to such a large base of young people will drive the growth momentum for population. For India as a whole, 75% of population growth in the coming decade will be due to this momentum.
In States like Assam, Gujarat and Haryana, which are about to reach replacement levels, it would be more effective to adopt policies for delaying childbearing rather than limiting births. Fertility reduction, where it still needs to take place, must come from increased availability and use of quality family planning services.
When States are clustered in terms of fertility levels, one foresees a predominantly youthful north and an ageing south. Most of the current and future demographic potential is locked in the northern States and largely located in Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh. In the south, there will be a dearth of young working people to keep up and expand the level of economic development. Investing in young people in the north to realise the demographic dividend will be a win-win situation for all India, north and south.
From the policy perspective, this means that for India as a whole, it is time for the emphasis to be on momentum-focussed policies and programmes.
Apr 28, 2017
Riaz Haq
#Pakistan (220 million incl #AJK) passes #Brazil (210 million) to become 5th-most populous nation https://shar.es/1ShVCE via @SkyNewsAust
Pakistan has surpassed Brazil to become the fifth-most populous country on earth, as the southern Asian nation's population surges beyond 220 million people, the latest figures show.
In March, the South Asian nation conducted its first population census in two decades, which was possible thanks to improved security after years of violence linked to al-Qaeda and Taliban militants.
The officials counted every individual and their housing unit in a countrywide door-to-door exercise that lasted for more than two months, said the Pakistan Bureau of Statistic, which conducted the census.
The government released the outcome on Friday. The figure came in much higher than the earlier estimate of around 200 million.
The population in the country's four provinces and the tribal regions near the Afghan border stood at 207.77 million, according to the bureau.
Another 15 million people live in the disputed regions of Kashmir and Gilgit- Baltistan in the north, near the country's border with China, a PBS official said.
But the population of these two regions are not included along with that of Pakistan's because of the disputes, although people from these areas are allowed to hold Pakistani passports.
Pakistan was previously the sixth-most populous country in the world, with an estimated population of around 200 million before the census, but it had now surpassed Brazil, which has a population of about 210 million.
Pakistan's population has been growing at an average rate of 2.4 per cent per year in the past two decades, despite efforts by the government to control the rapid increase in population, the data shows.
'This is a surprising factor. The rate is much higher than estimates,' said Shakeel Ahmed Ramay, a researcher with Islamabad-based Sustainable Development Policy Institute.
For a country like Pakistan with limited resources, such a huge population could become a burden if innovative policies are not made to turn the youth bulge into an asset, Ramay added.
'You got to have some policy framework to promote entrepreneurship to engage a sea of people ... Otherwise, more individuals means more consumption of resources,' he explained.
Aug 25, 2017
Riaz Haq
1998 (134 milion) to 2017 (208 million) 2.34%
Aug 25, 2017
Riaz Haq
8 takeaways from the population census 2017 results
https://www.samaa.tv/pakistan/2017/08/8-takeaways-from-the-populati...
The provisional results for the 6th Population and Housing Census 2017 of Pakistan are out and here are some takeaways from the facts and figures.







1. Pakistan's total population has grown by 2.40% since 1998
Ever since the last census was conducted (1998), Pakistan's population has increased from 132,362,279 to 207,774,520, recording an increase of 2.4 percent.
2. Islamabad Capital Territory has recorded the highest population growth rate since 1998
Other provinces or areas of the country have registered growth rates of 2 percent. However, the Islamabad Capital Territory has registered a growth rate of 4.91--the highest among all. It's population has enlarged to 2,006,572 from 805,235 in 1998.
3. A decline in population growth rate has been observed on the national scale
On a national scale, the population growth rate has seen a decline. Punjab and Sindh have also seen a decline in the population growth rate while Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Balochistan have registered an increase in the population growth rate.
4. Men are more in number than women according to the population census
Men have outnumbered women in the survey. The pie chart below makes it more clearer as men are 51% of the total population, women are 48.76% while transgenders form 0.24%.
The number of men in our population stand at 106.449 million while women stand at 101.314 million. 10,418 have been identified as transgenders in the population.
5. Here's how much of the population is living in urban areas of the country--36.38%
According to the Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, the trend of urbanization in Pakistan has seen an increase. In 1998, it was clocked in at 32.52% and has risen to 36.38% in 2017.
6. Urbanization trend has seen the only decline--and a sharp one--in Islamabad Capital Territory
One look at the table and you can clearly witness that the urbanization trend has seen a sharp decline in Islamabad Capital Territory. Back in 1998, 65.72% of the population in Islamabad was living in urban areas and this dropped to 50.58%.
7. In Sindh, more than half the population lives in urban areas
More than half of Sindh's population resides in urban areas of the province. It has seen an increase in percentage as in 1998 48.75% of the population of the province resided in urban areas which swelled to 52.02%.
8. Sindh is the most urbanized province of all as per the results of the census
Sindh is the most urbanized province as more than half (52.02%) of its population resides in urban areas. Islamabad Capital Territory follows in at number 2, Punjab at 3, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa at 4, Balochistan at 5 and FATA at 6.
Aug 25, 2017
Riaz Haq
1998 (134 milion) to 2017 (208 million) 2.34%
1981 (84 million) to 1998 (131 million) 2.65%
1961 (43 million) to 1981 (84 million) 3.4%
http://www.investopedia.com/calculator/cagr.aspx
Aug 25, 2017
Riaz Haq
#Pakistan #Census2017 : Urbanization helps shrink family size from 6.9 per household in 1998 to 6.45 in 2017
https://tribune.com.pk/story/1491353/census-2017-family-size-shrinks/
There are 32.21 million households in Pakistan, bringing the average size of household to 6.45 persons, suggesting that the family size is shrinking in the country because of the rising share of people living independently as well as the declining fertility rate.
The sixth population and housing census results showed that the number of households in Pakistan increased by 13 million or 67.6% against the data compiled 19 years ago. Of the total 32.21 million, as many as 12.1 million or 37.85% of total households are in cities. The number of urban households in all provinces has increased over 100% during past 19 years when the country had the last housing census.
In 1998, there were 19.21 million households and the average size of family was 6.889 persons. Urban households units in 1998 were six million or 31.39% of total households. In 1998, the annual growth rate was 2.69%.
However, over the past 19 years, the annual growth rate was 2.4% — the lowest since 1981. This resulted in slight shrinkage in the size of household.
The latest housing census showed that there were 3.85 million households in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa – higher by 1.64 million or 74.2% over 19 years ago. The share of urban households in total units increased from 16.74% to about one-fourth. However, the urban households doubled in the past 19 years.
In FATA, households increased from 340,000 to 560,000 – an increase of 64.7%. Urban households in FATA have increased to 200,000 or 35.7% of the total households of the region.
In Punjab, the number of households now stands at 17.1 million – an increase of 6.56 million units or 62.2%. Urban units stand at 6.4 million or 37.37% of the total households in the province. Urban units have doubled over the past 19 years. Punjab’s households are 53% of the national housing units.
In Sindh, there are 8.59 million households – an addition of 3.57 million units or 71.2% more than the previous census. The share of urban housing units currently stands at 51.22% in total provincial households, matching the province’s urban population. In absolute terms, urban households in Sindh stand at 4.4 million.
In Balochistan there are 1.78 million housing units – an addition of 810,000 or 83.5% over the past 19 years. The urban units stood at 470,000 or 26.4% of the province’s total households.
In Islamabad, total households remain 340,000, higher by 280,000 units, registering a 215% growth in the past 19 years. Urban units in Islamabad stand at 170,000 – half of the total units of the federal capital territory. In 1998, the share of urban households was 69.2%, which has since declined because of high cost of living in notified urban areas.
Aug 26, 2017
Riaz Haq
SOUND BYTES: Movement towards urban centres is significant: Rais
https://www.dawn.com/news/1354148/sound-bytes-movement-towards-urba...
ACCORDING to the provisional figures of the sixth national census conducted in May, Pakistan’s population today stands at 207.77 million with an annual growth rate of 2.4 per cent.
The census, conducted after 19 years, shows that the Islamabad Capital Territory has witnessed the highest population growth rate of 4.91pc. Balochistan has a growth rate of 3.37pc, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa 2.89pc, Sindh 2.41pc and Punjab 2.13pc.
It also shows that the number of females is lower, at 101.3m, than males, at 106.449m.
We spoke to Dr Rasul Bakhsh Rais, Professor of Political Science in the Department of Humanities and Social Sciences at the Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS), to assess what these basic population figures mean for the development of the country. Here is what he says.
Q: What will be the impact of this result of the sixth census?
A: Well, in the first place, this census is a great effort which was conducted after 19 years. It’s very important to have numbers of population for development of the country but unfortunately the previous governments failed to organise a census. So this successful attempt itself will leave a huge impact on our future development.
Q: Do you think these numbers are accurate?
A: These are very accurate numbers. These were gathered through a comprehensive exercise. These are much larger than I had estimated.
Q: So what is the most significant element of these new population figures?
A: The movement towards urban areas is very significant. But we need to see how have they defined the urban centres; whether they have included towns and tehsil headquarters having population of 20,000 to 70,000 in urban centres. There are many such towns in districts like Rahim Yar Khan, so we need to assess it closely. But generally this trend will impact national development, and social and political scene in the coming years.
Q: How will this trend impact society?
A: It will leave its impact in many ways but the most significant will be the change of political dynasty and opinion. Pakistan is the largest urban growing country in South Asia. So besides other changes, I think the most important will be that people will come out of the shackles of the feudal and political lords in rural areas. I think, by shifting to urban centres, they will incline towards political parties and other social systems instead of ‘pirs’ and ‘waderas’, which I think is very positive.
Q: Why has Lahore grown so rapidly and why did we not see a huge increase in Karachi’s population as estimated before the census?
A: There are several factors but the main factor is development and unrest. Karachi has been hostage to unrest for several decades. Hold of an ethnic party, the MQM, over the city for many years has impacted negatively. Though many people came to Karachi after things got worst in Fata, a constant law and order situation in the city itself forced many others to leave this city as well. Then the Pakhtun people, they are now having more opportunities in Balochistan, Punjab and other areas, so it helped them to shift to areas other than Karachi.
As far as Lahore’s growth is concerned, this city has seen more development and industrialisation during the past decade. So the trend of a population pull towards this city is obvious.
Aug 27, 2017