PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
India lost 6.8 million salaried jobs and 3.5 million entrepreneurs in November alone. Many among the unemployed can no longer afford to buy food, causing a significant spike in hunger. The country's economy is finding it hard to recover from COVID waves and lockdowns, according to data from multiple sources. At the same time, the Indian government has reported an 8.4% jump in economic growth in the July-to-September period compared with a contraction of 7.4% for the same period a year earlier. This raises the following questions: Has India had jobless growth? Or its GDP figures are fudged? If the Indian economy fails to deliver for the common man, will Prime Minister Narendra Modi step up his anti-Pakistan and anti-Muslim rhetoric to maintain his popularity among Hindus?
 |
| Labor Participation Rate in India. Source: CMIE |
Unemployment Crisis:
India lost 6.8 million salaried jobs and its labor participation rate (LPR) slipped from 40.41% to 40.15% in November, 2021, according to the Center for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE). In addition to the loss of salaried jobs, the number of entrepreneurs in India declined by 3.5 million. India's labor participation rate of 40.15% is lower than Pakistan's 48%. Here's an except of the latest CMIE report:
"India’s LPR is much lower than global levels. According to the World Bank, the modelled ILO estimate for the world in 2020 was 58.6 per cent (https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SL.TLF.CACT.ZS). The same model places India’s LPR at 46 per cent. India is a large country and its low LPR drags down the world LPR as well. Implicitly, most other countries have a much higher LPR than the world average. According to the World Bank’s modelled ILO estimates, there are only 17 countries worse than India on LPR. Most of these are middle-eastern countries. These are countries such as Jordan, Yemen, Algeria, Iraq, Iran, Egypt, Syria, Senegal and Lebanon. Some of these countries are oil-rich and others are unfortunately mired in civil strife. India neither has the privileges of oil-rich countries nor the civil disturbances that could keep the LPR low. Yet, it suffers an LPR that is as low as seen in these countries".
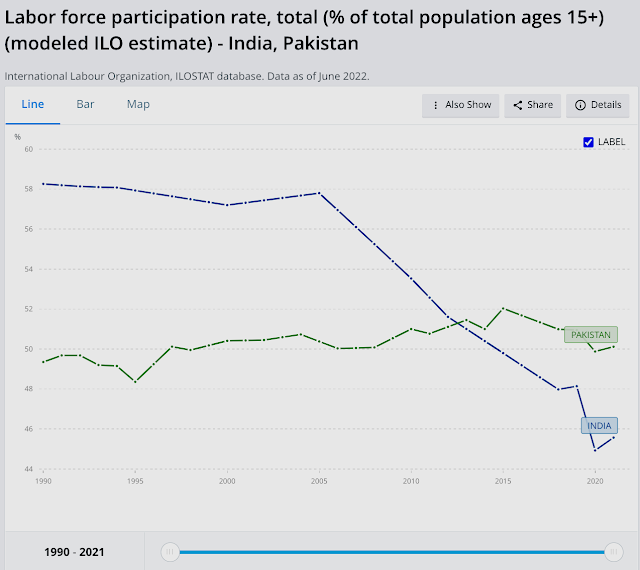 |
| Labor Participation Rates in India and Pakistan. Source: World Bank/ILO |
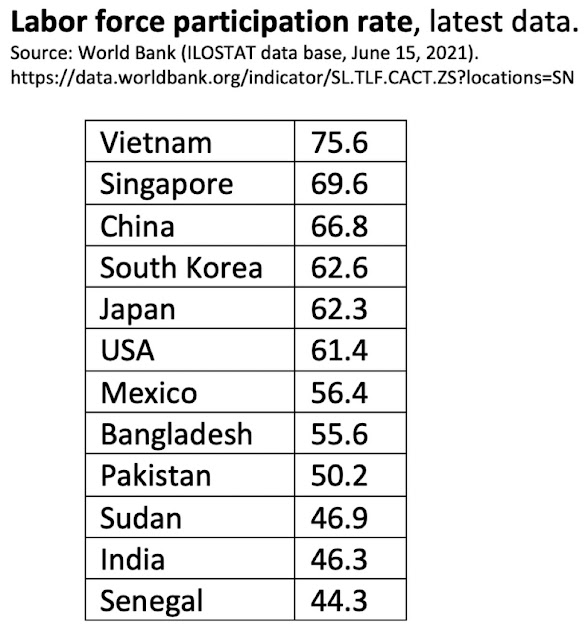 |
| Labor Participation Rates for Selected Nations. Source: World Bank/ILO |
Youth unemployment for ages15-24 in India is 24.9%, the highest in South Asia region. It is 14.8% in Bangladesh 14.8% and 9.2% in Pakistan, according to the International Labor Organization and the World Bank.
 |
| Youth Unemployment in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan. Source: ILO, WB |
In spite of the headline GDP growth figures highlighted by the Indian and world media, the fact is that it has been jobless growth. The labor participation rate (LPR) in India has been falling for more than a decade. The LPR in India has been below Pakistan's for several years, according to the International Labor Organization (ILO).
 |
| Indian GDP Sectoral Contribution Trend. Source: Ashoka Mody |
 |
| Indian Employment Trends By Sector. Source: CMIE Via Business Standard |
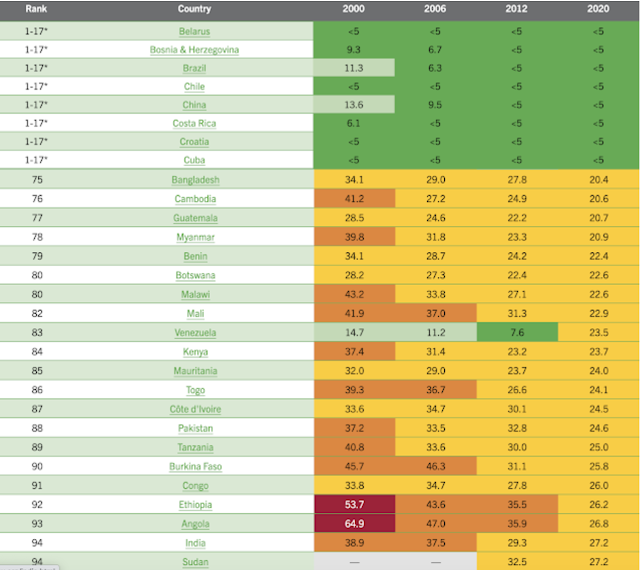 |
| World Hunger Rankings 2020. Source: World Hunger Index Report |
Hunger and malnutrition are worsening in parts of sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia because of the coronavirus pandemic, especially in low-income communities or those already stricken by continued conflict.
India has performed particularly poorly because of one of the world's strictest lockdowns imposed by Prime Minister Modi to contain the spread of the virus.
Hanke Annual Misery Index:
Pakistan's Real GDP:
Vehicles and home appliance ownership data analyzed by Dr. Jawaid Abdul Ghani of Karachi School of Business Leadership suggests that the officially reported GDP significantly understates Pakistan's actual GDP. Indeed, many economists believe that Pakistan’s economy is at least double the size that is officially reported in the government's Economic Surveys. The GDP has not been rebased in more than a decade. It was last rebased in 2005-6 while India’s was rebased in 2011 and Bangladesh’s in 2013. Just rebasing the Pakistani economy will result in at least 50% increase in official GDP. A research paper by economists Ali Kemal and Ahmad Waqar Qasim of PIDE (Pakistan Institute of Development Economics) estimated in 2012 that the Pakistani economy’s size then was around $400 billion. All they did was look at the consumption data to reach their conclusion. They used the data reported in regular PSLM (Pakistan Social and Living Standard Measurements) surveys on actual living standards. They found that a huge chunk of the country's economy is undocumented.
Pakistan's service sector which contributes more than 50% of the country's GDP is mostly cash-based and least documented. There is a lot of currency in circulation. According to the State Bank of Pakistan (SBP), the currency in circulation has increased to Rs. 7.4 trillion by the end of the financial year 2020-21, up from Rs 6.7 trillion in the last financial year, a double-digit growth of 10.4% year-on-year. Currency in circulation (CIC), as percent of M2 money supply and currency-to-deposit ratio, has been increasing over the last few years. The CIC/M2 ratio is now close to 30%. The average CIC/M2 ratio in FY18-21 was measured at 28%, up from 22% in FY10-15. This 1.2 trillion rupee increase could have generated undocumented GDP of Rs 3.1 trillion at the historic velocity of 2.6, according to a report in The Business Recorder. In comparison to Bangladesh (CIC/M2 at 13%), Pakistan’s cash economy is double the size. Even a casual observer can see that the living standards in Pakistan are higher than those in Bangladesh and India.
Related Links:
Haq's Musings
South Asia Investor Review
Pakistan Among World's Largest Food Producers
Food in Pakistan 2nd Cheapest in the World
Indian Economy Grew Just 0.2% Annually in Last Two Years
Pakistan to Become World's 6th Largest Cement Producer by 2030
Pakistan's 2012 GDP Estimated at $401 Billion
Pakistan's Computer Services Exports Jump 26% Amid COVID19 Lockdown
Coronavirus, Lives and Livelihoods in Pakistan
Vast Majority of Pakistanis Support Imran Khan's Handling of Covid19 Crisis
Pakistani-American Woman Featured in Netflix Documentary "Pandemic"
Incomes of Poorest Pakistanis Growing Faster Than Their Richest Counterparts
Can Pakistan Effectively Respond to Coronavirus Outbreak?
How Grim is Pakistan's Social Sector Progress?
Pakistan Fares Marginally Better Than India On Disease Burdens
Trump Picks Muslim-American to Lead Vaccine Effort
COVID Lockdown Decimates India's Middle Class
Pakistan Child Health Indicators
Pakistan's Balance of Payments Crisis
How Has India Built Large Forex Reserves Despite Perennial Trade Deficits
Conspiracy Theories About Pakistan Elections"
PTI Triumphs Over Corrupt Dynastic Political Parties
Strikingly Similar Narratives of Donald Trump and Nawaz Sharif
Nawaz Sharif's Report Card
Riaz Haq's Youtube Channel

Riaz Haq
Only a cheaper rupee can spur Indian growth
https://www.ft.com/content/c3a28628-5b92-4db7-a8c2-0f41bea05969
Elite interest favours a strong currency, to the detriment of the nation
ASHOKA MODY
While other Asian policymakers, such as those in South Korea and China, have strategically used sizeable depreciations of their currencies to bolster export competitiveness, Indian elites bemoan every infinitesimal decline in the rupee’s value as a national humiliation. A unique economic and political confluence first entrenched this bogus pride in the country’s psyche in the mid-1960s. And since the 1990s, the country’s corporate leaders and new rich have wanted to maintain a strong rupee. As a result, the country’s export-based growth has suffered, as have jobs for low-skilled workers.
India is triply handicapped in exporting manufactured goods: it has a poorly educated workforce, few women in its factories and an overvalued currency. Education and female labour force participation are key to raising productivity, but take years to achieve. Today, only a much cheaper currency — about 100 rupees per dollar rather than the current 82 — can spur Indian exports. It is low-hanging fruit.
In a rare sane moment in 1949, a newly independent India devalued the rupee from Rs3.3 to Rs4.8 per dollar, bringing relief to its uncompetitive economy. Indian manufacturers could earn profits even when they lowered dollar sale prices, which helped increase exports. Costlier imports slowed import growth, helping reduce the current-account deficit. But the task was never completed. With low productivity and high inflation, India could not match countries such as Japan in labour-intensive manufactured exports. The World Bank and the IMF financed India’s large current account deficit, creating the illusion that it did not need currency devaluation.
When those two institutions finally threatened to stop financing that deficit, the country’s officials foolishly negotiated the rate to Rs7.5 per dollar in June 1966. This too-little-too-late devaluation did not compensate for the rise in domestic production costs. Taiwan and South Korea raced ahead, helped by currency devaluations; Indian exports languished.
The perceived failure of the 1966 devaluation to spur exports forever tarnished Indian belief in an activist exchange rate policy. Rather than encouraging more aggressive nominal devaluation to offset the rise in production costs and thus achieve real depreciation, devaluation “by stealth” was always too little, too late. In the 1980s, China used aggressive exchange rate depreciation as key to its monumental export push.
India’s 1991 financial crisis was another all too brief moment of sanity. Authorities devalued the rupee in July 1991 and let it float in March 1993. But new forces strengthened the currency. Software exports and remittances from workers in the Middle East had a bolstering effect. More importantly, once global money managers began funding large Indian companies, a strong rupee helped that small elite minimise the costs of repaying international creditors and investors. A strong rupee also helped aspirants to elite status shop for fast cars and handbags, often in Milan and Singapore.
Reflecting the national sense of pride and elite preference, political gamesmanship conditioned policymakers to focus on stemming the currency’s decline. In 2013, prime ministerial candidate Narendra Modi bemoaned the fall in the currency, saying: “Our rupee has been admitted into the ICU.” After Modi became prime minister, hot money flowed in and the rupee appreciated briefly. But when it fell again, leaders of the opposition trolled the government by repeating Modi’s phrase: the rupee was in the ICU.
Aug 6, 2023
Riaz Haq
Only a cheaper rupee can spur Indian growth
https://www.ft.com/content/c3a28628-5b92-4db7-a8c2-0f41bea05969
Elite interest favours a strong currency, to the detriment of the nation
ASHOKA MODY
Sadly, the nominal depreciation was not enough. According to the Bank for International Settlements, between 1994 and now, India’s domestic costs of export production have risen by about 60 per cent relative to competitors. As a result, the real exchange rate, which determines international competitiveness, has strengthened by 12 per cent. Vietnamese manufactured exports, following the East Asian playbook, are poised to exceed India’s manufactured exports.
India’s accumulated cost-of-production disadvantage requires the rupee to drop to about Rs90 per dollar; Rs100 per dollar would provide an ideal cushion. But Indian authorities continue to avoid an activist exchange rate policy, and rely on dodgy policy tools: tax cuts and subsidies for corporate India, tariff barriers to shield inefficient producers and weaker labour protections. Such measures simply make the rich richer, while doing little for low-skilled workers. An exchange value of Rs100 per dollar would temporarily give Indian exports a much-needed boost. The time to act is now.
Aug 6, 2023
Riaz Haq
Ritesh Kumar Singh
@RiteshEconomist
India's premature #deindustrialisation: 12 out of the 23 #manufacturing industries that make up the IIP (Index of Industrial Production) are at levels lower than 7 years ago
@moneycontrolcom
https://twitter.com/RiteshEconomist/status/1691499535170674698?s=20
-----------------
India's industrial growth falls to 3.7% in June
https://www.moneycontrol.com/europe/?url=https://www.moneycontrol.c....
India's industrial output grew by 3.7 percent in June, according to data released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation on August 11.
At 3.7 percent, the latest industrial growth figure as per the Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is at a three-month low. It is also below the consensus estimate of 5 percent.
Industrial growth had come in at 5.2 percent in May - now revised to 5.3 percent - and was 12.6 percent in June 2022.
For the first quarter of 2023-24, IIP growth stood at 4.5 percent, down from 12.9 percent in April-June 2022 when the data was boosted by a favourable base effect.
Industrial growth in June was dragged down by a weaker increase in the manufacturing output, which rose by 3.1 percent year-on-year compared to 5.8 percent in May.
The performance of the manufacturing sector has an outsized impact on the headline industrial growth number as the sector accounts for more than three-fourths of the IIP.
While manufacturing output grew at a slower pace, that of mining and electricity rose at a faster clip. In June, mining output rose by 7.6 percent, up from 6.4 percent in May, and electricity production was up 4.2 percent. In May, electricity production was up a mere 0.9 percent.
The improved performance of mining and electricity sectors was down the low rainfall in June as drier conditions allow increased mining activity.
"IIP growth print in June has disappointed," said Suman Chowdhury, chief economist and head of research at Acuité Ratings & Research.
"Clearly, the manufacturing sector has not been able to sustain the growth trend that had been seen in the first two months of the last quarter. The manufacturing output grew only by 3.1 percent and actually saw a sequential contraction of almost 1 percent," Chowdhury added.
"Within manufacturing, output in metals exhibited a healthy performance while export-intensive categories such as textiles and wearing apparel continued to remain pressured," noted Rajani Sinha, chief economist at CareEdge.
In terms of the use-based classification of goods, there were some big shocks. While production of primary and intermediate good rose at a greater rate in June - 5.2 percent and 4.5 percent, respectively - there were weaknesses in other spheres, with output of consumer durables falling 6.9 percent in June after rising for the for the first time in six months in May.
Capital goods' output was up just 2.2 percent - down from 8.1 percent in May - while that of consumer non-durables rose a mere 1.2 percent. in May, it had posted a growth of 8.4 percent.
Output of infrastructure goods grew by 11.3 percent - the same as in May.
According to Aditi Nayar, ICRA's chief economist, the performance of most high-frequency indicators improved in July relative to June, although there were some laggards in the form of vehicle registrations and finished steel consumption.
"Based on these trends, ICRA expects the IIP growth to witness an uptick to 4-6 percent in July," Nayar said.
Aug 15, 2023