PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
Is Pakistan's Social Sector Making Progress?
If you read Pakistan media headlines and donation-seeking NGOs and activists' reports these days, you'd conclude that the social sector situation is entirely hopeless. However, if you look at children's education and health trend lines based on data from credible international sources, you would feel a sense of optimism. This exercise gives new meaning to what former US President Bill Clinton has said: Follow the trend lines, not the headlines. Unlike the alarming headlines, the trend lines in Pakistan show rising school enrollment rates and declining infant mortality rates.
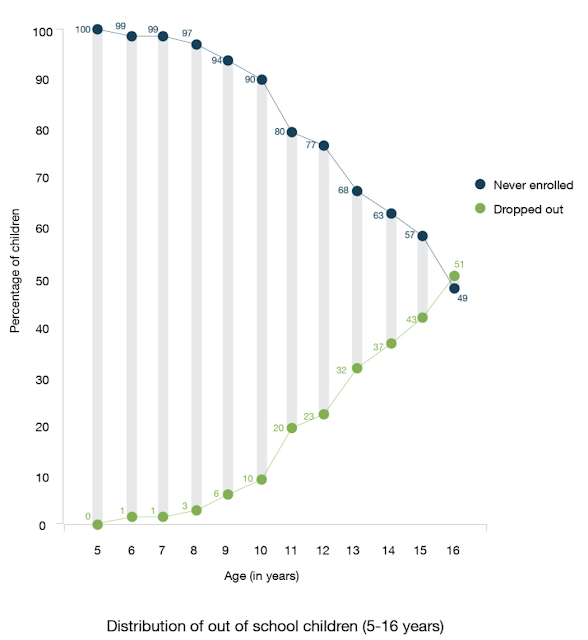 |
| Pakistan Children 5-16 In-Out of School. Source: Pak Alliance For M... |
 |
| Source: World Bank Education Statistics |
 |
| Pakistan Child Mortality Rates. Source: PDHS 2017-18 |
During the 5 years immediately preceding the survey, the infant mortality rate (IMR) was 62 deaths per 1,000 live births. The child mortality rate was 13 deaths per 1,000 children surviving to age 12 months, while the overall under-5 mortality rate was 74 deaths per 1,000 live births. Eighty-four percent of all deaths among children under age 5 in Pakistan take place before a child’s first birthday, with 57% occurring during the first month of life (42 deaths per 1,000 live births).
 |
| Pakistan Human Development Trajectory 1990-2018.Source: Pakistan HD... |
Human Development Ranking:
It appears that improvements in education and health care indicators in Pakistan are slower than other countries in South Asia region. Pakistan's human development ranking plunged to 150 in 2018, down from 149 in 2017.
| Expected Years of Schooling in Pakistan by Province |
There was a noticeable acceleration of human development in #Pakistan during Musharraf years. Pakistan HDI rose faster in 2000-2008 than in periods before and after. Pakistanis' income, education and life expectancy also rose faster than Bangladeshis' and Indians' in 2000-2008.
Now Pakistan is worse than Bangladesh at 136, India at 130 and Nepal at 149. The decade of democracy under Pakistan People's Party and Pakistan Muslim League (Nawaz) has produced the slowest annual human development growth rate in the last 30 years. The fastest growth in Pakistan human development was seen in 2000-2010, a decade dominated by President Musharraf's rule, according to the latest Human Development Report 2018.
UNDP’s Human Development Index (HDI) represents human progress in one indicator that combines information on people’s health, education and income.
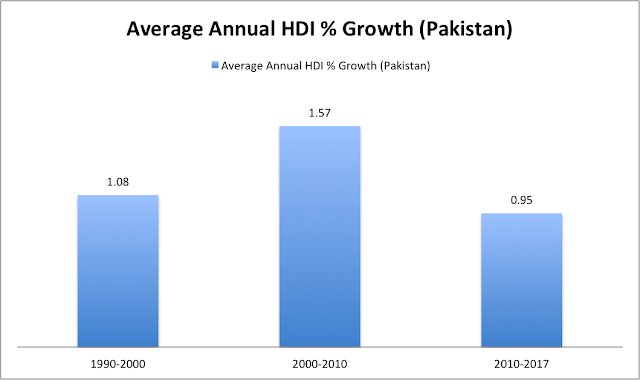 |
| Pakistan's Human Development Growth Rate By Decades. Source: HDR 2018 |
Pakistan saw average annual HDI (Human Development Index) growth rate of 1.08% in 1990-2000, 1.57% in 2000-2010 and 0.95% in 2010-2017, according to Human Development Indices and Indicators 2018 Statistical Update. The fastest growth in Pakistan human development was seen in 2000-2010, a decade dominated by President Musharraf's rule, according to the latest Human Development Report 2018.
 |
| Pakistan Human Development Growth 1990-2018. Source: Pakistan HDR 2019 |
Pakistan@100: Shaping the Future:
Pakistani leaders should heed the recommendations of a recent report by the World Bank titled "Pakistan@100: Shaping the Future" regarding investments in the people. Here's a key excerpt of the World Bank report:
"Pakistan’s greatest asset is its people – a young population of 208 million. This large population can transform into a demographic dividend that drives economic growth. To achieve that, Pakistan must act fast and strategically to: i) manage population growth and improve maternal health, ii) improve early childhood development, focusing on nutrition and health, and iii) boost spending on education and skills for all, according to the report".
 |
| Pakistani Children 5-16 Currently Enrolled. Source: Pak Alliance Fo... |
Summary:
The state of Pakistan's social sector is not as dire as the headlines suggest. There's reason for optimism. Key indicators show that education and health care in Pakistan are improving but such improvements are slower than in other countries in South Asia region. Pakistan's human development ranking plunged to 150 in 2018, down from 149 in 2017. It is worse than Bangladesh at 136, India at 130 and Nepal at 149. The decade of democracy under Pakistan People's Party and Pakistan Muslim League (Nawaz) has produced the slowest annual human development growth rate in the last 30 years. The fastest growth in Pakistan human development was seen in 2000-2010, a decade dominated by President Musharraf's rule, according to the latest Human Development Report 2018. One of the biggest challenges facing the PTI government led by Prime Minister Imran Khan is to significantly accelerate human development rates in Pakistan.
South Asia Investor Review
Pakistan's Expected Demographic Dividend
Can Imran Khan Lead Pakistan to the Next Level?
Democracy vs Dictatorship in Pakistan
Pakistan Child Health Indicators
Pakistan's Balance of Payments Crisis
Panama Leaks in Pakistan
Conspiracy Theories About Pakistan Elections"
PTI Triumphs Over Corrupt Dynastic Political Parties
Strikingly Similar Narratives of Donald Trump and Nawaz Sharif
Nawaz Sharif's Report Card
Riaz Haq's Youtube Channel
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 25, 2023 at 7:27pm
-
Education Technology in Pakistan | EdTech Hub
https://edtechhub.org/where-we-work/pakistan/
EdTech Hub develops and delivers evidence in EdTech. We work in partnership with researchers and stakeholders in-country to find specific, effective solutions to education challenges.
Since 2020, EdTech Hub has been assisting many players in Pakistan’s education sector. Because the education sector in Pakistan is very decentralised, EdTech Hub’s work requires close collaboration with the Government at the federal and provincial levels, as well as local partners, EdTech entrepreneurs and policy think tanks.
More specifically, EdTech Hub works with the Pakistani Ministry of Federal Education and Professional Training (MoFEPT), the Federal Directorate of Education (FDE), the FCDO, World Bank, and UNICEF to achieve large-scale impact.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 28, 2023 at 7:17am
-
A mobile library reaching children in remote villages of Pakistan
The camel library is a unique project to improve access to literacy
https://www.independent.co.uk/asia/south-asia/pakistan-library-came...
There is something special about the library in Tharparkar, one of the most deprived areas of the southeastern province of Sindh in Pakistan.
This mobile library was started almost two years ago in the village of Dhano Dodandal in the district of Tharparkar. It involves loading books onto a camel, which is then taken from village to village. Recently, the project has expanded to the another village, Sokliyo.
Mehdi Raza, who supervises this project in the area of Nagarparkar, says that Dr Asghar Naqvi of Karachi put him in touch with the educational NGO Alif Laila – who provided the team with books for children.
The camel library facilitates learning for children from village to village, without the need for hefty investment. Children not only read the books themselves but also take them to the adults in their homes, which furthers spreads awareness.
Children in the small village school look forward to the two days of the week when books are brought to them by the camel library.
Teacher Badal tells Independent Urdu he is happy that his students can access books in this novel way – and that the library is a helpful resource in their learning.
Pana Bhai, who is fond of reading, says she comes with the children of her village as soon as the camel library arrives.
Mehdi Raza explains that this service was started with just a single camel, but in the future it is hoped the project will be able expand further using more camels.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 31, 2023 at 8:30am
-
Camelback counters trek wilderness for Pakistan (first digital) census
https://www.dawn.com/news/1745167
“We even have to live for days out in the mountains among the people we're counting," says census supervisor.
Plodding over the horizon of Balochistan, camel-riding officials spy on a far-flung cluster of rough wooden homes and start tallying its tribespeople as the national census gets underway.
Beyond the reach of roads, power lines and TV signals in central Balochistan, this arid settlement of five reed huts has no name and hosts barely 15 nomads — three families herding goats and sheep.
“We ride for hours,” said local census supervisor Faraz Ahmad. “We even have to live for days out in the mountains among the people we’re counting.”
In cities and towns, teams wend their way from door to door on motorbikes. But in rural Balochistan, the tarmac gives way to craggy trails that then dissolve altogether in a wilderness of khaki rockland.
A fleet of gurning camels is the only option to get the job done.
“It takes a while to convince them to share their details,” census taker Mohammad Junaid Marri told AFP in Kohlu district, 210 kilometres east of Quetta and one hour by camel from the nearest discernible road.
“In some cases, it’s kind of funny. Since every census team has a security escort, sometimes people run away,” the 30-year-old said after his garlanded camel Bhoora bowed to let him slide off its hump and start peppering families with questions.
Between five and 10 per cent of Kohlu residents live in areas so inaccessible that camels are the only practical transport, estimates 34-year-old Ahmad.
They are rented for 1,000 rupees a day and the price includes a cameleer — a man trudging ahead to lead the bristly beasts on a leash.
In a nation divided along ethnic lines, enumerating citizens — 207 million at last count and an estimated 220m today — is a politically charged act that can alter claims to power and scant state resources.
The data will also be used to outline constituencies in future elections. Balochistan — Pakistan’s largest and least populous province — is rich in natural resources but poor by all other measures.
A separatist insurgency has long simmered in the region, fuelled by the grievance that Islamabad has failed to share the spoils of wealth extracted from Balochistan.
As Marri and Ahmad approach the hamlet on one camel — trailed by another carrying a guard wielding a weathered machine gun — they are eyed by a teenager through a pair of binoculars as children in traditional red floral dresses gather around.
“There’s a lack of awareness among people about the census — they don’t understand the benefits and downsides,” said Ahmad. “They don’t trust us and fear we may cheat them.”
Elsewhere, police guarding census teams in the nation’s remote and restive northwest have been killed by the Taliban.Despite the decidedly low-tech mode of transport, this is the first time Pakistan’s census will be compiled digitally — on tablets rather than reams of paper. Nonetheless, the old grievances remain.
“What benefits will we get from the census?” asked Mir Khan, 53, in another nearby speck of a settlement at the foot of mountains.
“We will get nothing. The influential people snatch everything the government wants to distribute to the poor.”
“We have never seen any support from the government,” grumbles his cousin Pando Khan, 58. “We see people when they’re campaigning for us to vote for them, and later they never return.”
However, after swapping their personal details with families according to local tribal customs, Ahmad and Marri convince them to answer 25 questions to give them a clearer picture of present-day Pakistan.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on April 2, 2023 at 12:45pm
-
Pakistan: Technology boosts education reform in remote areas
https://www.globalpartnership.org/results/stories-of-change/pakista...
STORY HIGHLIGHTS
Education in Pakistan’s Balochistan and Sindh provinces has been hampered by natural disasters, poor infrastructure and remoteness, and further exacerbated by political, economic and security problems.
From WhatsApp groups to biometric fingerprint systems, innovative technology has helped with building and restoring schools and improving teacher retention in these remote regions.
Since 2014, GPE’s support has led to 53,000 previously out-of-school children enrolled in school in Balochistan, and the tracking of educational data in all 29 districts in Sindh.
Supported by a US$34 million GPE grant, the government of Balochistan set up digital profiles to record land transfers and follow school construction, supporting the completion of schools and allowing education officials to track progress.
Large-scale surveys gathered geospatial data, an innovative and cost-effective way to identify abandoned buildings that could be transformed into schools.
Balochistan also established criteria for the selection of school sites, ensuring no other school existed within a 1.5 km radius and that locations enabled at least 20 out-of-school children to attend. This resulted in schools being built in remote areas with the most need.
Since 2015, 700 schools with new or renovated buildings have been completed and more than 100 girls’ primary schools upgraded to secondary. With GPE support, education authorities began to track real-time data in 14,000 schools, including teacher attendance and enrollment.
This has helped with the allocation of funding to locations with the greatest need. Android apps also record the physical infrastructure of schools, providing timely information on the functionality of toilets, drinking water and electricity.
School monitoring using technology
Both provinces use tech solutions to support management and ensure accountability in the education system. In Balochistan, apps keep track of teacher attendance, recording when teachers are within a certain geo-radius of the school; they work offline in more remote areas, uploading information when there is network access.
Through a US$66 million GPE grant, the Sindh province used tech tools to ensure teachers were deployed to the areas where they were most needed. Fingerprint-based biometric and photograph systems supported by GPS coordinates are also able to track teaching hours.
Greater incentive and validation for teachers
In a significant boost to quality learning, GPE supported the recruitment and training of qualified teachers, with emphasis placed on hiring female teachers to increase girls’ enrollment. Since 2015, 1,200 teachers have been recruited in Balochistan after passing the national testing service exam.
Better teaching and consistently open schools have helped increase student enrollment, with over 56,000 more girls enrolling in public elementary, primary and middle schools in Sindh.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on April 16, 2023 at 8:02am
-
Meet Ayesha Siddiqui, a TCF Alumna studying at the prestigious Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS)!
Despite cultural barriers and opposition from the community in her village (Bhai Pheru, Punjab), her father, a daily wage laborer and her mother, a house help, stood by her side and encouraged her to pursue her dreams!
https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:70531400607323...
-----------
Meet Ayesha Siddiqui, a TCF Alumna studying at the Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS)! Ayesha's journey from Bhai Pheru Village to LUMS was anything but easy. But despite cultural barriers and opposition from her community, her father, a daily wager and her mother, a house help, stood by her side and encouraged her to pursue her dreams!
https://business.facebook.com/citizensfoundationcanada/photos/a.375...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on April 23, 2023 at 6:44pm
-
In Pakistan, Quality Education Requires A Different Approach—and More Investment
JUAN BARON MAY BEND
https://blogs.worldbank.org/endpovertyinsouthasia/pakistan-quality-...
Our recent Human Capital Review highlights that quality education for all children in Pakistan will require a different approach and substantial financial efforts, estimated to be 5.4 percent of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Low public spending on education, combined with limited effectiveness at producing positive student outcomes, such as universal school enrollments and effective learning, limits Pakistan’s citizens from more actively participating in economic and social activities and contributing to productivity and economic growth. The challenges –notably the large number of out-of-school children and high learning poverty–seem complex the costs of addressing them unsurmountable. Nevertheless, there are actions Pakistan can take to change this trajectory.
Pakistan’s education sector faces critical challenges, which are believed to have been deepened by COVID-19 and the 2022 Floods. These catastrophes have only added to the world’s second-highest population of out-of-school children, which was at 20.3 million before them. Even before the pandemic, Pakistan had 75% Learning Poverty, which means that prior to the floods it started with already a very high percentage of 10-year-olds that cannot read and understand a simple age-appropriate text. The most vulnerable are disproportionately affected by the sector’s challenges. For example, learning poverty is highest for the poorest, and the most impoverished children – mainly in rural areas – are more likely to be out of school.
A different approach would require using available information to better target education programs in order to maximize the impact of limited resources.
For example, conversations and analyses tend to group all out-of-school children into a single category. This severely limits the effectiveness of policy actions to reduce out-of-school children. Understanding the different characteristics of out-of-school children will help, and here are some of them:
The majority are girls. Before the pandemic, 37 percent of girls and 27 percent of boys aged 5–16 were not in school.
They are more likely to live in rural areas. About 35 percent—or 15 million-- rural children aged 5 to 16 were out of school, compared with 20 percent –or 4.4 million--of urban children. This gap has remained constant over the past two decades.
They tend to be older. More children are out after primary school. During the 2018/19 school year, 40 percent of secondary school-age children were out of school (40 compared to 25 percent of middle school-age children and 23 percent of primary school–age children.
The number and share of out-of-school children drastically differs across provinces. About 53 percent of all out-of-school children live in Punjab and 23 percent in Sindh. That is almost 14 million. However, Balochistan and Sindh show the country's highest provincial rates of out-of-school children.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on April 23, 2023 at 6:44pm
-
In Pakistan, Quality Education Requires A Different Approach—and More Investment
JUAN BARON MAY BEND
https://blogs.worldbank.org/endpovertyinsouthasia/pakistan-quality-...
A different approach not only targets out-of-school children more effectively, but also calls for a relentless focus on learning in everything the education sector does. The statistics in Pakistan are telling: 65 percent of students still need to achieve a minimum proficiency level in reading by the end of primary education (Learning Poverty Brief).
There are several barriers to learning. Research points to outdated teaching practices, lack of quality and availability of pedagogical material, difficulty transitioning from languages spoken at home to the language used in schools, and teacher shortages. In addition, poverty, undernutrition, lack of school readiness, and distance to school make learning more challenging for students.
A different approach and implementing programs for impact would require at least three elements. First, it requires policies and solutions tailored to the characteristics of distinct groups of out-of-school children to maximize impact. For example, bringing children who are in the 13-16 age range and who have never been in school to regular school does not answer their needs. Alternatively, providing these children with literacy, numeracy, and life skills would support their needs in life.
Second, it requires focusing on what works. There is plenty of evidence from Pakistan and elsewhere that highlight the policy options and programs that are the most cost-effective to increase enrollment and learning, but prioritizing which ones to implement is critical. Third, it will require increasing the efficiency and level of public expenditure, this can be achieved by targeting funding every year to where education outcomes are the lowest.
There are several tested and impactful approaches that Pakistan has used successfully and that can deliver results at a reasonable cost. These can be scaled to expand educational services for children in Pakistan.
A few examples here can have a real impact. First, public-private partnerships have worked in Punjab. They can be expanded to cover more children in other levels of the system, particularly middle school, but be better regulated. Second, public and community schools can be revamped and improved, ensuring teachers are present – including consideration of double shifts when appropriate in the public sector. Third, multigrade classrooms should take true multigrade approaches in terms of funding, planning, and pedagogical execution. Making multigrade more effective is necessary to make rural education affordable and impactful. Several countries have done it successfully, including Pakistan, in the past.
Finally, the Human Capital Review provides a back-of-the-envelope estimate of how much Pakistan would require to keep all children in school – with gains in quality: 5.4 percent of GDP. This is assuming increases in efficiency in the public sector of 20 percent, for example, by using more targeted programs, investing in cost-efficient programs, and minimizing the use of high-cost, low-impact programs such as laptop distribution with no underlying pedagogical strategy.
An increase in expenditure is necessary from the low base of 2.5 percent of GDP Pakistan currently spends on education. Expanding levels of education should go in parallel with a serious effort to increase the efficiency of public expenditure in access, quality, and equity. Just bringing children to school is not enough. They must learn the skills to contribute to their own lives, families, communities, and country.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 29, 2023 at 7:18pm
-
Global Social Mobility Index 2020 | World Economic Forum
The Global Social
Mobility Report 2020
Equality, Opportunity
and a New Economic
Imperative
https://www3.weforum.org/docs/Global_Social_Mobility_Report.pdf
The World Economic Forum’s Global Social Mobility Index provides a new, holistic assessment of 82 global economies according to their performance on five key dimensions of social mobility distributed over 10 pillars: 1. Health; 2. Education (access, quality and equity, lifelong learning); 3. Technology; 4. Work (opportunities, wages, conditions); 5. Protection and Institutions (social protection and inclusive institutions). Economies with greater social mobility provide more equally shared opportunities—namely, an equal and meritocratic footing irrespective of socio-economic background, geographic location, gender or origin. There is a direct and linear relationship between a country’s income inequality and its social mobility score on the index. Low social mobility entrenches historical inequalities and higher income inequalities fuel lower social mobility. Enhancing social mobility can convert this vicious cycle into a virtuous one and has positive benefits on broader economic growth. The Global Social Mobility Index equips policy-makers with a tool to identify areas for improving social mobility and promoting equally shared opportunities for the entirety of their citizens, regardless of their development stage. The index is supplemented by a deep dive into the situation in the United States, through innovative metrics developed in partnership between the World Economic Forum and three private sector companies which hold unique data sets and provide new insights into the distribution of advantages and disadvantages across the population.
62 Tunisia 51.7
63 Panama 51.4
64 Turkey 51.3
65 Colombia 50.3
66 Peru 49.9
67 Indonesia 49.3 68
El Salvador 47.4
69 Paraguay 46.8
70 Ghana 45.5
71 Egypt 44.8
72 Lao PDR 43.8
74 Morocco 43.7
73 Honduras 43.5
75 Guatemala 43.5
76 India 42.7
77 South Africa 41.4
78 Bangladesh 40.2
79 Pakistan 36.7
81 Cameroon 36.0
80 Senegal 36.0
82 Côte d'Ivoire 34.5
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 6, 2023 at 5:12pm
-
No School Stands Alone
How market dynamics affect the performance of public and private schools
https://www.educationnext.org/no-school-stands-alone-how-market-dyn...
Jishnu Das
In the United States, 9 percent of K–12 students attend private schools, but in low- and middle-income countries, private schools account for 20 percent of all primary enrollment and are rapidly gaining ground. In Pakistan, the number of private schools rose to more than 70,000 by 2015, up from 3,000 in 1982; by 2015, these schools educated 34 percent of Pakistani children enrolled in primary schools. In contrast to private schools in the United States, Pakistan’s are highly affordable, and the majority are secular.
This growth in private schooling comes at a unique moment in global education: low-income countries have managed to substantially increase enrollments at all levels of schooling, but they have yet to improve what children learn. For instance, the unprecedented speed at which primary (and now secondary and college) enrollment has risen in low-income countries dwarfs the historical experience of today’s rich countries. Yet, in countries such as India and Pakistan, when children are tested at the end of 3rd grade, one-third of them cannot subtract two-digit numbers, less than a sixth can read a simple sentence in English, and less than half can read a simple sentence in the vernacular language, Urdu. Across low-income countries, test scores are so low that the situation has been dubbed a global learning crisis by organizations such as the World Bank and UNESCO.
The growth in private schools, coming at the same time as the shift in focus from enrollment to learning, has polarized the education community in low- and middle-income countries. Some people favor heavily regulating or even shutting down private schools, based on the belief that they provide substandard education to children of parents who are unable to assess the quality of schools; others believe that private schools should be encouraged and indeed subsidized through the public purse because they provide a valuable option in places with failing public schools. Missing from this debate is a detailed empirical picture of what the growth of private schools means for education markets more broadly. How does the rise in private schooling affect demand for schools in both the private and public sectors, and how do schools respond to any changing demand? Does more competition increase quality? Should governments maintain their focus on improving the quality of public schools, alleviate constraints on private alternatives—or perhaps do both?
Learning from the LEAPS Project
Research from the Learning and Education Achievement in Pakistan Schools project, or LEAPS, sheds light on these questions and holds implications for public policy in Pakistan and around the globe. To understand how the growth of private schools was transforming the education landscape in low-income countries, in 2003 I teamed up with Tahir Andrabi of Pomona College and Asim Ijaz Khwaja of Harvard University to launch the LEAPS project, a study of all the schools in 112 villages in the province of Punjab. The province has more than 100,000 schools, of which 60,000 were private in 2015. (By comparison, the state of California, with the largest public-education system in the United States, has about 10,000 public schools.) The villages in the LEAPS project were selected from those that had at least one private school in 2003; these villages are larger and somewhat wealthier than the average village in Punjab, which in turn has the lowest poverty rate of all Pakistani provinces. At the time the project began, about 60 percent to 70 percent of the province’s rural population lived in villages with at least one private school. Between 2003 and 2011, the LEAPS team tracked more than 800 schools in these villages, interviewed more than 1,000 principals and 2,000 teachers, and tested more than 70,000 children to gauge their foundational skills in literacy and numeracy.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 6, 2023 at 5:12pm
-
https://www.educationnext.org/no-school-stands-alone-how-market-dyn...
Jishnu Das
The high concentration of private and public schools in Punjab Province has transformed education markets there. Figure 1 shows a village in the LEAPS sample. It took me (and two young children) 15 minutes to traverse the village, yet it has five private and two public schools. Data gathered by the LEAPS team show that in 2003, the average fee for private schools in rural Punjab was equivalent to about $1.50 a month, or less than the price of a cup of tea every day. The number of schools in the village portrayed here is typical of the sample—in fact, the average LEAPS village in 2003 had 678 households and 8.2 schools, of which 3 were private.
The proliferation of private schools in Punjab has enabled such considerable school choice that, once we account for urban areas, some 90 percent of children in the province now live in neighborhoods and villages like the one illustrated in Figure 1. Such “schooling markets” are not just a Pakistani or South Asian phenomenon. Schooling environments in Latin America and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa also offer extensive variety for local families.
One question widely examined by education researchers is whether children in private schools learn more than those in public schools. Is there a private-school “premium” that can be measured in terms of test results or other metrics? One impediment to answering that question is that children enrolled in private schools are not randomly drawn from the local population, and researchers often cannot convincingly correct for this selection problem. In my view, though, a larger obstacle is that the concept of an “average” private-school premium is elusive when families can choose from multiple public and private schools and the quality of schools differs vastly within both sectors. Comparing a high-performing public school to a low-performing private school will yield a very different result than comparing a high-performing private school to a low-performing public school.
The LEAPS research team looked at this question in a study published in 2023. We defined school value-added as the gain in test scores in Urdu, math, and English that a randomly selected child would experience when enrolled in a specific school. The team found that the value-added variation among schools was so large that, compounded over the primary school years, the average difference between the best- and the worst-performing school in the same village was comparable to the difference in test scores between low- and high-income countries.
Figure 2 shows what this variation implies for estimates of private-school effectiveness. Each vertical line in the figure represents one of the 112 LEAPS villages. Schools in each village are arranged on the line according to their school value-added, with public schools indicated by red triangles and private schools by black dots. The red band tracks the average quality of public schools in the villages, from weakest to strongest, and the gray band shows the average quality of private schools in the villages. The private schools are, on average, more successful in raising test scores than their public-sector counterparts. As is clear, however, every village has private and public schools of varying quality, and the measure of any “private-school premium” depends entirely on which specific schools are being compared. In fact, the study shows that the causal impact of private schooling on annual test scores can range from –0.08 to +0.39 standard deviations. The low end of this range represents the average loss across all villages when children move from the best-performing public school to the worst-performing private school in the same village. The upper end represents the average gain across all villages when children move from the worst-performing public school to the best-performing private school, again within the same village.
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Trump Administration Seeks Pakistan's Help For Promoting “Durable Peace Between Israel and Iran”
US Secretary of State Marco Rubio called Pakistan Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif to discuss promoting “a durable peace between Israel and Iran,” the State Department said in a statement, according to Reuters. Both leaders "agreed to continue working together to strengthen Pakistan-US relations, particularly to increase trade", said a statement released by the Pakistan government.…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on June 27, 2025 at 8:30pm — 4 Comments
Clean Energy Revolution: Soaring Solar Energy Battery Storage in Pakistan
Pakistan imported an estimated 1.25 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of lithium-ion battery packs in 2024 and another 400 megawatt-hours (MWh) in the first two months of 2025, according to a research report by the Institute of Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA). The report projects these imports to reach 8.75 gigawatt-hours (GWh) by 2030. Using …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on June 14, 2025 at 10:30am — 3 Comments
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network