PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
India in Crisis: Unemployment and Hunger Persist After Waves of COVID
India lost 6.8 million salaried jobs and 3.5 million entrepreneurs in November alone. Many among the unemployed can no longer afford to buy food, causing a significant spike in hunger. The country's economy is finding it hard to recover from COVID waves and lockdowns, according to data from multiple sources. At the same time, the Indian government has reported an 8.4% jump in economic growth in the July-to-September period compared with a contraction of 7.4% for the same period a year earlier. This raises the following questions: Has India had jobless growth? Or its GDP figures are fudged? If the Indian economy fails to deliver for the common man, will Prime Minister Narendra Modi step up his anti-Pakistan and anti-Muslim rhetoric to maintain his popularity among Hindus?
 |
| Labor Participation Rate in India. Source: CMIE |
Unemployment Crisis:
India lost 6.8 million salaried jobs and its labor participation rate (LPR) slipped from 40.41% to 40.15% in November, 2021, according to the Center for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE). In addition to the loss of salaried jobs, the number of entrepreneurs in India declined by 3.5 million. India's labor participation rate of 40.15% is lower than Pakistan's 48%. Here's an except of the latest CMIE report:
"India’s LPR is much lower than global levels. According to the World Bank, the modelled ILO estimate for the world in 2020 was 58.6 per cent (https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SL.TLF.CACT.ZS). The same model places India’s LPR at 46 per cent. India is a large country and its low LPR drags down the world LPR as well. Implicitly, most other countries have a much higher LPR than the world average. According to the World Bank’s modelled ILO estimates, there are only 17 countries worse than India on LPR. Most of these are middle-eastern countries. These are countries such as Jordan, Yemen, Algeria, Iraq, Iran, Egypt, Syria, Senegal and Lebanon. Some of these countries are oil-rich and others are unfortunately mired in civil strife. India neither has the privileges of oil-rich countries nor the civil disturbances that could keep the LPR low. Yet, it suffers an LPR that is as low as seen in these countries".
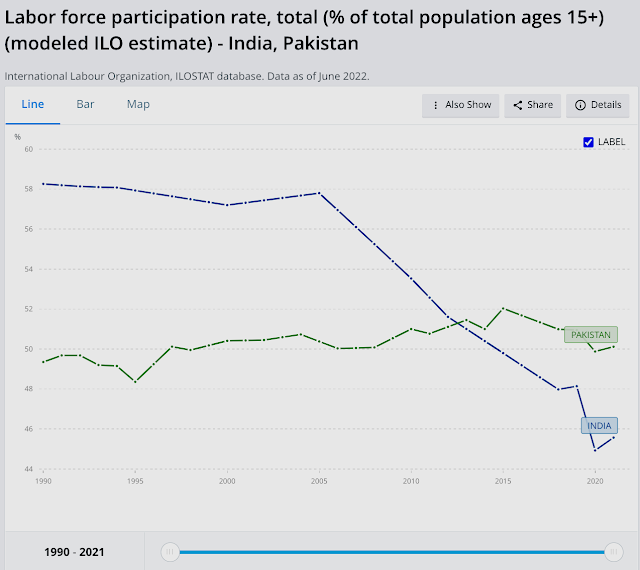 |
| Labor Participation Rates in India and Pakistan. Source: World Bank... |
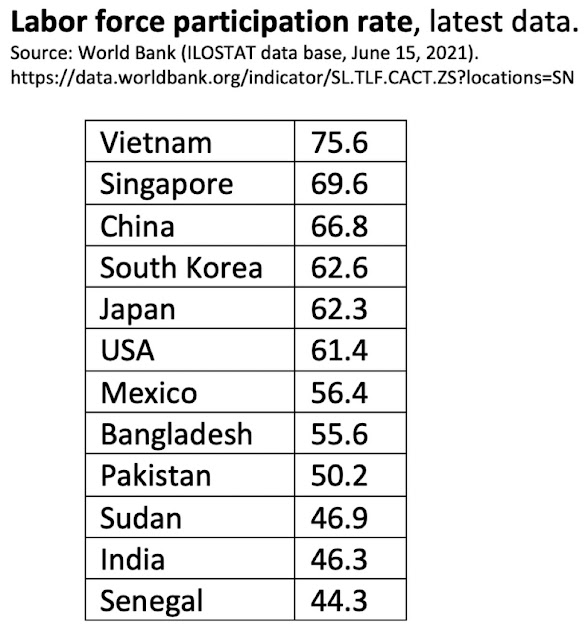 |
| Labor Participation Rates for Selected Nations. Source: World Bank/ILO |
Youth unemployment for ages15-24 in India is 24.9%, the highest in South Asia region. It is 14.8% in Bangladesh 14.8% and 9.2% in Pakistan, according to the International Labor Organization and the World Bank.
 |
| Youth Unemployment in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan. Source: ILO, WB |
In spite of the headline GDP growth figures highlighted by the Indian and world media, the fact is that it has been jobless growth. The labor participation rate (LPR) in India has been falling for more than a decade. The LPR in India has been below Pakistan's for several years, according to the International Labor Organization (ILO).
 |
| Indian GDP Sectoral Contribution Trend. Source: Ashoka Mody |
 |
| Indian Employment Trends By Sector. Source: CMIE Via Business Standard |
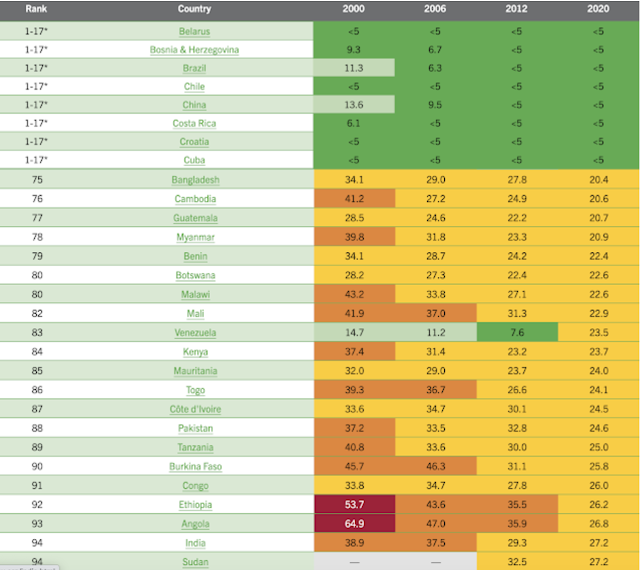 |
| World Hunger Rankings 2020. Source: World Hunger Index Report |
Hunger and malnutrition are worsening in parts of sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia because of the coronavirus pandemic, especially in low-income communities or those already stricken by continued conflict.
India has performed particularly poorly because of one of the world's strictest lockdowns imposed by Prime Minister Modi to contain the spread of the virus.
Hanke Annual Misery Index:
Pakistan's Real GDP:
Vehicles and home appliance ownership data analyzed by Dr. Jawaid Abdul Ghani of Karachi School of Business Leadership suggests that the officially reported GDP significantly understates Pakistan's actual GDP. Indeed, many economists believe that Pakistan’s economy is at least double the size that is officially reported in the government's Economic Surveys. The GDP has not been rebased in more than a decade. It was last rebased in 2005-6 while India’s was rebased in 2011 and Bangladesh’s in 2013. Just rebasing the Pakistani economy will result in at least 50% increase in official GDP. A research paper by economists Ali Kemal and Ahmad Waqar Qasim of PIDE (Pakistan Institute of Development Economics) estimated in 2012 that the Pakistani economy’s size then was around $400 billion. All they did was look at the consumption data to reach their conclusion. They used the data reported in regular PSLM (Pakistan Social and Living Standard Measurements) surveys on actual living standards. They found that a huge chunk of the country's economy is undocumented.
Pakistan's service sector which contributes more than 50% of the country's GDP is mostly cash-based and least documented. There is a lot of currency in circulation. According to the State Bank of Pakistan (SBP), the currency in circulation has increased to Rs. 7.4 trillion by the end of the financial year 2020-21, up from Rs 6.7 trillion in the last financial year, a double-digit growth of 10.4% year-on-year. Currency in circulation (CIC), as percent of M2 money supply and currency-to-deposit ratio, has been increasing over the last few years. The CIC/M2 ratio is now close to 30%. The average CIC/M2 ratio in FY18-21 was measured at 28%, up from 22% in FY10-15. This 1.2 trillion rupee increase could have generated undocumented GDP of Rs 3.1 trillion at the historic velocity of 2.6, according to a report in The Business Recorder. In comparison to Bangladesh (CIC/M2 at 13%), Pakistan’s cash economy is double the size. Even a casual observer can see that the living standards in Pakistan are higher than those in Bangladesh and India.
Related Links:
Haq's Musings
South Asia Investor Review
Pakistan Among World's Largest Food Producers
Food in Pakistan 2nd Cheapest in the World
Indian Economy Grew Just 0.2% Annually in Last Two Years
Pakistan to Become World's 6th Largest Cement Producer by 2030
Pakistan's 2012 GDP Estimated at $401 Billion
Pakistan's Computer Services Exports Jump 26% Amid COVID19 Lockdown
Coronavirus, Lives and Livelihoods in Pakistan
Vast Majority of Pakistanis Support Imran Khan's Handling of Covid1...
Pakistani-American Woman Featured in Netflix Documentary "Pandemic"
Incomes of Poorest Pakistanis Growing Faster Than Their Richest Cou...
Can Pakistan Effectively Respond to Coronavirus Outbreak?
How Grim is Pakistan's Social Sector Progress?
Pakistan Fares Marginally Better Than India On Disease Burdens
Trump Picks Muslim-American to Lead Vaccine Effort
COVID Lockdown Decimates India's Middle Class
Pakistan Child Health Indicators
Pakistan's Balance of Payments Crisis
How Has India Built Large Forex Reserves Despite Perennial Trade De...
Conspiracy Theories About Pakistan Elections"
PTI Triumphs Over Corrupt Dynastic Political Parties
Strikingly Similar Narratives of Donald Trump and Nawaz Sharif
Nawaz Sharif's Report Card
Riaz Haq's Youtube Channel
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 23, 2022 at 7:29pm
-
In mid-April, India is forecast to surpass China as the world's most populous country.
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-63957562
It could, for example, strengthen India's claim of getting a permanent seat in the UN Security Council, which has five permanent members, including China.
India is a founding member of the UN and has always insisted that its claim to a permanent seat is just. "I think you have certain claims on things [by being the country with largest population]," says John Wilmoth, director of the Population Division of the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs.
The way India's demography is changing is also significant, according to KS James of the Mumbai-based International Institute for Population Sciences.
Despite drawbacks, India deserves some credit for managing a "healthy demographic transition" by using family planning in a democracy which was both poor and largely uneducated, says Mr James. "Most countries did this after they had achieved higher literacy and living standards."
More good news. One in five people below 25 years in the world is from India and 47% of Indians are below the age of 25. Two-thirds of Indians were born after India liberalised its economy in the early 1990s. This group of young Indians have some unique characteristics, says Shruti Rajagopalan, an economist, in a new paper. "This generation of young Indians will be the largest consumer and labour source in the knowledge and network goods economy. Indians will be the largest pool of global talent," she says.
India needs to create enough jobs for its young working age population to reap a demographic dividend. But only 40% of of India's working-age population works or wants to work, according to Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE).
More women would need jobs as they spend less time in their working age giving birth and looking after children. The picture here is bleaker: only 10% of working-age women were participating in the labour force in October, according to CMIE, compared with 69% in China.
Then there's migration. Some 200 million Indians have migrated within the country - between states and districts - and their numbers are bound to grow. Most are workers who leave villages for cities to find work. "Our cities will grow as migration increases because of lack of jobs and low wages in villages. Can they provide migrants a reasonable living standard? Otherwise, we will end up with more slums and disease," says S Irudaya Rajan, a migration expert at Kerala's International Institute of Migration and Development.
Demographers say India also needs to stop child marriages, prevent early marriages and properly register births and deaths. A skewed sex ratio at birth - meaning more boys are born than girls - remains a worry. Political rhetoric about "population control" appears to be targeted at Muslims, the country's largest minority when, in reality, "gaps in childbearing between India's religious groups are generally much smaller than they used to be", according to a study from Pew Research Center.
And then there's the ageing of India
Demographers say the ageing of India receives little attention.
In 1947, India's median age was 21. A paltry 5% of people were above the age of 60. Today, the median age is over 28, and more than 10% of Indians are over 60 years. Southern states such as Kerala and Tamil Nadu achieved replacement levels at least 20 years ago.
"As the working-age population declines, supporting an older population will become a growing burden on the government's resources," says Rukmini S, author of Whole Numbers and Half Truths: What Data Can and Cannot Tell Us About Modern India.
"Family structures will have to be recast and elderly persons living alone will become an increasing source of concern," she says.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 24, 2022 at 7:08pm
-
Indian economy grew 8.7% in last fiscal year to surpass pre-Covid levels, IMF says
Growth expected to moderate to 6.8% in current year amid tighter financial conditions
https://www.thenationalnews.com/business/economy/2022/12/23/indian-...
India’s real gross domestic product grew by 8.7 per cent in the 2021-2022 fiscal year, boosting its total output above pre-coronavirus levels despite global macroeconomic headwinds, the International Monetary Fund has said.
India, Asia's third-largest economy and the world's fifth largest, rebounded from the deep pandemic-induced downturn on the back of fiscal measures to address high prices and monetary policy tightening to address elevated inflation, the Washington-based lender said in a report on Friday.
“Economic headwinds include inflation pressures, tighter global financial conditions, the fallout from the war in Ukraine and associated sanctions on Russia, and significantly slower growth in China and advanced economies,” the fund said.
“Growth has continued this fiscal year, supported by a recovery in the labour market and increasing credit to the private sector.”
In October, the IMF cut its global economic growth forecast for next year, amid the Ukraine conflict, broadening inflation pressures and a slowdown in China, the world’s second-largest economy.
The fund maintained its global economic estimate for this year at 3.2 per cent but downgraded next year's forecast to 2.7 per cent — 0.2 percentage points lower than its July forecast.
There is a 25 per cent probability that growth could fall below 2 per cent next year, the IMF said in its World Economic Outlook report at the time.
Global economic growth in 2023 is expected to be as weak as in 2009 during the financial crisis as a result of the Ukraine conflict and its impact on the world economy, according to the Institute of International Finance.
Economic growth in India is expected to moderate, reflecting the less favourable outlook and tighter financial conditions, the IMF said.
Real GDP is projected to grow at 6.8 per cent for the current financial year to the end of March, and by 6.1 per cent in 2023-2024 fiscal year, according to the fund's estimates.
Reflecting broad-based price pressures, inflation in India is forecast at 6.9 per cent in the 2022-2023 fiscal year and expected to moderate only gradually over the next year.
Rising inflation can further dampen domestic demand and affect vulnerable groups, according to the fund.
India’s current account deficit is expected to increase to 3.5 per cent of GDP in the 2022-2023 fiscal year as a result of both higher commodity prices and strengthening import demand, the lender said.
“A sharp global growth slowdown in the near term would affect India through trade and financial channels,” it said.
“Intensifying spillovers from the war in Ukraine can cause disruptions in the global food and energy markets, with significant impact on India. Over the medium term, reduced international co-operation can further disrupt trade and increase financial markets’ volatility.”
However, the successful introduction of wide-ranging reforms or greater-than-expected dividends from the advances in digitalisation could increase India’s medium-term growth potential, the IMF said.
Additional monetary tightening should be carefully calibrated and communicated, it said.
“The exchange rate should act as the main shock absorber, with intervention limited to address disorderly market conditions,” the report said.
The IMF also recommended that India’s financial sector policies should continue to support the exit of non-viable companies and encourage banks to build capital buffers and recognise problem loans.
Reforms to strengthen governance and reduce the government’s footprint are needed to support strong medium-term growth, it said.
The lender also highlighted the need for structural reforms to promote resilient, green and inclusive growth.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 26, 2022 at 7:38pm
-
#Indian #Railways: The #job-seekers tricked into counting #trains. The men believed they were training for a job with the Indian Railways. #Employment #SCAM https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-64093555
Police in India's capital Delhi are investigating a complaint about a job fraud in which around 28 men were tricked into counting trains for days.
The men believed they were training for a job with the Indian Railways.
A former army official, who said he unknowingly put the men in contact with the alleged scammers, alerted the police about the fraud.
The victims paid between 200,000 rupees ($2,400; £2,000) and 2.4m rupees each to get the job, local media reported.
The Delhi police's economic offences wing started investigating the alleged scam in November but the news became public only last week.
The men, who are from the southern Tamil Nadu state, were asked to stand at different platforms of the main railway station in Delhi for eight hours every day for about a month. There, they counted the trains that passed through the station every day, news agency Press Trust of India reported.
The men were promised they would be hired as ticket examiners, traffic assistants or clerks in the railways, one of India's largest employers.
One of the victims told The Indian Express newspaper that he had been looking for ways to support his family after the Covid-19 pandemic.
"We went to Delhi for training - all we had to do was count trains. We were sceptical of the activity, but the accused was a good friend of our neighbour. I feel ashamed now," he said.
Subbuswamy, the former army man who filed the complaint with the police, told PTI that he had been helping young men from his hometown in Tamil Nadu Virudhunagar district find jobs "without any monetary interest" for himself.
He said he met a person called Sivaraman who claimed to have connections with lawmakers and ministers and offered to find government jobs for the unemployed men.
He then put Subbuswamy and the victims in touch with another man, who even took the candidates for fake medical examinations. The man later stopped answering phone calls from them.
Some of the victims said they borrowed money to pay the scammers.
Scams for government jobs are often reported in India, where millions of young people are desperate for stable, secure employment. In March 2021, police in the southern Hyderabad city said they had arrested two men believed to have tricked around a hundred candidates who thought they were being hired by the railways.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 1, 2023 at 8:06am
-
India's Unemployment Rate For December Is 8.3%, A 16-Month High: Report
https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/indias-unemployment-rate-for-decemb...
Mahesh Vyas, managing director of CMIE, said this is "not as bad as it may seem" as it came on top of a healthy increase in the labour participation rate
India's unemployment rate rose to 8.3 per cent in December, the highest in 16 months, from 8 per cent in the previous month, data from the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) showed today.
The urban unemployment rate rose to 10.09 per cent in December from 8.96 per cent in the previous month, while rural unemployment rate slipped to 7.44 per cent from 7.55 per cent, the data showed.
Mahesh Vyas, managing director of the CMIE, said the rise in the unemployment rate was "not as bad as it may seem" as it came on top of a healthy increase in the labour participation rate, which shot up to 40.48 per cent in December, the highest in 12 months.
"Most importantly, the employment rate has increased in December to 37.1 per cent, which again is the highest since January 2022," he told Reuters.
Containing high inflation and creating jobs for millions of young people entering the job market remain the biggest challenge for Prime Minister Narendra Modi's administration ahead of national elections in 2024.
The main opposition Congress launched a march in September from the Kanyakumari to Srinagar to mobilise public opinion on issues such as high prices, unemployment and what it says are the "divisive politics" of the BJP.
"India needs to move from a single focus on GDP growth to growth with employment, skilling of youth and creating production capacities with export prospects," Congress leader Rahul Gandhi, who is leading the 3,500-km march on foot, told reporters yesterday.
The unemployment rate had declined to 7.2 per cent in the July-September quarter compared to 7.6 per cent in the previous quarter, according to separate quarterly data compiled by National Statistical Office (NSO) and released in November.
In December, the unemployment rate rose to 37.4 per cent in Haryana, followed by 28.5 per cent in Rajasthan and 20.8 per cent in Delhi, CMIE data showed.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 3, 2023 at 8:49am
-
#India's numerous #jobs #scams show the depth of its #unemployment crisis. Just one such ring has reportedly conned at least 50,000 people since 2020, making it one of India’s biggest job frauds in recent times. #Modi #BJP #economy https://finance.yahoo.com/news/indias-numerous-jobs-scams-show-1055... via @YahooFinance
India’s latest organised job scam episode has affected people in the Indian states of Gujarat, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, and Odisha. They were duped of crores of rupees after being promised jobs, reports said.
“The scam was being run by a group of tech-savvy engineers from Uttar Pradesh with the help of some expert website developers. This core group was assisted by around 50 call center employees. These employees were paid 15,000 rupees ($181) per month and were from Jamalpur and Aligarh localities of Uttar Pradesh,” according to Jai Narayan Pankaj, a senior Odisha police officer.
Candidates paid up to Rs70,000 for training and other orientation programmes, including Rs3,000 in registration fees. However, the training never happened, Pankaj said.
In another incident unearthed in December, around 30 people were tricked into counting the arrival and departure of trains at the New Delhi Railway Station for a month, BBC reported. They were told this was part of their training for the positions of travel ticket examiner, traffic assistant, and clerk. Each of the duped candidates had paid up between Rs2 lakh and Rs24 lakh for the coveted Indian Railways job.
Scammers are not limited to operating within India’s borders either. Some work through agents even in Dubai and Bangkok. Aspirants are sometimes persuaded to move to countries like Thailand. Many are taken illegally to Myanmar, Laos, and Cambodia where they are held captive and forced into cybercrime.
India is just not creating enough jobs
In September and October, India added over 8.5 million jobs in the formal sector. However, that was not enough, considering the number of applicants, along with fresh graduates, exceeded the number of available jobs.
In December, India’s unemployment rate rose to 8.3%, the highest in 16 months, data from the Mumbai-based Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) showed.
Worsening this is the global inflationary pressure and fears of an impending recession, sparking layoffs in recent months. This is besides the enduring effects of the pandemic years.
“One of the alarming possibilities for India...is the fact that our additions to the labour workforce are likely to slow down as it happened in China or in Europe and other developed economies,” TeamLease Services co-founder Rituparna Chakraborty told The Indian Express newspaper.
A study by CMIE and the Centre of Economic Data and Analysis of Ashoka University showed that over 12.5 million people aged 15-29 years not only lost jobs in 2020 but also stopped looking for new ones.
The number of farm jobs, meanwhile, increased during this time but that only underscored the economy’s weakness, the study found.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 3, 2023 at 5:34pm
-
The year 2023 marks a historic turning point for Asia's demography: For the first time in the modern era, India is projected to surpass China as the most populous country.
https://asia.nikkei.com/Spotlight/Asia-Insight/Old-Japan-young-Indi...
Besides China (1.426 billion) and India (1.417 billion), five other Asian countries had over 100 million people as of 2022, the U.N. figures show. Indonesia had 276 million, Pakistan's population was at 236 million, Bangladesh counted 171 million, Japan had 124 million and the Philippines had 116 million. Vietnam, with 98 million, is expected to join the club soon.
------------
Even though economists expect India's gross domestic product to grow around 7% in 2023 -- the highest among major economies -- and although the worst of the COVID-19 pandemic appears to be over, India continues to face high unemployment rates of around 8%, according to the Center for Monitoring Indian Economy, a local private researcher. That shows the country is not creating enough jobs to support the growing population.
---------
Kumagai also said that India's growing demand for food could be felt beyond its borders.
"The challenge for India concerning food is that the production of agricultural products is easily affected by the weather," he said. "On the other hand, domestic demand is increasing rapidly. As such, when production is low, domestic supply is prioritized, which eventually may lead to restrictions on exports, just as India restricted wheat exports in 2022, which could cause food problems in other countries as well."
--------
While the South Asian nation's growing and youthful population spells opportunities for development, it also creates layers of challenges, from poverty reduction to education. Experts say soaring demand for food could affect India's trade with other countries, while the World Bank recently estimated that India will need to invest $840 billion into urban infrastructure over the next 15 years to support its swelling citizenry.
"This is likely to put additional pressure on the already stretched urban infrastructure and services of Indian cities -- with more demand for clean drinking water, reliable power supply, efficient and safe road transport amongst others," the bank's report said.
India's dilemmas are only part of a complex and diverging Asian population picture -- split between young, growing countries and aging, declining ones. Humanity's latest milestone turns a spotlight on this gap and the problems on both sides of it.
---
Reaching a world of 8 billion people signals significant improvements in public health that have increased life expectancy, the U.N. said. But it also pointed out, "The world is more demographically diverse than ever before, with countries facing starkly different population trends ranging from growth to decline."
Nowhere is this more apparent than in Asia. The region has young countries with a median age in the 20s, such as India (27.9 years old), Pakistan (20.4) and the Philippines (24.7), as well as old economies with median ages in the 40s, including Japan (48.7) and South Korea (43.9). The gap between the young and the old has gradually widened over the past decades.
While India faces a lack of jobs and infrastructure to support its growing population, Japan faces a serious reduction in births, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which its government says is a "critical situation." Either way, the population trends are increasingly impacting economies and societies.
Even though economists expect India's gross domestic product to grow around 7% in 2023 -- the highest among major economies -- and although the worst of the COVID-19 pandemic appears to be over, India continues to face high unemployment rates of around 8%, according to the Center for Monitoring Indian Economy, a local private researcher. That shows the country is not creating enough jobs to support the growing population.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 3, 2023 at 6:04pm
-
Concern grows in Modi's India over hunger deaths, food aid, and data gapsThe government is accused of failing to log starvation deaths, while the safety net isn’t catching all it should.The government hasn’t logged a single death from starvation since 2016, but Mrinalini Paul, who works with the Right to Food and Work Network (RTFWN), a local NGO, said it’s clear Sardar’s death should have been recorded as one, as should many others.
The Sardar family was eligible for 35 kilos of rice and grain monthly from a government-run aid programme but had been approved for just two kilos because they lacked the right ID documents, according to Paul. “They had been without even these minimal benefits for six months,” she told The New Humanitarian.
Sunil Agarwala, the district magistrate of Jhargram, refuted the allegations, telling The Hindu newspaper they were "baseless", while insisting that Sardar’s death “was due to illness, TB, and other reasons”.
According to the World Health Organization, undernutrition is a key driver of TB, while malnutrition also makes TB therapy less effective and raises the risk of TB-related death.
The recently published Medical Certification Cause of Death (MCCD), 2020 report found that fewer than a quarter of the 81,15,882 registered deaths in India that year had known causes. Hunger activists are alarmed that a country with 1.4 billion people can only verify the causes of 22.5% of its documented fatalities.
Swati Narayan, assistant professor at the School for Public Health and Human Development at O.P. Jindal Global University, told The New Humanitarian that medical workers are unlikely to catch if the cause of death is starvation given how post-mortems are typically carried out.
She said it was crucial to also consider the person's socioeconomic position and the condition of their body, including the weight of their organs, visceral fat, and diseases brought on by a weaker immune system and malnutrition.
“The post-mortem reports are not an accurate reflection of hunger or starvation deaths in the country,” Narayan said. “Oral autopsies are much better at determining if the cause of death was hunger.”
Worsening hunger and the fight for a stronger safety net
Question marks around Sardar’s death and others like it – a similar case involving three “hunger deaths” in the same family went before the high court last month in Jharkhand, which borders West Bengal to the east – come amid signs of growing food insecurity in India.
The 2022 Global Hunger Index ranks India at 107 out of 121 nations, six places lower than its previous ranking, and below the likes of Ethiopia, Bangladesh, and Pakistan.
While India remains in the “serious” category rather than “alarming” or “very alarming”, it recorded the highest percentage (19.3%) of any country of children under five who are “wasting”, meaning they’re below average weight for their height.
The pandemic made hunger worse, but income losses and rising debt continued to drive it up long after the worst of the health crisis had passed. A survey by the Right to Food Campaign in late 2021/early 2022 found that nearly 80% of respondents faced food insecurity, and almost half had run out of food the previous month.
However, the hunger problems also pre-date COVID. India’s last National Family Health Survey, which used data from 2019, found that stunting – a sign of chronic malnutrition – had risen in 11 out of the 17 states. In 13 states, wasting had also increased.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 4, 2023 at 11:02am
-
India’s economy is growing at the fastest pace of any major country, fueled by corporate earnings and middle-class consumption of the sorts of goods these companies (delivery companies) are rushing to deliver.
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/01/04/business/india-delivery-apps.html
But there has been no commensurate growth in steady jobs in India’s deeply unequal society. That has left the legions of working poor who toil as delivery drivers to serve a middle class that they have fewer and fewer hopes of ever entering.Millions have been pushed into gig work as Prime Minister Narendra Modi has moved to privatize public entities and cut red tape, enacting a series of changes to labor regulations that have diluted protections for workers.
The number of gig workers is projected to reach 23.5 million in 2030, nearly triple the number in 2020, according to a June report by Niti Aayog, a government research agency.
With India’s public sector shrinking, the informal sector now accounts for more than nine out of 10 jobs, International Labor Organization data show. Such jobs, without guaranteed health insurance, social security or pensions, range from the treacherous — construction work without hard hats or other protective gear, or assembly-line labor in illegal firetrap factories — to the merely miserable.
Work as a delivery driver can seem a better alternative. Delivery app companies dangle offers of 45,000 rupees per month, or more than $540, in targeted ads on social media, about double the country’s median income.
But drivers say they rarely earn anything close. What they do get is constant hounding by customers and automated calls from the companies to go faster. The algorithms that assign orders, they say, reward drivers with high ratings, which are based on the speed and number of past deliveries. Drivers say delays — regardless of the reason — can mean a reduction in assignments or even a suspension, pressure that sometimes pushes drivers to put themselves in danger.
Mr. Niralwar joins other delivery app drivers every evening as they mill about in a dusty, unpaved parking area in Hyderabad. They chat between orders, lifting pant legs to compare motorcycle injuries.
Ankit Bhatt, 33, moved to Hyderabad four years ago so that his wife could take a job at a call center. Without a college degree, he had more limited employment options: low-paying retail or informal manual labor.
Ready to begin his evening shift for Swiggy Instamart, Mr. Bhatt tried to log in but found that his ID had been temporarily blocked — punishment, he said, for failing to deliver an order after his motorcycle clutch had given out.
“You could be sick, you could have an accident, your bike could have mechanical issues. You will be penalized for that,” Mr. Bhatt said.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 7, 2023 at 8:18pm
-
Why Does #Modi Not Want #India's #Census2021? Would it Expose #BJP's Lies About Progress in Open Defecation, Village #Electrification, #Poverty, #Hunger?? https://www.economist.com/asia/2023/01/05/postponing-indias-census-...
Narendra Modi often overstates his achievements. For example, the Hindu-nationalist prime minister’s claim that all Indian villages have been electrified on his watch glosses over the definition: only public buildings and 10% of households need a connection for the village to count as such. And three years after Mr Modi declared India “open-defecation free”, millions of villagers are still purging al fresco. An absence of up-to-date census information makes it harder to check such inflated claims. It is also a disaster for the vast array of policymaking reliant on solid population and development data.
----------
Three years ago India’s government was scheduled to pose its citizens a long list of basic but important questions. How many people live in your house? What is it made of? Do you have a toilet? A car? An internet connection? The answers would refresh data from the country’s previous census in 2011, which, given India’s rapid development, were wildly out of date. Because of India’s covid-19 lockdown, however, the questions were never asked.
Almost three years later, and though India has officially left the pandemic behind, there has been no attempt to reschedule the decennial census. It may not happen until after parliamentary elections in 2024, or at all. Opposition politicians and development experts smell a rat.
----------
For a while policymakers can tide themselves over with estimates, but eventually these need to be corrected with accurate numbers. “Right now we’re relying on data from the 2011 census, but we know our results will be off by a lot because things have changed so much since then,” says Pronab Sen, a former chairman of the National Statistical Commission who works on the household-consumption survey. And bad data lead to bad policy. A study in 2020 estimated that some 100m people may have missed out on food aid to which they were entitled because the distribution system uses decade-old numbers.
Similarly, it is important to know how many children live in an area before building schools and hiring teachers. The educational misfiring caused by the absence of such knowledge is particularly acute in fast-growing cities such as Delhi or Bangalore, says Narayanan Unni, who is advising the government on the census. “We basically don’t know how many people live in these places now, so proper planning for public services is really hard.”
The home ministry, which is in charge of the census, continues to blame its postponement on the pandemic, most recently in response to a parliamentary question on December 13th. It said the delay would continue “until further orders”, giving no time-frame for a resumption of data-gathering. Many statisticians and social scientists are mystified by this explanation: it is over a year since India resumed holding elections and other big political events.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 22, 2023 at 8:15pm
-
The Squeeze on India’s Spenders Is Yet to Lift
Analysis by Andy Mukherjee | Bloomberg
https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/the-squeeze-onindias-spende...
Manufacturing of wants is hard anywhere for marketers, but the challenge is bigger when the bottom half of the population takes home only 13% of national income. While India’s rapid economic growth since the 1990s has undoubtedly expanded the spending capacity of its 1.4 billion people, acute and rising inequality — among the worst in the world — makes for a notoriously budget-conscious median consumer. Companies can take nothing for granted: For Unilever’s local Indian unit, a late winter crimped sales of skin-care products last quarter.
Still, the maker of Dove body wash and Surf detergent managed to eke out an overall 5% increase in sales volume from a year earlier, lifting net income to 25.1 billion rupees ($309 million), slightly better than expected. That was achieved by price cuts — passing along the benefit of lower palm-oil costs to soap buyers — and a step up in promotion and advertising. Still, not all players have the market leader’s financial chops. Investors who look closely at Hindustan Unilever Ltd.’s earnings for a pulse on India’s consumer demand will note with dismay the slide in industry-wide volumes for cleaning liquids, personal care items and food, the categories in which the firm competes.
This isn’t new. Consumer demand in India has been moderating since August 2021. Village households, many of which had to liquidate their gold holdings and other assets to treat Covid-19 patients during that summer’s lethal delta outbreak, were not in a mood to spend even after the surge in deaths and hospitalization ebbed.
Then, as major economies began to open up and crude oil and other commodities began to get pricier, firms like Unilever responded to the squeeze by reducing how much they put in a pack. Their idea was to hold on to psychologically crucial “magic price points” — such as five or 10 rupees — in the hope that customers will replenish more often. But when inflation accelerated after the start of the war in Ukraine, there was no option except to shatter the illusion of affordability by raising prices. Volumes flat-lined in the March quarter.
“The worst of inflation is behind us,” Sanjiv Mehta, the chief executive officer, said in a statement after last week’s earnings report. That seems to be the case indeed. India’s aggregate price index rose a slower-than-expected 5.7% in December, the third straight month of cooling. That’s why perhaps instead of pushing four 100-gram bars of Lux soap for 140 rupees, Unilever is charging 156 rupees for five, according to the Business Standard. In offering an 11% price cut by bulking up pack sizes, the company is betting that most households’ budget can now accommodate an extra outlay of 16 rupees.
It’s a reasonable gamble. A bumper wheat harvest is expected this spring. Rural India, which employs two out of three workers, found jobs for a disproportionately larger share of new entrants to the labor force in November and December, according to Mahesh Vyas of CMIE, a private firm that fills in for reliable official jobs data. “Most of the additional employment is happening in rural India and not in the towns,” he says.
And that may well put the spotlight next year on faltering spending in cities. The tech industry is wobbling globally. In India, too, startups are firing employees in large numbers; some former darlings of venture capital, such as online test-prep and education firms, are becoming irrelevant now that Covid-19 restrictions on physical classes have ended.
Meanwhile, India’s software-exports industry — a large employer in metropolises — has become wary of hiring because of slowing global growth. “The pain in urban consumption seems to be showing up,” JM Financial analysts Richard Liu and others wrote last week after Asian Paints Ltd.’s earnings.
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Pakistanis' Insatiable Appetite For Smartphones
Samsung is seeing strong demand for its locally assembled Galaxy S24 smartphones and tablets in Pakistan, according to Bloomberg. The company said it is struggling to meet demand. Pakistan’s mobile phone industry produced 21 million handsets while its smartphone imports surged over 100% in the last fiscal year, according to …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on April 26, 2024 at 7:09pm
Pakistani Student Enrollment in US Universities Hits All Time High
Pakistani student enrollment in America's institutions of higher learning rose 16% last year, outpacing the record 12% growth in the number of international students hosted by the country. This puts Pakistan among eight sources in the top 20 countries with the largest increases in US enrollment. India saw the biggest increase at 35%, followed by Ghana 32%, Bangladesh and…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on April 1, 2024 at 5:00pm
© 2024 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()

You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network