PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
Will Russia Sanctions Accelerate Inflation, Devalue US Dollar and Strengthen Chinese Yuan?
Russia is a commodities superpower. The nation's Eurasian landmass is rich in all kinds of natural resources from food to fuel to metals. To punish Moscow for invading Ukraine, the US and G-7 nations have imposed sanctions on Russia. These sanctions have effectively removed Russian commodities from the global supply chain, triggering double digit price increases for food, fuels and metals. Will the G-7 actions leave the US dollar much weaker? Will the Chinese currency, backed by commodities, gain strength at the expense of the US dollar and Euro? Will the era of commodity-backed money return? In a note to clients, Credit Suisse investment strategist Zoltan Pozsar has answered some of these questions. He says "this (Russia) crisis is not anything we have seen since President Nixon took the U.S. dollar off gold in 1971". "After this war is over, "money" will never be the same again.....and bitcoin (if it still exists then) will probably benefit from all this,” he adds.
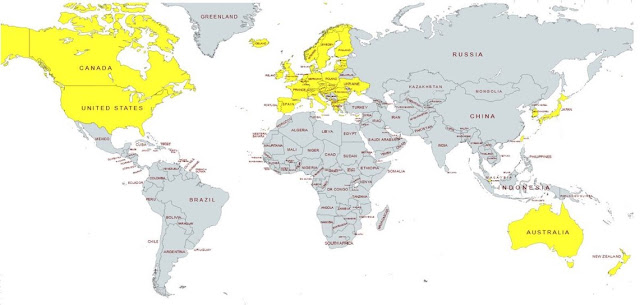 |
| Map of "International Community" Sanctioning Russia |
Post World War II History:
The current global financial system was created in Bretton Woods located in the US State of New Hampshire. Over 700 delegates representing 44 countries met in Bretton Woods in July 1944. The Bretton Woods System, now referred to as Bretton Woods I, required a currency peg to the U.S. dollar which was in turn pegged to the price of gold. This system collapsed in the 1970s but created a lasting influence on international currency exchange and trade through its development of the IMF and World Bank. Zoltan Pozsar believes it is now time for Bretton Woods III. What is Bretton Woods III? Here's how Zoltan Pozsar explains it:
"From the Bretton Woods era backed by gold bullion, to Bretton Woods II backed by inside money (Treasuries with un-hedgeable confiscation risks), to Bretton Woods III backed by outside money (gold bullion and other commodities)".
 |
| Russia's Commodity Exports. Source: Bloomberg |
Commodity Superpower:
Russia is a vast country. Russian landmass extends from Europe to East Asia. It is one of the largest suppliers of oil, gas, metals and wheat. Russia is also a major exporter of fertilizer. China will likely take advantage of the western sanctions to buy up Russian commodities at lower prices.
Pozsar argues that while Western central banks cannot close the gap between Russian and non-Russian commodity prices as sanctions lead them in opposite directions, the People’s Bank of China can “as it banks for a sovereign who can dance to its own tune.”
“If you believe that the West can craft sanctions that maximize pain for Russia while minimizing financial stability risks and price stability risks in the West, you could also believe in unicorns,” Pozsar wrote.
 |
| Pre-Ukraine War Inflation in US. Source: Wall Street Journal |
Bretton Woods III:
Pozsar argues that the Bretton Woods II collapsed when the G7 countries seized Russia’s foreign exchange (FX) reserves, leading to a rise of outside money – reserves kept as commodities – over inside money – reserves kept as liabilities of global financial institutions.
 |
| East vs West Economic Output. Source: Wall Street Journal |
"We are witnessing the birth of Bretton Woods III – a new world (monetary) order centered around commodity-based currencies in the East (Chinese Yuan) that will likely weaken the Eurodollar system and also contribute to inflationary forces in the West,” Zoltan wrote.
Related Links:
Pakistani-American Banker Heads SWIFT, the World's Largest Interban...
Pakistani-Ukrainian Billionaire Zahoor Sees "Ukraine as Russia's Af...
Ukraine Resists Russia Alone: A Tale of West's Broken Promises
Ukraine's Lesson For Pakistan: Never Give Up Nuclear Weapons
Can the Chinese Yuan Replace the US Dollar?
Ukraine's Muslim Billionaire Akhmetov Holds Balance of Power
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 9, 2023 at 7:10pm
-
#Pakistan joins global trend in dumping #US #Dollar for #Chinese #yuan. The first shipment of over 750,000 barrels of #Russian #oil is expected to arrive in June, with Pakistan agreeing to a discounted per-barrel price of around $50–$52. #energy
https://www.cryptopolitan.com/pakistan-joins-in-dumping-usd-for-yuan/
Pakistan decides to purchase discounted Russian oil using the Chinese yuan, joining the global trend of de-dollarization.
The first shipment of over 750,000 barrels is expected to arrive in June, with Pakistan agreeing to a discounted per-barrel price of around $50–$52.
The decision follows sanctions imposed on Russia by the EU, G7, and their allies in response to Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
In a move reflecting the global shift towards de-dollarization, Pakistan has decided to purchase discounted Russian oil using the Chinese yuan.
As part of the BRICS economic bloc’s efforts to conduct international trade in currencies other than the US dollar, Pakistan’s decision signals another transaction conducted using an alternative currency.
Alternative payment for Pakistan amid sanctions
Pakistan is set to pay for Russian oil with the Chinese yuan, as local media report that the first cargo of over 750,000 barrels is expected to arrive in June.
Although the exact amount and mode of payment have not been disclosed, sources reveal that Pakistan has agreed to a discounted per-barrel price of around $50–$52, significantly lower than the G7 price cap on Russian oil of $60 per barrel.
This development follows sanctions imposed on Russia by the EU, G7, and their allies, including a ban on seaborne oil exports and a price cap on Russian oil.
These measures were in response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and aimed to distance the nation from the West. Amid the focus on the Chinese yuan, talks of a BRICS trading currency are expected to progress at the annual BRICS summit.
The growing influence of the Chinese Yuan
With the first shipment of 750,000 barrels anticipated to dock in June, Pakistan plans to pay for Russian crude oil using Chinese yuan. The Bank of China is expected to facilitate the transaction.
However, the mode of payment and the discount offered to Pakistan remain undisclosed, as publicizing such information is not considered beneficial for either party.
An official from Pakistan’s Ministry of Energy stated that Russia would supply URAL crude in the test cargo, which Pakistan Refinery Limited (PRL) will likely refine.
Meanwhile, other sources report that Pakistan has agreed to a per-barrel price of around $50-52, lower than the G7 price cap on Russian oil of $60 per barrel.
The decision to use the Chinese yuan for this transaction illustrates the currency’s growing acceptance in international trade, as well as concerns about the US abusing its dollar hegemony through sanctions.
The yuan’s stability, China’s economic strength, and its large consumer market make it an increasingly reliable choice for international settlements.
In recent months, several countries have expressed their inclination to settle trade deals in the yuan instead of the US dollar. Iraq’s central bank announced in February that it would trade with China using the yuan.
Argentina followed suit in April, declaring that it would start paying for Chinese imports in yuan rather than in US dollars.
According to data from multiple sources, the yuan became the most widely used currency for cross-border transactions in China in March, overtaking the dollar for the first time.
The yuan was used in 48.4 percent of all cross-border transactions, while the dollar’s share declined to 46.7 percent from 48.6 percent a month earlier.
This shift towards the Chinese yuan can be attributed to China’s ongoing efforts to open its financial sector, making it easier for global investors to participate in its domestic financial market.
As the yuan’s role in global payment and settlement, foreign exchange reserves, and investment and financing expands, the de-dollarization trend is expected to continue.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 16, 2023 at 4:34pm
-
Top 10 Countries that Export the Most Goods and Services (Current US$ millions - World Bank 2020)
https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/exports-by-country
Rank Country Exports (Current US$)
1 China $2,723,250.43
2 United States $2,123,410.00
3 Germany $1,669,993.51
4 Japan $785,365.75
5 United Kingdom $770,478.62
6 France $733,165.40
7 Netherlands $711,504.80
8 Hong Kong (China SAR) $612,566.52
9 Singapore $599,216.28
10 South Korea $596,945.20
Profiles of the world's largest exporters
1. China
Aside from the European Union (which is a collective of many countries), China is the world’s largest exporter. In 2020, China exported an estimated $2.72 trillion worth of goods and services, primarily electronic equipment and machinery such as broadcast equipment, computers, integrated circuits, office machine parts, and telephones. In 2018, China’s exports made up about 10.78% of the global total.
2. United States
The U.S. is the second-largest exporter in the world, with an estimated $2.12 trillion in exports for 2020. The largest exports of the U.S. are crude and refined petroleum; integrated circuits; pharmaceuticals and medical instruments; and aircraft including planes, spacecraft, and helicopters as well as their replacement parts. One of the reasons that the United States lags behind China in exports is the cost of labor. Many goods cannot be produced, manufactured, or assembled in the U.S. for a price comparable to that in China.
3. Germany
Having exported an estimated $1.67 trillion worth of goods and services in 2020, Germany is the world’s third-largest exporter. As one of the most technologically advanced countries in the world, Germany’s main exports include automobiles (BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Audi, Volkswagen), pharmaceuticals (Bayer), aircraft, machinery, electronics, and chemicals. Germany is the third of three countries to have exports exceeding $1 trillion, behind only China and the United States.
4. Japan
Japan’s exports for 2020 were valued at an estimated $785.4 billion. Japan’s major exports include automobiles (Toyota, Honda, Nissan, Mazda, Suzuki, more) and automobile parts, integrated circuits and electronic devices (Nintendo, Panasonic, Sony, and many more). Japan's largest export customers are China, the United States, South Korea, Taiwan, and Hong Kong.
5. United Kingdom
The United Kingdom ranked as the fifth-highest exporter in the world in terms of dollar value in 2020, shipping an estimated $770.5 billion in goods and services to international customers. The U.K.'s top exports include cars (Bentley, Jaguar, Mini, Rolls-Royce, more), gas turbines, gold, medicines, hard liquor, antiques, and crude petroleum (which is often first imported from Norway, then exported to the rest of Europe, as well as China and South Korea).
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on August 7, 2023 at 7:12am
-
#European companies suffer €100 billion hit from #Russia operations. Losses concentrated in #energy sector. #Germany is the biggest loser. #UkraineWar https://www.ft.com/content/c4ea72b4-4b02-4ee9-b34c-0fac4a4033f5
Energy and utility groups have reported more than half the combined losses, according to FT analysis of direct impact of the Ukraine war
Europe’s biggest companies have suffered at least €100bn in direct losses from their operations in Russia since President Vladimir Putin’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine last year, according to analysis by the Financial Times.
A survey of 600 European groups’ annual reports and 2023 financial statements shows that 176 companies have recorded asset impairments, foreign exchange-related charges and other one-off expenses as a result of the sale, closure or reduction of Russian businesses.
The aggregate figure does not include the war’s indirect macroeconomic impacts such as higher energy and commodities costs. The war has also delivered a profit boost for oil and gas groups and defence companies.
Moscow’s decision to seize control of the Russian businesses of gas importers Fortum and Uniper in April, followed by the expropriation of Danone and Carlsberg last month, suggests more pain lies ahead, according to analysts.
More than 50 per cent of the 1,871 European-owned entities in Russia before the war are still operating in the country, according to data compiled by the Kyiv School of Economics. European companies still present in Russia include Italy’s UniCredit, Austria’s Raiffeisen, Switzerland’s Nestlé and the UK’s Unilever.
“Even if a company lost a lot of money leaving Russia, those who stay risk much bigger losses,” said Nabi Abdullaev, partner at strategic consultancy Control Risks. “It turns out that cut and run was the best strategy for companies deciding what to do at the start of the war. The faster you left, the lower your loss.”
The heaviest costs of withdrawal are concentrated in a few exposed sectors. Those with the biggest writedowns and charges are oil and gas groups, where three companies alone — BP, Shell and TotalEnergies — reported combined charges of €40.6bn. The losses were far outweighed by higher oil and gas prices, which helped these groups report bumper aggregate profits of about €95bn ($104bn) last year. Defence companies’ shares have been buoyed by the conflict.
Utilities took a direct hit of €14.7bn, while industrial companies, including carmakers, have suffered a €13.6bn blow. Financial companies including banks, insurers and investment firms, have recorded €17.5bn in writedowns and other charges.
Simon Evenett, economics professor at University of St Gallen, said: “You have a small number of companies which have taken a big hit. Once you get away from big ticket charges, the average writedown is probably fairly manageable given the limited Russian footprint.”
Looking at global investment flows into Russia, “even if Europeans were the only investors there, which they are not, the country would account for just 3.5 per cent of their total outward investments”, he said.
BP reported a $25.5bn charge, announcing three days after the invasion that it would sell its 19.75 per cent stake in state-owned oil group Rosneft.
It took TotalEnergies longer to report a total cost of $14.8bn. The French energy group has yet to write down its 20 per cent stake in the Yamal LNG project. Shell took a $4.1bn charge, while Norwegian oil and gas group Equinor and Austria’s OMV have reported €1bn and €2.5bn respectively.
German group Wintershall Dea in January said the Kremlin’s expropriation of its Russia business had wiped €2bn of cash from its bank accounts. In turn Wintershall’s owner BASF wrote down its stake in the energy explorer by €6.5bn.
Uniper, which was bailed out by the German state last year, booked €5.7bn in impairments, while Finland’s Fortum took a €5.3bn hit.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 5, 2023 at 4:44pm
-
A new Huawei phone has defeated US chip sanctions against China
https://qz.com/a-new-huawei-phone-has-defeated-us-chip-sanctions-ag...
The new Kirin 9000s chip in Huawei’s latest phone uses an advanced 7-nanometer processor fabricated in China by the country’s top chipmaker, Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corp. (SMIC), according to a teardown of the phone that TechInsights conducted for Bloomberg.
Huawei’s latest smartphone, the Mate 60 Pro, offers proof that China’s homegrown semiconductor industry is advancing despite the US ban on chips and chipmaking technology.
The new Kirin 9000s chip in Huawei’s latest phone uses an advanced 7-nanometer processor fabricated in China by the country’s top chipmaker, Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corp. (SMIC), according to a teardown of the phone that TechInsightsconducted for Bloomberg
A brief recent timeline of US chip sanctions against China
August 2022: The US Congress passes the CHIPS and Science Act, a law that approves subsidies and tax breaks to help jumpstart the production of advanced semiconductors on American soil.
September 2022: The Biden administration bans federally funded US tech firms from building advanced facilities in China for a decade.
October 2022: The US commerce department bars companies from supplying advanced chips and chipmaking equipment to China, calling it an effort to curb China’s ability to produce cutting-edge chips for weapons and other defense technology, rather than a bid to cripple the country’s consumer electronics industry.
November 2022: The US bans the approval of communications equipment from Chinese companies like Huawei Technologies and ZTE, claiming that they pose “an unacceptable risk” to the country’s national security.
May 2023: Beijing bans its “operators of critical information infrastructure” from doing business with Micron Tech, an Idaho-based chipmaker.
“In the AI garden, the seeds are the AI software frameworks—which China already has access to. The plants in the garden are the AI models in use, which again are already available to Chinese AI companies. Nvidia provides the best shovels and pruning shears to tend the garden, but not the only means to tend it. So it doesn’t make sense to try to build a high wall around it...[T]o over-regulate these chips creates the risk that the US could fumble away its technology leadership. Would you rather have Chinese AI customers continue to fuel Nvidia’s growth and success? Or would you rather they spend their yuan to fuel the growth and success of Chinese suppliers?”
—Patrick Moorhead, a tech analyst, writing in Forbes in July 2023
One big number: China’s hoard of Nvidia chips
$5 billion: The value of orders that China’s tech giants have placed with Nvidia for its A800 and A100 chips, to be delivered this year, according to an August report by the Financial Times. The biggest internet giants—Baidu, ByteDance, Tencent, and Alibaba—have placed orders totalling $1 billion to buy around 100,000 A800 processors. Given that the US is mulling new export controls, Chinese companies are rushing to hoard the best chips on the market to train their AI models and run their data centers.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 27, 2023 at 11:05am
-
Arnaud Bertrand
@RnaudBertrand
SCMP editorial: https://scmp.com/comment/opinion/article/3242880/dollar-still-king-...
"The increasingly close relationship between China and Saudi Arabia has taken another significant step forward. The central banks of both countries have agreed on their first currency swap...
In the longer term, it augurs a petroyuan future as the two countries are already the most important trading partners of each other.
In a global political economy long dominated by the petrodollar, this could be the beginning of a seismic shift."
https://x.com/RnaudBertrand/status/1728923824996139481?s=20
---------------------
The increasingly close relationship between China and Saudi Arabia has taken another significant step forward. The central banks of both countries have agreed on their first currency swap worth a maximum of 50 billion yuan (HK$55 billion) over the next three years.
In immediate terms, the pact will foster bilateral commerce denominated in both the yuan and the riyal. In the longer term, it augurs a petroyuan future as the two countries are already the most important trading partners of each other.
In a global political economy long dominated by the petrodollar, this could be the beginning of a seismic shift. It has been a very long time coming.
Almost a year ago, President Xi Jinping made a historic visit to Riyadh, followed by Hong Kong Chief Executive John Lee Ka-chiu in February. A flurry of deals followed.
The Shanghai Stock Exchange and its Saudi counterpart have started collaboration on cross-listings, including exchange-traded funds (ETFs), financial technology (fintech), environmental, social and governance (ESG) and data exchange.
China, Saudi Arabia central banks sign currency swap accord to foster trade
21 Nov 2023
The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) building in Beijing on Tuesday, April 18, 2023. Photo: Bloomberg
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority, the city’s de facto central bank, and the Saudi Central Bank have enhanced ties covering the latest technologies in regulatory supervision and monitoring, and in financial fields such as tokenisation and new payment systems.
However, the latest currency swap pact will be the most important. It means trade can be conducted in local currencies, instead of defaulting to the US dollar. This may be seen as a challenge to US dollar dominance. Perhaps in the longer term, it is. But there is a good economic reason.
The current US federal interest rate of 5-plus per cent has pushed the dollar to historical levels against most other currencies, making trade denominated in the dollar more expensive.
There are obvious advantages for two big trade partners like China and Saudi Arabia to be able to utilise a local-currency option, which will help relieve pressures from having to trade in a more expensive currency.
Global “de-dollarisation” may take a while yet, but the trend already reflects cracks in a global economy long used to US currency settlements.
The yuan may or may not pose a challenge to dollar hegemony, but its internationalisation continues apace – to the benefit of both the Chinese and global economies.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 31, 2024 at 2:23pm
-
The era of US dollar dominance is 'finished,' says Wall Street veteran who just retired after 54 years
https://markets.businessinsider.com/news/currencies/dick-bove-banks..."The dollar is finished as the world's reserve currency," Dick Bove, who retired as a financial analyst after 54 years this month, told The New York Times. Bove, 83, predicted that China's economy would surpass America's in size.
The dollar's reign as the world's reserve currency is nearly over, Dick Bove says.
The newly retired bank analyst blamed corporate offshoring and flagged the threat posed by China.
Bove highlighted the de-dollarization trend and said other analysts are too bought in to admit it.
The US dollar has been the lifeblood of global finance and trade since World War II — but one Wall Street veteran thinks the end of that era is nigh.
"The dollar is finished as the world's reserve currency," Dick Bove, who retired as a financial analyst after 54 years this month, told The New York Times.
Bove, 83, predicted that China's economy would surpass America's in size. He blamed the outsourcing of US manufacturing to other countries, arguing that trend has given other countries more control of international production, the global economy, and worldwide money flows.
He also suggested that cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin could help fill the void left by the dollar's shrinking influence.
Dollar-denominated assets make up nearly 60% of international reserves, per the International Monetary Fund. However, several countries are embracing "de-dollarization" — working to erode dollar dominance — especially after the US took advantage of Russia's reliance on the greenback to levy sanctions against it following its invasion of Ukraine in 2022.
Nations ranging from Brazil and Argentina to India and Bangladesh are exploring the use of backup currencies and assets, such as the Chinese yuan and bitcoin, for trade and payments.
Several governments have blasted the excessive influence of US monetary policy on other economies and currencies, the dollar's strength for pricing out poor countries from imports, and the diminishing need for a petrodollar now the US has achieved energy independence through domestic shale oil and green energy production.
Bove, who worked at 17 brokerages during his career, told the Times that analysts who aren't forecasting dollar doom are simply "monks praying to money" who are unwilling to bite the hand that feeds them: the traditional financial system.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 10, 2024 at 9:50am
-
US Congressman Says Countries Tired of Inflation Tax, Could Abandon US Dollar
https://sputnikglobe.com/20240520/us-congressman-says-countries-tir...
WASHINGTON (Sputnik) - Countries are growing weary of the US dollar and could abandon the currency due to inflation, US Congressman Thomas Massie said on Monday.
“The whole world is holding dollars, so when we devalue the dollar, we’re not just taxing our own people, we’re taxing the entire world,” Massie said in an interview with Glenn Beck.
“The rest of the world is getting tired of being used that way… and when they start using alternate forms of money to do their transactions, or holding different assets in their own sovereign wealth funds, then we’re not going to be able to do that trick on anybody except for US citizens.”
Last week, Massie introduced bills to audit and abolish the Federal Reserve, citing their contribution to inflation. The Federal Reserve devalued the dollar and enabled free money policies that caused high inflation, Massie said.
The legislation to end the Federal Reserve now has over 20 cosponsors in the House of Representatives, Massie said.
https://x.com/SputnikInt/status/1790041974902247876
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 9, 2024 at 5:30pm
-
Saudi Arabia privately hinted earlier this year it might sell some European debt holdings if the Group of Seven decided to seize almost $300 billion of Russia's frozen assets, people familiar with the matter said, according to Bloomberg.
https://www.middleeasteye.net/news/saudi-arabia-threatened-sell-eur...
Like other Gulf states, Saudi Arabia’s currency is pegged to the dollar and it sells its oil in greenbacks, boosting the dollar’s position as the world’s reserve currency.
In January 2023, Saudi Arabia said it was considering trading in currencies other than the US dollar after reports that it was in discussions with China about selling some crude in yuan.
It’s not clear how much European debt Saudi Arabia holds, but its central bank’s net foreign currency reserves stand at $445bn. Saudi Arabia holds $135.9bn in US treasuries, placing it 17th among investors in the US bonds.
US President Joe Biden’s pledge to make Saudi Arabia “a pariah” over the murder of Middle East Eye and Washington Post columnist Jamal Khashoggi crystallised fears that Washington could one day turn on its decades-old ally.
Biden has since pivoted and is leaning on Saudi Arabia to seal a normalisation deal with Israel and play a role in post-war governance of the Gaza Strip.
-------
Like other Gulf states, Saudi Arabia’s currency is pegged to the dollar and it sells its oil in greenbacks, boosting the dollar’s position as the world’s reserve currency.
In January 2023, Saudi Arabia said it was considering trading in currencies other than the US dollar after reports that it was in discussions with China about selling some crude in yuan.
It’s not clear how much European debt Saudi Arabia holds, but its central bank’s net foreign currency reserves stand at $445bn. Saudi Arabia holds $135.9bn in US treasuries, placing it 17th among investors in the US bonds.
US President Joe Biden’s pledge to make Saudi Arabia “a pariah” over the murder of Middle East Eye and Washington Post columnist Jamal Khashoggi crystallised fears that Washington could one day turn on its decades-old ally.
Biden has since pivoted and is leaning on Saudi Arabia to seal a normalisation deal with Israel and play a role in post-war governance of the Gaza Strip.
Saudi Arabia’s threat underscores concerns in wealthy Gulf states that the West could one day apply similar economic levers it is pulling against Russia to Gulf powers' overseas assets, if criticism of human rights issues in the Gulf or their foreign policy decisions resurfaces.
Russian President Vladimir Putin has courted Saudi Arabia, as he relies on the oil-rich kingdom to counter Moscow’s isolation on the world stage and shore up energy markets.
Putin made a rare visit to Saudi Arabia and the UAE in December.
Comment
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- Next ›
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Pakistani Prosthetics Startup Aiding Gaza's Child Amputees
While the Israeli weapons supplied by the "civilized" West are destroying the lives and limbs of thousands of Gaza's innocent children, a Pakistani startup is trying to provide them with free custom-made prostheses, according to media reports. The Karachi-based startup Bioniks was founded in 2016 and has sold prosthetics that use AI and 3D scanning for custom designs. …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on July 8, 2025 at 9:30pm
Indian Military Begins to Accept Its Losses in "Operation Sindoor" Against Pakistan
The Indian military leadership is finally beginning to slowly accept its losses in its unprovoked attack on Pakistan that it called "Operation Sindoor". It began with the May 31 Bloomberg interview of the Indian Chief of Defense Staff General Anil Chauhan in Singapore where he admitted losing Indian fighter aircraft to Pakistan in an aerial battle on May 7, 2025. General Chauhan further revealed that the Indian Air Force was grounded for two days after this loss. …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on July 5, 2025 at 10:30am — 6 Comments
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network