PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
India's "Indigenous" Weapons of Mass Destruction
Along with raising the alarm, the Indian report offered the usual excuse for the alleged missile gap by boasting that "unlike Pakistan, our program is indigenous".
Let's explore the reality of the "indigenous" claim repeated ad infintum by Indian government and New Delhi's defense establishment.
US-European Origins of Indian Missile Program:
APJ Abul Kalam is credited with designing India's first satellite launcher SLV3. Its design is virtually identical to the American Scout rocket used in the 1960s. According to the details published in the Bulletin of Atomic Scientists, Abul Kalam spent four months in training in the United States in 1963-1964. He visited NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia, where the U.S. Scout rocket was conceived, and the Wallops Island Flight Center on the Virginia coast, where the Scout was being flown. Soon after Abul Kalam's visit, India requested and received detailed technical reports on the Scout's design, which was unclassified.
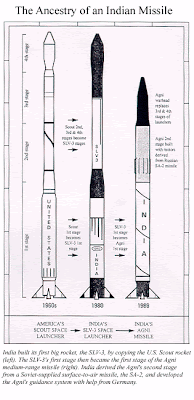
US Scout and India's SLV3 are both 23 meters long, use four similar solid-fuel stages and "open loop" guidance, and lift a 40-kilogram payload into low earth orbit. The SLV's 30-foot first stage later became the first stage of the Agni.
The United States was followed by others. Between 1963 and 1975, more than 350 U.S., French, Soviet, and British sounding rockets were launched from India's Thumba Range, which the United States helped design. Thumba's first group of Indian engineers had learned rocket launching and range operation in the United States.
India's other missile, the "Prithvi" (earth), which uses a liquid-propelled motor to carry a one-ton payload 150 miles, resembles the widely sold Soviet Scud-B. Indian sources say that the Agni's second stage is a shortened version of the Prithvi, according to Gary Milhollin of the Wisconsin Project.
France also launched sounding rockets from India, and in the late 1960s allowed India to begin building "Centaure" sounding rockets under license from Sud Aviation.
The aid of the United States and France, however, was quickly surpassed by substantial West German help in the 1970s and 1980s. Germany assisted India in three key missile technologies: guidance, rocket testing, and the use of composite materials. All were supposed to be for the space program, but all were also used for military missiles.
The cryogenic stage used in a recent failed satellite launch by India was a copy of the Russian cryogenic rocket engine and the cryogenic technology transferred to India in the 1990s. According to Non-proliferation review of 1997, it has emerged that Russia continued transferring rocket engine technology to India in 1993 after its agreements with the United States stop such transfer under MTCR. This reportedly resulted in the completion of 60 to 80 percent of the transfers to India.
North American Origins of India's Nuclear Bomb:
India's nuclear program would not have advanced without a lot of help from Canadians that resulted in Indian copies of Canadian reactors to produce plutonium for its nuclear bombs.
India conducted its first atomic bomb test in 1974. Indians used 40 MW Canadian Cirus reactor and U.S. heavy water both imported under guarantees of peaceful use and used them openly to make plutonium for its 1974 nuclear blast.
In 1972, Canadian-built 100 MWe Rajasthan-1 nuclear power reactor became operational, serving as the model for later unsafeguarded reactors. Another Rajasthan unit started operating in 1980 and two units in 2000. In 1983, India's 170 MW Madras-1, a copy of Canadian Rajhastan-1 reactor, became operational. A second Madras unit followed in 1985. According to the Risk Report Volume 11 Number 6 (November-December 2005), the heavy water and other advanced materials and equipment for these plants were smuggled to India from a number of countries, including the USSR, China and Norway. Some of the firms, such as West German firm Degussa, were caught and fined by the United States for re-exporting to India 95 kg of U.S.-origin beryllium, usable as a neutron reflector in fission bombs.
In May 1998, India conducted two rounds of nuclear weapon tests. Last year, the media reports indicated that Kasturiranga Santhanam, the coordinator of India's 1998 nuclear tests, went public with allegations that India's Pokhran II test of a thermonuclear bomb in 1998 was actually a fizzle. The device, designed to generate 45 kilotons, yielded an explosion equivalent to only 15 to 20 kilotons of TNT.
Summary:
There is plenty of evidence and documentation from sources such as the Wisconsin Project to show that the Indian missiles and bombs are no more indigenous than Pakistan's. The fact is that neither India nor Pakistan were first to split the atom, or to develop modern rocket science. The Industrial Revolution didn't exactly start in India or Pakistan or even in Asia; it began in Europe and the rest of the world learned from it, even copied it.
The differences between India and Pakistan in terms of the technology know-how and the knowledge base are often highly exaggerated to portray India as "technology power house" and Pakistan as a backwater. Some of these analyses by Indian Brahman pundits and commentators have racial and religious overtones implying that somehow Brahmin or Hindu minds are superior to those of the people of other religions or castes in South Asia.
What is often ignored by such anti-Pakistan Indian analysts is the fact that neither of the two Indian pioneers, nuclear scientist Homi Bahbha and rocket scientist Abul Kalam, belong to the Hindu faith or the Brahmin caste. The false sense of Indian superiority is pushed by self-serving Indian and some western analysts to justify their own biased conclusions.
These analysts have fed what George Perkovich described in his book "India's Nuclear Bomb" on page 410 as "general Indian contempt for Pakistan's technical capabilities" and may cause serious miscalculations by the Indian security establishment about Pakistan's defense capabilities. Indian chauvinistic analyses have been put in perspective by another piece in Newsday (Friday, May 15, 1998; Page A5: "India Errs Nuclear Power Isn't Real Power"), in which George Perkovich talked about the rise in India of a radicalized, ultra-nationalistic BJP for the "glory of the Hindu race and rashtra (nation)". Perkovich added that "the Bharatiya Janata Party, has long felt that nuclear weapons offer a quicker ride to the top. Like atavistic nationalists elsewhere, they believe that pure explosive power will somehow earn respect and build pride."
The extreme right-wing influence on South Asian analysts has the potential for serious miscalculations by either India or Pakistan in the nuclear and the missile arena, and it does not augur well for the future of Indo-Pak region and the world at large.
Related Links:
India's Nuclear Bomb by George Perkovich
Cyberwars Across India, Pakistan and China
Pakistan's Defense Industry Going High-Tech
India-Pakistan Military Balance
Scientist Reveals Indian Nuke Test Fizzled
The Wisconsin Project
The Non-Proliferation Review Fall 1997
India, Pakistan Comparison 2010
Can India "Do a Lebanon" in Pakistan?
Global Firepower Comparison
Evaluation of Military Strengths--India vs. Pakistan
Only the Paranoid Survive
India Races Ahead in Space
21st Century High-Tech Warfare
World Military Spending
Indian Attempts to Scuttle F-16s For Pakistan
Attrition Rates For IAF and PAF
Mockery of National Sovereignty
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 28, 2012 at 8:22pm
-
Here are a few excerpts of an MIT doctoral thesis by Christopher Clary on future India-Pakistan conflict:
Conventional wisdom suggests that India has gained sufficient conventional superiority to fight and win a limited war, but the reality is that India is unlikely to be able to both achieve its political aims and prevent dangerous escalation.
------------
While India is developing limited options, my analysis suggests India's military advantage over Pakistan is much less substantial than is commonly believed.
------------
Most analyses do not account adequately for how difficult it would be for the navy to have a substantial impact in a short period of time. Establishing even a partial blockade takes time, and it takes even more time for that blockade to cause shortages on land that are noticeable. As the British strategist Julian Corbett noted in 1911, "it is almost impossible that a war can be decided by naval action alone. Unaided, naval pressure can only work by a process of exhaustion. Its effects must always be slow…."7 Meanwhile, over the last decade, Pakistan has increased its ability to resist a blockade. In addition to the main commercial port of Karachi, Pakistan has opened up new ports further west in Ormara and Gwadar and built road infrastructure to distribute goods from those ports to Pakistan's heartland. To close off these ports to neutral shipping could prove particularly difficult since Gwadar and the edge of Pakistani waters are very close to the Gulf of Oman, host to the international shipping lanes for vessels exiting the Persian Gulf. A loose blockade far from shore would minimize risks from Pakistan's land-based countermeasures but also increase risks of creating a political incident with neutral vessels.
-------------
The air balance between India and Pakistan is also thought to heavily favor the larger and more technologically sophisticated Indian Air Force. While India has a qualitative and quantitative advantage, the air capabilities gap narrowed rather than widened in the last decade. The Pakistan Air Force has undergone substantial modernization since 2001, when Pakistan exited from a decade of US-imposed sanctions. With purchases from US, European, and Chinese vendors, Pakistan has both dramatically increased the number of modern fighter aircraft with beyond-visual-range capability as well as new airborne early warning and control aircraft. Meanwhile, India's fighter modernization effort has been languid over the last decade. India's largest fighter procurement effort—the purchase of 126 Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft—began in 2001 and has been slowed considerably by cumbersome defense procurement rules designed to avoid the appearance of corruption.
---------------
The ground forces balance has received the most attention from outside observers, in large part because the Indian Army has publicized its efforts at doctrinal innovation, most often referred to under the "Cold Start" moniker. However, India's ground superiority is unlikely to be sufficient to achieve a quick victory.
----------
The net result of this analysis is to conclude that India's limited military options against Pakistan are risky and uncertain. Pakistan has options to respond to limited Indian moves, making counter-escalation likely. At least in the near-term, Pakistan appears to have configured its forces in such a way as to deny India "victory on the cheap." Therefore, India might well have to fight a full-scale war that could destroy large segments of Pakistan's army to achieve its political aims, which would approach Pakistan's stated nuclear redlines. Such a conclusion should induce caution among Indian political elites who are considering military options to punish or coerce Pakistan in a future crisis. ...web.mit.edu/cis/precis/2012spring/india_pakistan.html
Comment
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Modi's AI Spectacle: Chaos and Deception in New Delhi
The India AI Impact Summit 2026, held at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi, has been marred by chaos, confusion and deception. The events on the ground have produced unintended media headlines for India's Prime Minister Narendra Modi who wants to be seen as the "vishwaguru" (teacher of the world) in the field of artificial intelligence as well. First, there was massive chaos on the opening day, with long…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on February 19, 2026 at 12:00pm — 9 Comments
India-Pakistan Cricket Match: The Biggest Single Event in the World of Sports
Why did Pakistan's decision to boycott the India-Pakistan match in solidarity with Bangladesh in this year's T20 World Cup send shockwaves around the world? And why did it trigger the International Cricket Council's and other cricket boards' urgent efforts to persuade Pakistan to return to the match? The reason has a lot to do with its massive financial impact, estimated to be as much as …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on February 11, 2026 at 4:00pm — 2 Comments
© 2026 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network