PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
World at 8 Billion: Pakistan is Fourth Largest Contributor to Last Billion
The global population increased by one billion over the last 12 years to reach 8 billion this year, according to the United Nations. Pakistan contributed 49 million people to the last billion, making it the fourth largest contributor after India (177 million), China (73 million) and Nigeria (51 million). Nigeria is expected to soon overtake Indonesia and Pakistan to become the world's 4th most populous nation. More than half of the projected increase in the global population up to 2050 will be concentrated in eight countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines and the United Republic of Tanzania. Rising working age population is turning Pakistan into a major global consumer market. It is also fueling Pakistan's growing surplus labor exports and record overseas worker remittances.
 |
|
|
 |
| World Population Visualization in 2022. Source: Visual Capitalist |
World's 7th Largest Consumer Market:
Pakistan's share of the working age population (15-64 years) is growing as the country's birth rate declines, a phenomenon called demographic dividend. With its rising population of this working age group, Pakistan is projected by the World Economic Forum to become the world's 7th largest consumer market by 2030. Nearly 60 million Pakistanis will join the consumer class (consumers spending more than $11 per day) to raise the country's consumer market rank from 15 to 7 by 2030. WEF forecasts the world's top 10 consumer markets of 2030 to be as follows: China, India, the United States, Indonesia, Russia, Brazil, Pakistan, Japan, Egypt and Mexico. Global investors chasing bigger returns will almost certainly shift more of their attention and money to the biggest movers among the top 10 consumer markets, including Pakistan. Already, the year 2021 has been a banner year for investments in Pakistani technology startups.
 |
| Consumer Markets in 2030. Source: WEF |
 |
| World Population in 2050. Source: Visual Capitalist |
Labor Exports:
With rapidly aging populations and declining number of working age people in North America, Europe and East Asia, the demand for workers will increasingly be met by major labor exporting nations like Bangladesh, China, India, Mexico, Pakistan, Russia and Vietnam. Among these nations, Pakistan is the only major labor exporting country where the working age population is still rising.
 |
| Working Age Population Declining Among Major Labor Exporters. Sourc... |
Over 10 million Pakistanis are currently working/living overseas, according to the Bureau of Emigration. Before the COVID19 pandemic hit in 2020, more than 600,000 Pakistanis left the country to work overseas in 2019. Nearly 700,000 Pakistanis have already migrated in this calendar year as of October, 2022. The average yearly outflow of Pakistani workers to OECD countries (mainly UK and US) and the Middle East was over half a million in the last decade.
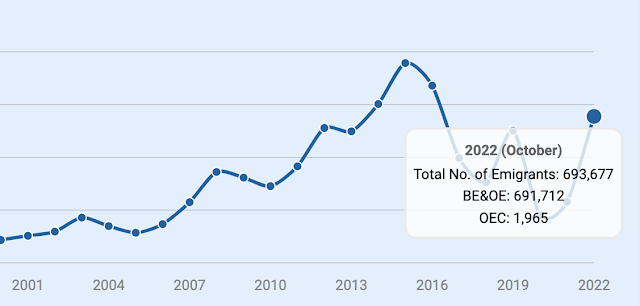 |
| Pakistani Workers Going Overseas. Source: Bureau of Emigration |
Haq's Musings
South Asia Investor Review
Pakistan is the 7th Largest Source of Migrants in OECD Nations
Pakistani-Americans: Young, Well-educated and Prosperous
Last Decade Saw 16.5 Million Pakistanis Migrate Overseas
Pakistan Remittance Soar 30X Since Year 2000
Pakistan's Growing Human Capital
Two Million Pakistanis Entering Job Market Every Year
Pakistan Projected to Be 7th Largest Consumer Market By 2030
Hindu Population Growth Rate in Pakistan
Do South Asian Slums Offer Hope?
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 17, 2022 at 9:46am
-
Migration Can Boost South Asia’s Recovery and Support Long-Term Development
https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2022/11/07/migratio...
Migration drives economic growth as it allows people to move to where they are more productive. International migrants from Bangladesh, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka who work in the Gulf states, for example, earn up to five times what they would at home and help generate some of the largest remittance inflows in the world. Nepal derives an estimated 20 percent of its income from remittance inflows, and in Bangladesh and Pakistan, remittance revenue accounts for 6 and 8 percent of GDP, respectively. Migration also allows people to adjust to local economic shocks, such as extreme-weather disasters, to which South Asia’s rural poor are highly vulnerable.
“While migration has numerous economic benefits, the costs of moving such as credit constraints, lack of information, and labor market frictions prevent them from being fully realized,” said Eaknarayan Aryal, Secretary, Ministry of Labor, Employment, and Social Security in Nepal. “Nepal and countries across South Asia must work to facilitate labor mobility as doing so is vital to the region’s recovery and resilience to future shocks.”
Poor South Asian migrants, many of whom hold temporary jobs in the informal sector, face several challenges such as precarious labor market conditions, visas tied to employment, and limited access to social protection. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed their long-standing vulnerabilities as they were disproportionately affected by restrictions to movement. However, the later phase of the pandemic has highlighted the crucial role migration can play in facilitating recovery. Survey data from the report suggests that in late 2021 and early 2022, migration flows are associated with movement from areas hit hard by the pandemic to those that were not, thus helping equilibrate demand and supply of labor in the aftermath of the COVID-19 shock. In Nepal, by late 2021, migrants were 13 percentage points more likely to be employed than those who did not migrate after facing job loss during the early months of the pandemic.
“Migration is picking up again in South Asia, but remains slow and uneven, raising concerns that the pandemic shock has had long-term impacts on the costs and frictions associated with it,” said Hans Timmer, World Bank Chief Economist for South Asia. “Policymakers must address these often-prohibitive costs and frictions and incorporate measures to de-risk migration.”
The report offers several recommendations on cutting the high costs of migration, including drawing bilateral and multilateral agreements, strengthening the remittance infrastructure, and offering information and training programs to help potential migrants make better decisions about moving. It also offers recommendations on de-risking migration through means such as more flexible visa policies, mechanisms to support migrant workers during shocks, and social protection programs.
“South Asia is the largest beneficiary of remittance in the world. Remittance has played a central role in alleviating poverty, coping with economic shocks, and making substantial progress toward sustainable development goals in Nepal,” said Dr. Biswash Gauchan, IIDS Executive Chair. “However, the socioeconomic and political cost of migration is also very high in the country where a substantial number of the working-age population has gone abroad in search of employment. IIDS is happy to host this regional conference on this crucial theme in Nepal in collaboration with the World Bank, particularly in the aftermath of the COVID-19.”
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 17, 2022 at 9:51am
-
The next wave of mass migration
FEDERICA SAINI FASANOTTI
Extreme weather events are likely to become the main cause behind waves of immigration toward Europe.
https://www.gisreportsonline.com/r/climate-migration/
urricane Ian, which disrupted the lives of millions when it swept over the Gulf of Mexico in late September this year, will not soon be forgotten. Torrential rains and winds of up to 240 kilometers per hour produced an extraordinary surge that flooded not only coastal areas but also their hinterland.
At the same time, Typhoon Noru was slamming into the Philippines. Earlier this year, Hurricane Fiona formed near Puerto Rico and hit Canada with unprecedented force, and Typhoon Nanmadol drove 9 million people to evacuate from their homes in Japan. Typhoon Merbok devastated Alaska with waves more than 50 feet high. Pakistan saw dramatic floods, aggravated by melting local glaciers. Leaving as much as one third of the country underwater, and more than 1,600 people and 800,000 livestock dead, the disaster will change the face of Pakistan for decades. The United Nations has called these phenomena the footprint of climate change.
Although Africa’s 54 states have not contributed significantly to the global emissions that accelerated climate change, the continent is one of the hardest hit. Desertification, dust storms and rising sea levels are poised to wreak havoc on large segments of the African populace.
By 2100, Africa is expected to account for 40 percent of the global population, which will grow to 11 billion. There will likely be 2.5 billion Africans by 2050. Amar Bhattacharya of the Brookings Institution writes that this growth will require an extraordinary increase in investment in “three critical areas: energy transitions and related investments in sustainable infrastructure; investments in climate change adaptation and resilience; and restoration of natural capital (through agriculture, food and land use practices) and biodiversity. … Altogether, Africa will need to invest around $200 billion per year by 2025 and close to $400 billion per year by 2030 on these priorities.”
African governments will be the first line of defense to safeguard the continent’s biological heritage, such as the rainforest of the Congo River Basin, which like the Amazon is crucial to removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Africa’s worst climate-related changes in recent decades are not hurricanes, but rather a persistent drought. The near extinction of Lake Chad is a prime example, as are the widening of the Sahel desert belt southward and the increasingly long periods without rain throughout the Maghreb. The population will grow but rainfall will decrease, thus rapidly shrinking the amount of arable land. And temperatures will rise – in a continent where only half of the 1.2 billion residents have access to electricity.
If these trends continue unchecked, much of Africa will ultimately become uninhabitable. In the Lake Chad basin, 5.3 million people (mostly fishermen and farmers) were displaced by climate-related changes. Experts predict that Africa’s glaciers will disappear: those of Mount Kenya by 2030 and those of Mount Kilimanjaro by 2040.
Already, small rural communities in the Maghreb struggle to produce enough to subsist. The same goes for intensive agriculture, which in Morocco, Tunisia and Algeria, generates up to a fifth of gross domestic product. Even slight disruptions will have exponential effects on those societies.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 17, 2022 at 2:11pm
-
Remittances as an economic and social engine
by José Cabral, Managing Director, Ria Money Transfer
https://ibsintelligence.com/blogs/remittances-as-an-economic-and-so...
The role remittances play in developing local economies through increased cash flows goes hand-in-hand with the social benefit they provide to the families and communities that receive them. The billions of dollars sent annually to developing countries can allow recipients to improve their standard of living through education, healthcare, food security, and savings. By giving people simplified access to finance by digital means, people across the world can achieve greater financial independence.
----------
For many of us, the ease of accessing digital financial services, such as contactless payments and electronic transactions, is often taken for granted. However, across many parts of the world, millions of people do not have access to digital bank accounts or credit and debit cards and rely instead on cash for daily transactions and savings.
In the age of globalisation and interconnectedness, more people than ever before are migrating to different countries in search of better opportunities. Many of the more than 280 million migrants around the world send money to loved ones back home. These cross-border transactions, called remittances, accounted for over $600 billion in income globally in 2021 and serve as a lifeline for many. Families receiving remittances invest them in education, healthcare, and food security.
The UK as a major remittance hotspot
Some countries around the world are hotspots for both immigration and remittances, as the two often go hand-in-hand. In the UK, over 14% of the country’s population in 2021 was foreign-born, totalling over 9.6 million people and a large portion of the job force. The majority hail either from other countries in Europe or from Asian countries such as India and Pakistan. With a significant migrant population comes a significant international cash flow; the UK is the source of billions of dollars in remittances sent annually, which make a sizeable impact on many recipient countries’ GDPs.
India is the country of origin for the largest portion of migrants in the UK, representing 9% of the country’s foreign-born population. It is also a leading recipient of remittances worldwide, and nearly 15% of UK remittances go to India. In 2020, India received over $3.9 billion in remittances from the UK alone, totalling almost 7% of all remittances sent to India in that year — only the US and the UAE had higher figures.
Nigeria receives the greatest total volume of remittances from the UK. An estimated $4.1 billion in remittances was sent from the UK to Nigeria in 2021, totalling 24% of all remittances sent to Nigeria that year. Other significant remittance flows from the UK include Pakistan, where almost 5% of the UK’s foreign-born population comes from and which received over $1.68 billion in remittances from the UK in 2020, and Poland, a country of origin to 7% of migrants in the UK and recipient of $1.14 billion in 2020.
The impact this has on economies
Remittance flows to the developing world have a powerful role in shaping local economies. Both Nigeria and India are global powerhouses with enormous economies, of which 4% and 3% respectively are derived from remittances. In Pakistan, remittances represent 8.7% of GDP, and over 6% of those remittances come from the UK. Cross-border money transfers to these regions are vital to the families who use this money to pay for food, medicine, and education, as well as to fund small businesses and make investments.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 17, 2022 at 5:52pm
-
Fueled by rapid growth in Africa, global population hits 8 billion
As the global population pushes 8 billion people, Africa and Asia are leading the growth. Nigeria could soon become the world’s fourth most populated country, while India is expected to overtake China as the world’s most populous country next year.
By Dan Ikpoyi and Chinedu Asadu Associated Press
November 15, 2022
|
LAGOS, NIGERIA
https://www.csmonitor.com/World/2022/1115/Fueled-by-rapid-growth-in...
Among them is Nigeria, where resources are already stretched to the limit. More than 15 million people in Lagos compete for everything from electricity to light their homes to spots on crowded buses, often for two-hour commutes each way in this sprawling megacity. Some Nigerian children set off for school as early as 5 a.m.
And over the next three decades, the West African nation’s population is expected to soar even more: from 216 million this year to 375 million, the U.N. says. That will make Nigeria the fourth-most populous country in the world after India, China, and the United States.
----
The upward trend threatens to leave even more people in developing countries further behind, as governments struggle to provide enough classrooms and jobs for a rapidly growing number of youth, and food insecurity becomes an even more urgent problem.
Nigeria is among eight countries the U.N. says will account for more than half the world’s population growth between now and 2050 – along with fellow African nations Congo, Ethiopia, and Tanzania.
“The population in many countries in sub-Saharan Africa is projected to double between 2022 and 2050, putting additional pressure on already strained resources and challenging policies aimed to reduce poverty and inequalities,” the U.N. report said.
It projected the world’s population will reach around 8.5 billion in 2030, 9.7 billion in 2050, and 10.4 billion in 2100.
Other countries rounding out the list with the fastest growing populations are Egypt, Pakistan, the Philippines, and India, which is set to overtake China as the world’s most populous nation next year.
In Congo’s capital, Kinshasa, where more than 12 million people live, many families struggle to find affordable housing and pay school fees. While elementary pupils attend for free, older children’s chances depend on their parents’ incomes.
“My children took turns” going to school, said Luc Kyungu, a Kinshasa truck driver who has six children. “Two studied while others waited because of money. If I didn’t have so many children, they would have finished their studies on time.”
Rapid population growth also means more people vying for scarce water resources and leaves more families facing hunger as climate change increasingly impacts crop production in many parts of the world.
“There is also a greater pressure on the environment, increasing the challenges to food security that is also compounded by climate change,” said Dr. Srinath Reddy, president of the Public Health Foundation of India. “Reducing inequality while focusing on adapting and mitigating climate change should be where our policy makers’ focus should be.”
Still, experts say the bigger threat to the environment is consumption, which is highest in developed countries not undergoing big population increases.
“Global evidence shows that a small portion of the world’s people use most of the Earth’s resources and produce most of its greenhouse gas emissions,” said Poonam Muttreja, executive director of the Population Foundation of India. “Over the past 25 years, the richest 10% of the global population has been responsible for more than half of all carbon emissions.”
According to the U.N., the population in sub-Saharan Africa is growing at 2.5% per year – more than three times the global average. Some of that can be attributed to people living longer, but family size remains the driving factor. Women in sub-Saharan Africa on average have 4.6 births, twice the current global average of 2.3.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 17, 2022 at 6:41pm
-
Remittances to Reach $630 billion in 2022 with Record Flows into Ukraine
https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2022/05/11/remittan...
WASHINGTON, May 11, 2022 — Officially recorded remittance flows to low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) are expected to increase by 4.2 percent this year to reach $630 billion. This follows an almost record recovery of 8.6 percent in 2021, according to the World Bank’s latest Migration and Development Brief released today.
-----------
Remittances to South Asia grew 6.9 percent to $157 billion in 2021. Though large numbers of South Asian migrants returned to home countries as the pandemic broke out in early 2020, the availability of vaccines and opening of Gulf Cooperation Council economies enabled a gradual return to host countries in 2021, supporting larger remittance flows. Better economic performance in the United States was also a major contributor to the growth in 2021. Remittance flows to India and Pakistan grew by 8 percent and 20 percent, respectively. In 2022, growth in remittance inflows is expected to slow to 4.4 percent. Remittances are the dominant source of foreign exchange for the region, with receipts more than three times the level of FDI in 2021. South Asia has the lowest average remittance cost of any world region at 4.3 percent, though this is still higher than the SDG target of 3 percent.
-------
Top 10 remittance receiving nation: India, China, Mexico, The Philippines,Egypt, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Germany and Nigeria.
https://www.worldremit.com/en/blog/money-transfer/top-10-remittance...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 18, 2022 at 8:59pm
-
India will become the world’s most populous country in 2023
China is now suffering from a demographic slump
https://www.economist.com/the-world-ahead/2022/11/14/india-will-bec...
China has been the world’s most populous country for hundreds of years. In 1750 it had an estimated 225m people, more than a quarter of the world’s total. India, not then a politically unified country, had roughly 200m, which ranked it second. In 2023 it will seize the crown. The un guesses that India’s population will surpass that of China on April 14th. India’s population on the following day is projected to be 1,425,775,850.
The crown itself has little value, but it is a signal of things that matter. That India does not have a permanent seat on the un Security Council while China does will come to seem more anomalous. Although China’s economy is nearly six times larger, India’s growing population will help it catch up. India is expected to provide more than a sixth of the increase of the world’s population of working age (15-64) between now and 2050.
China’s population, by contrast, is poised for a steep decline. The number of Chinese of working age peaked a decade ago. By 2050 the country’s median age will be 51, 12 years higher than now. An older China will have to work harder to maintain its political and economic clout.
Both countries took draconian measures in the 20th century to limit the growth of their populations. A famine in 1959-61 caused by China’s “great leap forward” was a big factor in persuading the Communist Party of the need to rein in population growth. A decade later China launched a “later, longer, fewer” campaign—later marriages, longer gaps between children and fewer of them. That had a bigger effect than the more famous one-child policy, introduced in 1980, says Tim Dyson, a British demographer. The decline in fertility, from more than six babies per woman in the late 1960s to fewer than three by the late 1970s, was the swiftest in history for any big population, he says.
It paid dividends. China’s economic miracle was in part the result of the rising ratio of working-age adults to children and oldsters from the 1970s to the early 2000s. With fewer mouths to feed, parents could invest more in each child than they otherwise would have. But having more parents than children, an advantage when the children are young, is a drawback as the parents age. The country will now pay a price as the economic-boomer generation retires and becomes dependent on the smaller generation following behind it.
India’s attempt to reduce fertility was less successful. It was the first country to introduce family planning on a national scale in the 1950s. Mass-sterilisation campaigns, encouraged by Western donors, grew and were implemented more forcefully during the state of emergency declared by Indira Gandhi, the prime minister, in 1975-77. Under the direction of her son Sanjay, the government forced men into vasectomy camps on pain of having their salaries docked or losing their jobs. Policemen nabbed poor men for sterilisation from railway stations. Around 2,000 men died from bungled procedures.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 18, 2022 at 8:59pm
-
India will become the world’s most populous country in 2023
China is now suffering from a demographic slump
https://www.economist.com/the-world-ahead/2022/11/14/india-will-bec...
Forced sterilisations ended after Indira Gandhi lost an election. Though brutal, the campaign was not thorough enough to cause a dramatic drop in India’s birth rate. India’s fertility has dropped, but by less, and more slowly than China’s. With a median age of 28 and a growing working-age population, India now has a chance to reap its own demographic dividend. Its economy recently displaced Britain’s as the world’s fifth-biggest and will rank third by 2029, predicts State Bank of India. But India’s prosperity depends on the productivity of its youthful people, which is not as high as in China. Fewer than half of adult Indians are in the workforce, compared with two-thirds in China. Chinese aged 25 and older have on average 1.5 years more schooling than Indians of the same age.
That will not spare China from suffering the consequences of the demographic slump it engineered. The government ended the one-child policy in 2016 and removed all restrictions on family size in 2021. But birth rates have kept falling. China’s zero-covid policy has made young adults even more reluctant to bear children. The government faces resistance to its plans to raise the average retirement age, which at 54 is among the lowest in the world. The main pension fund may run out of money by 2035. Yet perhaps most painful for China will be the emergence of India as a superpower on its doorstep.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 21, 2022 at 8:42am
-
There was a dip in Pakistani worker migration due to COVID in the last couple year. However, the numbers have picked up again with nearly 700,000 Pakistanis going to work overseas as of October this year.
https://beoe.gov.pk/?__cf_chl_jschl_tk__=b1b4890b1c9705af3b244646c1...
Overseas migration of Pakistanis is also diversifying, with an increasing number of migrants going to America and Europe. This is reflected in remittance sources. EU countries are now the fastest growing source of remittances to Pakistan.
https://www.riazhaq.com/2022/05/european-union-fastest-growing-sour...The data shows that a lot more of the migrants are now skilled labor while the share of unskilled migrants is declining.
Here's an ILO report excerpt:
"Pakistani migrant workers were skilled
(42%) and involved in semi-skilled jobs such as welders, secretaries, masons, carpenters, plumbers and so
on. Another proportion of the labour migration was composed of unskilled labourers (39%) such as
agriculturists, labourers or farmers. Projections about future trends indicate that the number of Pakistani
labour migrants will continue rising to reach 15.5 million in 2020 (Government of Pakistan, 2018"https://migration.iom.int/sites/g/files/tmzbdl1461/files/reports/Pa...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 21, 2022 at 9:05am
-
PAKISTAN MIGRATION SNAPSHOT AUGUST 2019
"While migration to Pakistan has a strong cross-border dimension, the main destination countries of the large Pakistani diaspora are scattered across the world. In 2017, 22 per cent of the 6 million Pakistani emigrants lived in Saudi Arabia, 18 per cent in India, 16 per cent in the United Arab Emirates, 15 per cent in Europe and 6 per cent in the United States of America (Figure 3)"
https://migration.iom.int/sites/g/files/tmzbdl1461/files/reports/Pa...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 21, 2022 at 9:15am
-
PAKISTAN MIGRATION SNAPSHOT
AUGUST 2019
https://migration.iom.int/sites/g/files/tmzbdl1461/files/reports/Pa...Table 1: Pakistan Key demographic indicators
Indicator Pakistan
Total area, in sq km, million 0.796
Population (2017), thousand d 197,016
Migrant population (2017), thousand d 3,398
Migrant population (2017), % total population d 1.7%
Urban Population (2017), % of total b 36.4%
Population Growth rate (2017), annual % b 1.9%
Human Development Index (2017) c 0.562
Country Rank out of 189 c 150/189
Unemployment (2017), % of labour force c 4.0%
Youth Unemployment (2017), % ages 15-24 c 7.7%
Multidimensional Poverty Headcount (2015), % 38.8%
Gini Coefficient (2010-2017)
c 30.7
Foreign Direct Investment (net inflows, 2017), current USD, billion b 2.815
Net Official Development Assistance Received (2017), current USD, billion b 2.953
Personal Remittances Received (2017), current USD, billion b 19.698
Personal Remittances Received (2017), % GDP b 6.5%
Source: b World Bank, 2018; c UNDP, 2018; d UNDESA, 2017;
e UNDP and OPHI (2016).
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Trump Leads America into an Unpopular War in the Middle East!
President Donald Trump joined Israel in yet another war of choice in the Middle East last week. Polls conducted in the United States immediately after the start of the Iran war show that the majority of Americans do not support it. A YouGov snap poll fielded Saturday — the day of the strikes — found 34% of Americans approve of the U.S. attacks on Iran, with 44%…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on March 3, 2026 at 10:00am — 3 Comments
India-Israel Axis Threatens Peace in South Asia
The bonhomie between Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu, an indicted war criminal, and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, accused of killing thousands of Muslims, was on full display this week in Israel. Both leaders committed to supporting the Afghan Taliban regime which is accused of facilitating cross-border terrorist attacks by the TTP in Pakistan. Mr. Modi was warmly welcomed by…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on February 27, 2026 at 10:45am — 2 Comments
© 2026 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()

You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network