PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
World at 8 Billion: Pakistan is Fourth Largest Contributor to Last Billion
The global population increased by one billion over the last 12 years to reach 8 billion this year, according to the United Nations. Pakistan contributed 49 million people to the last billion, making it the fourth largest contributor after India (177 million), China (73 million) and Nigeria (51 million). Nigeria is expected to soon overtake Indonesia and Pakistan to become the world's 4th most populous nation. More than half of the projected increase in the global population up to 2050 will be concentrated in eight countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines and the United Republic of Tanzania. Rising working age population is turning Pakistan into a major global consumer market. It is also fueling Pakistan's growing surplus labor exports and record overseas worker remittances.
 |
|
|
 |
| World Population Visualization in 2022. Source: Visual Capitalist |
World's 7th Largest Consumer Market:
Pakistan's share of the working age population (15-64 years) is growing as the country's birth rate declines, a phenomenon called demographic dividend. With its rising population of this working age group, Pakistan is projected by the World Economic Forum to become the world's 7th largest consumer market by 2030. Nearly 60 million Pakistanis will join the consumer class (consumers spending more than $11 per day) to raise the country's consumer market rank from 15 to 7 by 2030. WEF forecasts the world's top 10 consumer markets of 2030 to be as follows: China, India, the United States, Indonesia, Russia, Brazil, Pakistan, Japan, Egypt and Mexico. Global investors chasing bigger returns will almost certainly shift more of their attention and money to the biggest movers among the top 10 consumer markets, including Pakistan. Already, the year 2021 has been a banner year for investments in Pakistani technology startups.
 |
| Consumer Markets in 2030. Source: WEF |
 |
| World Population in 2050. Source: Visual Capitalist |
Labor Exports:
With rapidly aging populations and declining number of working age people in North America, Europe and East Asia, the demand for workers will increasingly be met by major labor exporting nations like Bangladesh, China, India, Mexico, Pakistan, Russia and Vietnam. Among these nations, Pakistan is the only major labor exporting country where the working age population is still rising.
 |
| Working Age Population Declining Among Major Labor Exporters. Sourc... |
Over 10 million Pakistanis are currently working/living overseas, according to the Bureau of Emigration. Before the COVID19 pandemic hit in 2020, more than 600,000 Pakistanis left the country to work overseas in 2019. Nearly 700,000 Pakistanis have already migrated in this calendar year as of October, 2022. The average yearly outflow of Pakistani workers to OECD countries (mainly UK and US) and the Middle East was over half a million in the last decade.
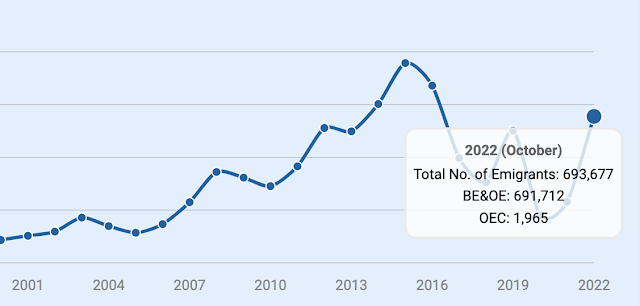 |
| Pakistani Workers Going Overseas. Source: Bureau of Emigration |
Haq's Musings
South Asia Investor Review
Pakistan is the 7th Largest Source of Migrants in OECD Nations
Pakistani-Americans: Young, Well-educated and Prosperous
Last Decade Saw 16.5 Million Pakistanis Migrate Overseas
Pakistan Remittance Soar 30X Since Year 2000
Pakistan's Growing Human Capital
Two Million Pakistanis Entering Job Market Every Year
Pakistan Projected to Be 7th Largest Consumer Market By 2030
Hindu Population Growth Rate in Pakistan
Do South Asian Slums Offer Hope?
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 28, 2022 at 6:56pm
-
What was Pakistan's Private Consumption Expenditure in 2022?
Pakistan Private Consumption Expenditure was reported at 324.824 USD bn in Dec 2022. This records an increase from the previous number of 290.625 USD bn for Dec 2021. See the table below for more data.
https://www.ceicdata.com/en/indicator/pakistan/private-consumption-...
Pakistan Private Consumption Expenditure was reported at 324.824 USD bn in Dec 2022. This records an increase from the previous number of 290.625 USD bn for Dec 2021.
Pakistan Private Consumption Expenditure data is updated yearly, averaging 31.179 USD bn from Dec 1960 to 2022, with 63 observations.
The data reached an all-time high of 324.824 USD bn in 2022 and a record low of 3.084 USD bn in 1960.
Pakistan Private Consumption Expenditure data remains in an active status in CEIC and is reported by CEIC Data.
The data is categorized under World Trend Plus’s Global Economic Monitor – Table: Nominal GDP: Private Consumption Expenditure: USD: Annual: Asia.
CEIC shifts year-end for annual Private Consumption Expenditure and converts it into USD. Private Consumption Expenditure is calculated as the sum of Household and NPISHs consumption. The Pakistan Bureau of Statistics provides Private Consumption Expenditure in local currency based on SNA 2008 with benchmark year 2015-2016. The State Bank of Pakistan average market exchange rate is used for currency conversions. Private Consumption Expenditure is reported in annual frequency, ending in June of each year. Private Consumption Expenditure prior to 2016 is based on SNA 2008 with benchmark year 2005-2006. Private Consumption Expenditure prior to 2000 is sourced from the World Bank.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 23, 2022 at 7:24pm
-
In mid-April, India is forecast to surpass China as the world's most populous country.
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-63957562
The Asian giants already have more than 1.4 billion people each, and for over 70 years have accounted for more than a third of the global population.
China's population is likely to begin shrinking next year. Last year, 10.6 million people were born, a little more than the number of deaths, thanks to a rapid drop in fertility rate. India's fertility rate has also fallen substantially in recent decades - from 5.7 births per woman in 1950 to two births per woman today - but the rate of decline has been slower.
So what does India overtaking China as the most populous country in the world mean?
China reduced its population growth rate by about half from 2% in 1973 to 1.1% in 1983.
Demographers say much of this was achieved by riding roughshod over human rights - two separate campaigns promoting just one child and then later marriages, longer gaps between children and fewer of them - in what was a predominantly rural and overwhelmingly uneducated and poor country,
India saw rapid population growth - almost 2% annually - for much of the second half of the last century. Over time, death rates fell, life expectancy rose and incomes went up. More people - especially those living in cities - accessed clean drinking water and modern sewerage. "Yet the birth rate remained high," says Tim Dyson, a demographer at the London School of Economics.
India launched a family planning programme in 1952 and laid out a national population policy for the first time only in 1976, around the time China was busy reducing its birth rate.
But forced sterilisations of millions of poor people in an overzealous family planning programme during the 1975 Emergency - when civil liberties were suspended - led to a social backlash against family planning. "Fertility decline would have been faster for India if the Emergency hadn't happened and if politicians had been more proactive. It also meant that all subsequent governments treaded cautiously when it came to family planning," Prof Dyson says.
East Asian countries such as Korea, Malaysia, Taiwan and Thailand, which launched population programmes much later than India, achieved lower fertility levels, cut infant and maternal mortality rates, raised incomes and improved human development earlier than India.
India has added more than a billion people since Independence in 1947, and its population is expected to grow for another 40 years. But its population growth rate has been declining for decades now, and the country has defied dire predictions about a "demographic disaster".
So India having more people than China is no longer significant in a "concerning" way, say demographers.
Rising incomes and improved access to health and education have helped Indian women have fewer children than before, effectively flattening the growth curve. Fertility rates have dipped below replacement levels - two births per woman - in 17 out of 22 states and federally administered territories. (A replacement level is one at which new births are sufficient to maintain a steady population.)
The decline in birth rates has been faster in southern India than in the more populous north. "It is a pity that more of India could not have been like south India," says Prof Dyson. "All things being equal, rapid population growth in parts of north India have depressed living standards".
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 23, 2022 at 7:25pm
-
In mid-April, India is forecast to surpass China as the world's most populous country.
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-63957562
It could, for example, strengthen India's claim of getting a permanent seat in the UN Security Council, which has five permanent members, including China.
India is a founding member of the UN and has always insisted that its claim to a permanent seat is just. "I think you have certain claims on things [by being the country with largest population]," says John Wilmoth, director of the Population Division of the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs.
The way India's demography is changing is also significant, according to KS James of the Mumbai-based International Institute for Population Sciences.
Despite drawbacks, India deserves some credit for managing a "healthy demographic transition" by using family planning in a democracy which was both poor and largely uneducated, says Mr James. "Most countries did this after they had achieved higher literacy and living standards."
More good news. One in five people below 25 years in the world is from India and 47% of Indians are below the age of 25. Two-thirds of Indians were born after India liberalised its economy in the early 1990s. This group of young Indians have some unique characteristics, says Shruti Rajagopalan, an economist, in a new paper. "This generation of young Indians will be the largest consumer and labour source in the knowledge and network goods economy. Indians will be the largest pool of global talent," she says.
India needs to create enough jobs for its young working age population to reap a demographic dividend. But only 40% of of India's working-age population works or wants to work, according to Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE).
More women would need jobs as they spend less time in their working age giving birth and looking after children. The picture here is bleaker: only 10% of working-age women were participating in the labour force in October, according to CMIE, compared with 69% in China.
Then there's migration. Some 200 million Indians have migrated within the country - between states and districts - and their numbers are bound to grow. Most are workers who leave villages for cities to find work. "Our cities will grow as migration increases because of lack of jobs and low wages in villages. Can they provide migrants a reasonable living standard? Otherwise, we will end up with more slums and disease," says S Irudaya Rajan, a migration expert at Kerala's International Institute of Migration and Development.
Demographers say India also needs to stop child marriages, prevent early marriages and properly register births and deaths. A skewed sex ratio at birth - meaning more boys are born than girls - remains a worry. Political rhetoric about "population control" appears to be targeted at Muslims, the country's largest minority when, in reality, "gaps in childbearing between India's religious groups are generally much smaller than they used to be", according to a study from Pew Research Center.
And then there's the ageing of India
Demographers say the ageing of India receives little attention.
In 1947, India's median age was 21. A paltry 5% of people were above the age of 60. Today, the median age is over 28, and more than 10% of Indians are over 60 years. Southern states such as Kerala and Tamil Nadu achieved replacement levels at least 20 years ago.
"As the working-age population declines, supporting an older population will become a growing burden on the government's resources," says Rukmini S, author of Whole Numbers and Half Truths: What Data Can and Cannot Tell Us About Modern India.
"Family structures will have to be recast and elderly persons living alone will become an increasing source of concern," she says.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 3, 2023 at 5:33pm
-
The year 2023 marks a historic turning point for Asia's demography: For the first time in the modern era, India is projected to surpass China as the most populous country.
https://asia.nikkei.com/Spotlight/Asia-Insight/Old-Japan-young-Indi...
Besides China (1.426 billion) and India (1.417 billion), five other Asian countries had over 100 million people as of 2022, the U.N. figures show. Indonesia had 276 million, Pakistan's population was at 236 million, Bangladesh counted 171 million, Japan had 124 million and the Philippines had 116 million. Vietnam, with 98 million, is expected to join the club soon.
------------
Even though economists expect India's gross domestic product to grow around 7% in 2023 -- the highest among major economies -- and although the worst of the COVID-19 pandemic appears to be over, India continues to face high unemployment rates of around 8%, according to the Center for Monitoring Indian Economy, a local private researcher. That shows the country is not creating enough jobs to support the growing population.
---------
Kumagai also said that India's growing demand for food could be felt beyond its borders.
"The challenge for India concerning food is that the production of agricultural products is easily affected by the weather," he said. "On the other hand, domestic demand is increasing rapidly. As such, when production is low, domestic supply is prioritized, which eventually may lead to restrictions on exports, just as India restricted wheat exports in 2022, which could cause food problems in other countries as well."
--------
While the South Asian nation's growing and youthful population spells opportunities for development, it also creates layers of challenges, from poverty reduction to education. Experts say soaring demand for food could affect India's trade with other countries, while the World Bank recently estimated that India will need to invest $840 billion into urban infrastructure over the next 15 years to support its swelling citizenry.
"This is likely to put additional pressure on the already stretched urban infrastructure and services of Indian cities -- with more demand for clean drinking water, reliable power supply, efficient and safe road transport amongst others," the bank's report said.
India's dilemmas are only part of a complex and diverging Asian population picture -- split between young, growing countries and aging, declining ones. Humanity's latest milestone turns a spotlight on this gap and the problems on both sides of it.
---
Reaching a world of 8 billion people signals significant improvements in public health that have increased life expectancy, the U.N. said. But it also pointed out, "The world is more demographically diverse than ever before, with countries facing starkly different population trends ranging from growth to decline."
Nowhere is this more apparent than in Asia. The region has young countries with a median age in the 20s, such as India (27.9 years old), Pakistan (20.4) and the Philippines (24.7), as well as old economies with median ages in the 40s, including Japan (48.7) and South Korea (43.9). The gap between the young and the old has gradually widened over the past decades.
While India faces a lack of jobs and infrastructure to support its growing population, Japan faces a serious reduction in births, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which its government says is a "critical situation." Either way, the population trends are increasingly impacting economies and societies.
Even though economists expect India's gross domestic product to grow around 7% in 2023 -- the highest among major economies -- and although the worst of the COVID-19 pandemic appears to be over, India continues to face high unemployment rates of around 8%, according to the Center for Monitoring Indian Economy, a local private researcher. That shows the country is not creating enough jobs to support the growing population.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 6, 2023 at 10:28am
-
India will soon overtake China as the world’s most populous country
But it will struggle to reap the benefits of a young workforce
https://www.economist.com/graphic-detail/2023/01/05/india-will-soon...
You might expect production to shift to labour-rich India. That is especially so as relations between China and the West become more hostile. But companies, especially in more advanced industries, tend to set up production in places where there are already suppliers and skilled workers. That is where India has a problem.
India’s development has relied less on industry than that of other emerging economies. Manufacturing generates 14% of Indian GDP, compared with 27% in China. What industry India does have clusters in the relatively prosperous south and west. But it is the poorer northern states that are making more babies (see map). Uttar Pradesh, for instance, is home to 17% of India’s population but has only 9% of its industrial jobs. That mismatch will hamper India’s economic growth.
Internal migration would help. Road, rail and air connections are improving. The government is investing massively in digitisation, which should encourage people to move by helping them to hold on to their ID cards, welfare benefits and voting rights and to communicate with their families at home.
Yet these efforts will take years, maybe decades, to pay dividends. Even as India’s population grows, it will struggle to capitalise on the potential of its young workforce.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 7, 2023 at 10:28am
-
Sadanand Dhume
@dhume
Contrary to all the hype, India’s market for consumer goods remains very small. The Chinese buy about 8X more iPhones and nearly 100X more BMWs than Indians. Starbucks has 20X as many outlets in China as in India. [My take] v
@WSJopinionhttps://www.wsj.com/articles/india-middle-class-free-trade-modi-tar...
https://twitter.com/dhume/status/1611155691540217858?s=20&t=FIh...
Sadanand Dhume
@dhume
This column has set off a mini firestorm here, so let me quickly respond to some of the objections. First, people point out that obviously China is a larger market than India. After all, it’s a larger economy. Chinese GDP in 2021: $17.73T. Indian GDP: $3.18T. 1/nhttps://twitter.com/dhume/status/1611369521146732553?s=20&t=FIh...
Sadanand Dhume
@dhume
But this doesn’t refute my central point—that contrary to popular belief India’s market is small by global standards. We should ask how China pulled so far ahead. In 1990 Chinese GDP ($360b) was similar to Indian GDP ($321b). Now China’s economy is 5.6X larger than India’s. 2/n
Sadanand Dhume
@dhume
Over the past decade, the gap between China and India has not shrunk. It has grown. In 2012, the Chinese economy was 4.7X larger than India’s. 3/nSadanand Dhume
@dhume
Moreover, as I show in my piece, mere GDP figures are misleading. For many consumer goods, the gap between the Chinese market and the Indian market is LARGER than the gap between Chinese and Indian GDP. 4/n
Sadanand Dhume
@dhume
Now to the second major objection: “Don’t talk about Starbucks, iPhones and Netflix subscriptions. These are luxury goods.” My response: The fact that they are luxury goods in India proves my point. If Indians had more disposable income they would not be seen as luxury goods. 5/n
Sadanand Dhume
@dhume
Or take cars, a middle class good in much of the world. In 2021, the Chinese bought 26.3m cars. Indians bought 3.7m cars. The Chairman of Maruti Suzuki recently pointed out that it could take 40 years for the Indian car market to catch up with China’s. 6/nIndia will take 40 yrs to draw level with China's car penetration: Bhargava
As a result, the small car market has been shrinking as two-wheeler customers shelve or delay plans to upgrade to a four-wheeled drivehttps://www.business-standard.com/article/companies/india-to-take-1...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 7, 2023 at 7:54pm
-
Postponing India’s census is terrible for the country
But it may suit Narendra Modi just fine
https://www.economist.com/asia/2023/01/05/postponing-indias-census-...
Three years ago India’s government was scheduled to pose its citizens a long list of basic but important questions. How many people live in your house? What is it made of? Do you have a toilet? A car? An internet connection? The answers would refresh data from the country’s previous census in 2011, which, given India’s rapid development, were wildly out of date. Because of India’s covid-19 lockdown, however, the questions were never asked.
Almost three years later, and though India has officially left the pandemic behind, there has been no attempt to reschedule the decennial census. It may not happen until after parliamentary elections in 2024, or at all. Opposition politicians and development experts smell a rat.
Narendra Modi often overstates his achievements. For example, the Hindu-nationalist prime minister’s claim that all Indian villages have been electrified on his watch glosses over the definition: only public buildings and 10% of households need a connection for the village to count as such. And three years after Mr Modi declared India “open-defecation free”, millions of villagers are still purging al fresco. An absence of up-to-date census information makes it harder to check such inflated claims. It is also a disaster for the vast array of policymaking reliant on solid population and development data.
India’s first proper census was conducted in 1881 by British colonial administrators, who calculated that finding out more about their subjects would help them consolidate power. Independent India continued to hold one every decade. Census data are used to determine who gets food aid, how much is paid to schools and hospitals across the country, and how constituency boundaries are drawn. They also form the basis for more detailed, representative-sample surveys on household consumption, a key measure of poverty, and on social attitudes and access to health care, education and technology.
For a while policymakers can tide themselves over with estimates, but eventually these need to be corrected with accurate numbers. “Right now we’re relying on data from the 2011 census, but we know our results will be off by a lot because things have changed so much since then,” says Pronab Sen, a former chairman of the National Statistical Commission who works on the household-consumption survey. And bad data lead to bad policy. A study in 2020 estimated that some 100m people may have missed out on food aid to which they were entitled because the distribution system uses decade-old numbers.
Similarly, it is important to know how many children live in an area before building schools and hiring teachers. The educational misfiring caused by the absence of such knowledge is particularly acute in fast-growing cities such as Delhi or Bangalore, says Narayanan Unni, who is advising the government on the census. “We basically don’t know how many people live in these places now, so proper planning for public services is really hard.”
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 7, 2023 at 7:55pm
-
Postponing India’s census is terrible for the country
But it may suit Narendra Modi just fine
https://www.economist.com/asia/2023/01/05/postponing-indias-census-...
The home ministry, which is in charge of the census, continues to blame its postponement on the pandemic, most recently in response to a parliamentary question on December 13th. It said the delay would continue “until further orders”, giving no time-frame for a resumption of data-gathering. Many statisticians and social scientists are mystified by this explanation: it is over a year since India resumed holding elections and other big political events.
True, the census process requires training some 3m “enumerators” to go door to door with the questionnaires, and the government’s ambition to register the answers digitally for the first time may make the task more complex. Teachers, who usually do much of this work, have only just returned to schools. The window for conducting the census is short, as the monsoon makes much of the country difficult to get around for much of the year. Yet such logistical hurdles never stopped previous administrators undertaking the census. Mr Modi should explain why his government appears unable to follow their lead.■
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 9, 2023 at 10:24am
-
Indians Are Leaving India in Droves, Most Going to Muslim Nations. Exodus Speeds Up Under Modi's Rule
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/nri/migrate/indians-are-leavin...
India had the largest diaspora population in the world with 18 million people from the country living outside their homeland in 2020, according to a report by the United Nations.
According to the 'International Migration 2020 Highlights', by the Population Division of the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA), the UAE, the US and Saudi Arabia host the largest number of migrants from India.
In 2020, 18 million persons from India were living outside their country of birth. Other countries with a large diaspora population included Mexico and Russia (11 million each), China (10 million) and Syria (8 million).
India's large diaspora is distributed across the United Arab Emirates (3.5 million), the United States of America (2.7 million) and Saudi Arabia (2.5 million). Other countries hosting large numbers of Indian migrants included Australia, Canada, Kuwait, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar and the United Kingdom, the report said.
Renouncing citizenships
More than 1.6 million Indians have renounced their citizenship since 2011, including 1,83,741 in 2022, according to government data.
The United States remains the main draw for Indians moving abroad and gaining citizenship in other countries.
As many as 1,63,370 Indians renounced their citizenship to become citizens of other countries in 2021, according to latest government data.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 9, 2023 at 10:44am
-
Between 2000 and 2020, the number of migrants grew in 179 countries or areas. Germany, Spain, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and the United States of America gained the largest number of migrants during that period. By contrast, in 53 countries or areas, the number of international migrants declined between 2000 and 2020. Armenia, India, Pakistan, Ukraine and the United Republic of Tanzania were among the countries that experienced the most pronounced declines. In many cases, the declines resulted from the old age of the migrant populations or the return of refugees and asylum seekers to their countries of origin.
https://www.un.org/en/desa/international-migration-2020-highlights
In 2020, Turkey hosted the largest number of refugees and asylum seekers worldwide (nearly 4 million), followed by Jordan (3 million), the State of Palestine (2 million) and Colombia (1.8 million).3 Other major destinations of refugees, asylum seekers or other persons displaced abroad were Germany, Lebanon, Pakistan, Sudan, Uganda and the United States of America.
In terms of regional migration corridors, Europe to Europe was the largest globally, with 44 million migrants in 2020, followed by the corridor Latin America and the Caribbean to Northern America, with nearly 26 million (figure 14). Between 2000 and 2020, some regional migration corridors grew very rapidly. The corridor Central and Southern Asia to Northern Africa and Western Asia grew the most, with 13 million migrants added between 2000 and 2020; more than tripling in size. The majority of that increase resulted from labour migration from Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, Nepal and Sri Lanka to the countries of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) (Valenta, 2020). While it is too soon to understand the full extent, the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 may have slowed the growth of this regional migration corridor. In many of the GCC countries, tens of thousands of migrant workers in the construction, hospitality, retail and transportation sectors lost their jobs due to the pandemic and were required to return home (UN-Habitat, 2020).
India’s diaspora, the largest in the world, is distributed across a number of major countries of destination, with the United Arab Emirates (3.5 million), the United States of America (2.7 million) and Saudi Arabia (2.5 million) hosting the largest numbers of migrants from India. Other countries hosting large numbers of migrants from India included Australia, Canada, Kuwait, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. China and the Russian Federation also have spatially diffused diasporas. In 2020, large numbers of migrants born in China were living in Australia, Canada, Italy, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Singapore and the United States of America. Migrants from the Russian Federation were residing in several countries of destination, many of which are member states of the CISFTA, including Belarus, Kazakhstan, Ukraine and Uzbekistan, as well as Germany and the United States of America.
Comment
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Next ›
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Trump Leads America into an Unpopular War in the Middle East!
President Donald Trump joined Israel in yet another war of choice in the Middle East last week. Polls conducted in the United States immediately after the start of the Iran war show that the majority of Americans do not support it. A YouGov snap poll fielded Saturday — the day of the strikes — found 34% of Americans approve of the U.S. attacks on Iran, with 44%…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on March 3, 2026 at 10:00am — 3 Comments
India-Israel Axis Threatens Peace in South Asia
The bonhomie between Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu, an indicted war criminal, and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, accused of killing thousands of Muslims, was on full display this week in Israel. Both leaders committed to supporting the Afghan Taliban regime which is accused of facilitating cross-border terrorist attacks by the TTP in Pakistan. Mr. Modi was warmly welcomed by…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on February 27, 2026 at 10:45am — 2 Comments
© 2026 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()

You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network