PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
Indian Students Score at Bottom on PISA & TIMSS International Rankings
Indian students rank near the bottom on PISA, a global test of learning standards conducted in 74 nations this year. TIMSS, another standardized international test, produced similar results earlier in 2003.
This is the first time that Indian students participated in PISA. Students from Himachal Pradesh and Tamil Nadu took the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) test, coordinated by the Paris-based Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Prior to this participation, students from Indian states of Orissa and Rajasthan took a similar test called Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) in 2003.
Tamil Nadu and Himachal Pradesh rank high on human development indicators among Indian states. The India Human Development Report 2011, prepared by the Institute of Applied Manpower Research (IAMR), categorized them as “median” states, putting them significantly ahead of the national average. IAMR is an autonomous arm of India's Planning Commission.
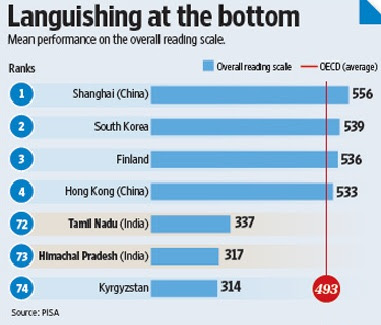
Himachal Pradesh ranked 4 and Tamil Nadu 11 in literacy rates on India's National Family Health Survey released in 2007. However, in the PISA study, Tamil Nadu ranked 72 and Himachal Pradesh 73, just ahead of the bottom-ranked Kyrgyzstan in mathematics and overall reading skills. Shanghai, China's biggest city, topped the PISA rankings in all three categories—overall reading skills, mathematical and scientific literacy. The new entrants included Costa Rica, Georgia, India (Himachal Pradesh & Tamil Nadu), Malaysia, Malta, Mauritius, Venezuela (Miranda), Moldova, United Arab Emirates. PISA 2009+ involved testing just over 46 000 students across these ten economies, representing a total of about 1,377,000 15-year-olds.
In Tamil Nadu, only 17% of students were estimated to possess proficiency in reading that is at or above the baseline needed to be effective and productive in life. In Himachal Pradesh, this level is 11%. “This compares to 81% of students performing at or above the baseline level in reading in the OECD countries, on an average,” said the study.
The average Indian child taking part in PISA2009+ is 40 to 50 points behind the worst students in the economic superstars. Even the best performers in Tamil Nadu and Himachal Pradesh - the top 5 percent who India will need in science and technology to complete globally - were almost 100 points behind the average child in Singapore and 83 points behind the average Korean - and a staggering 250 points behind the best in the best.
The average child in HP & TN is right at the level of the worst OECD or American students (only 1.5 or 7.5 points ahead). Contrary to President Obama's oft-expressed concerns about American students ability to compete with their Indian counterparts, the average 15-year-old Indian placed in an American school would be among the weakest students in the classroom, says Lant Pritchett of Harvard University. Even the best TN/HP students are 24 points behind the average American 15 year old.
The 2003 TIMSS study ranked India at 46 among 51 countries. Indian students' score was 392 versus average of 467 for the group. These results were contained in a Harvard University report titled "India Shining and Bharat Drowning".
These results are not only a wake-up call for the "India Shining" brigade, but also raise serious questions about the credibility of India's western cheerleaders like Indian-American journalist Fareed Zakaria and New York Times' columnist Tom Friedman.
Related Links:
India Shining, Bharat Drowning
Learning Levels and Gaps in Pakistan by Jishnu Das and Priyanka Pandey
Pasi Sahlberg on why Finland leads the world in education
CNN's Fixing Education in America-Fareed Zakaria
Poor Quality of Education in South Asia
Infections Cause Low IQs in South Asia, Africa?
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 29, 2011 at 8:24pm
-
Whys is India not a scientific power, asks an Op Ed in The Hindu:
.....It is the robustness of scientific research and innovation that sets apart great powers from the mediocre ones.
We have good scientists, but why has India not produced outstanding scientists who make path-breaking discoveries that will make the world sit up and take notice? Should we continue to be satisfied with tweaking borrowed technologies? Is reverse engineering an innovative phenomenon?
All debates about scientific research inevitably end up zeroing in on the deficiencies of our educational system as the root cause of the abysmal record in scientific research. This is only part of the story.
A nation's culture — belief systems, values, attitudes — plays a significant role in determining the quality of scientific research. The Oriental attitudes differ from the Occidental values in many respects. Asian societies are basically collectivist, that is, the collective good of society ranks higher than individual happiness and achievements. People do not ask what they can do for their country; they are always asking what the country will do for them. They look up to the state for guidance, leadership and direction. There is no burning individual ambition to excel and achieve something new.
In the West, individuals try to achieve their potential through their own efforts, aided and facilitated by enabling laws and institutions. Self-reliance is the key objective of life. An independent life requires a free and questioning mindset that takes nothing for granted and constantly challenges conventional wisdom. Children are encouraged to push the frontiers of knowledge by self-examination and open-minded enquiry. It is only a sceptical and dissenting mind that often thinks out of the box to explore new vistas of knowledge.
Collectivism promotes conformism and deference to authority whether it is parents, elders, teachers or the government. It is heresy to question established values and customs.
We pass on our passivity and uncritical attitudes to our children. No wonder, the educational system encourages rote learning and unquestioning acceptance of what is taught in the classrooms and stated in the textbooks. How can we expect our children to suddenly develop an enquiring and inquisitive attitude when they have been brought up in a milieu that discourages ‘disruptive' thoughts?
India and China were once advanced nations before foreign rule drained their resources and sapped their willpower and scientific traditions. Cultures tend to become conservative and defensive when subjected to long spells of colonial exploitation.
Indians are great believers in destiny. But our tradition does not frown upon free will and individual excellence. We must realise that our ability for free action remains unhampered despite what destiny may hold in store for us.
Fear of failureAnother flaw in our culture that prevents individual excellence is the fear of failure. The stigma associated with failure makes our children risk-averse while choosing their courses and careers.
Scientific research is a long-drawn war on received wisdom that requires many battles before it can be won. Science was not built in a day. Some of the battles can end in defeat. In the West, they celebrate failure as a stepping stone to success.
Educational reforms must be preceded by mental deconditioning of parents, teachers, educationists and policymakers — throwing away the cobwebs of uncritical submissiveness to conventional knowledge. Let us bring up a generation that will not hesitate to ask inconvenient questions. This generation will be the torch-bearer of a scientific revolution that will unleash cutting-edge research to make the Nobel Prize committee sit up and take notice....
http://www.thehindu.com/opinion/open-page/article2704625.ece
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 29, 2011 at 11:33pm
-
Here's a Financial Times Report on the inadequacy of India's primary education:
Primary education standards in India are as bad as in Papua New Guinea and crisis-torn Afghanistan and Yemen, according to a team of Indian development economists.
In a study of schools in the country’s most populous states they found that fast-paced economic growth has failed to improve India’s basic educational standards over the past 15 years. The Public Report on Basic Education Revisited showed some children were unable to read after three years of schooling across the Hindi-speaking northern belt.
“When the investigators arrived, half of the government schools were still devoid of any teaching activity,” the report said. “In a functioning democracy, this would be a major national concern. Yet little notice has been taken in the corridors of power.”
According to Jean Drèze, one of the report’s researchers and a prominent Indian policymaker, India now finds itself in an adult-literacy peer group that includes Afghanistan, Papua New Guinea and Yemen.
The ratio of students to teachers in Indian primary schools was three times higher than in China, with a typical class in Bihar, one of the poorest states, having as many as 92 pupils.
“After 20 years of meteoric economic growth, there’s been so little improvement in terms of the living standards of the people,” Mr Drèze said. “There’s a very serious crisis. We have to wake up to the fact that we are relying too heavily on economic growth.”
There are 5.5m teachers in India, but at least 1.2m more are required. “The reason there aren’t any teachers in school is because states have not recruited them for many years,” said Kapil Sibal, minister of Human Resources Development.
The report’s authors said that it had taken years to analyse and verify data collected in states such as Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. One team member, A.K. Shiva Kumar, said that he and his colleagues had also reviewed educational data for the 2009-2010 year and found them to be “identical” to those of 2006.
The UN Development Programme’s Human Development Report for 2010 said Indians received just 4.4 years of schooling on average, compared with 7.5 years for China’s citizens. Sri Lanka outscores both with 8.2 years of schooling and is on par with China’s 99 per cent literacy rate for young female adults.
“Most developing countries are talking of [offering their children] 10 years of schooling,” said Mr Kumar, who is also a development economist and advises Unicef, the UN’s child welfare agency. “Here there’s lots of focus on growth rates but we are not looking at how India gets to 10 years of schooling.”
Meera Samson, a researcher at the Delhi-based Collaborative Research and Dissemination and report co-author, said head teachers had not been appointed at 20 per cent of the schools surveyed. At another 12 per cent of schools, only one teacher had been offered a position.
Last year, India’s parliament passed legislation requiring the state to provide universal education.
http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/3b2c9da2-cf01-11e0-86c5-00144feabdc0.html...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 6, 2012 at 6:44pm
-
Here's an uplifting story in Express Tribune about a Pakistani with 28 A's in O Level exams:
Prime Minister Yousaf Raza Gilani has presented a cheque of Rs1 million as a token of appreciation to a student from Taxila who had set a world record in the O-level examinations.
Zohaib Asad, a student of Beaconhouse, earned 28 As in the University of Cambridge International O-Level Examinations in 2011. He overtook a record of 23 As, also set by a Pakistani student from Islamabad Ibrahim Shahid.
Gilani invited Asad to the Prime Minister House on Thursday and lauded him for making Pakistan’s youth proud. He said that Asad’s achievement will inspire other young students to excel in life through sheer hard work.
Asad is currently enrolled at McGill University in Montreal, Canada, where he is pursuing an undergraduate degree in economics and international development.
Speaking to the prime minister, he said that he was determined to return to Pakistan after completion of his education to serve the country that has given so much in life at an early age.
Gilani appreciated Asad’s sense of devotion to the country the country and said that young people like him were Pakistan’s hope for a brighter future.
Asad’s family members were also present in the meeting.
http://tribune.com.pk/story/317004/pm-honours-student-who-set-o-lev...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on February 25, 2012 at 9:18pm
-
Here's Russian analyst Anatol Karlin on India's prospects and its comparison with China:
It is not a secret to longtime readers of this blog that I rate India’s prospects far more pessimistically than I do China’s. My main reason is I do not share the delusion that democracy is a panacea and that whatever advantage in this sphere India has is more than outweighed by China’s lead in any number of other areas ranging from infrastructure and fiscal sustainability to child malnutrition and corruption. However, one of the biggest and certainly most critical gaps is in educational attainment, which is the most important component of human capital – the key factor underlying all productivity increases and longterm economic growth. China’s literacy rate is 96%, whereas Indian literacy is still far from universal at just 74%.
-----------
The big problem, until recently, was that there was no internationalized student testing data for either China or India. (There was data for cities like Hong Kong and Shanghai, but it was not very useful because they are hardly representative of China). An alternative approach was to compare national IQ’s, in which China usually scored 100-105 and India scored in the low 80′s. But this method has methodological flaws because the IQ tests aren’t consistent across countries. (This, incidentally, also makes this approach a punching bag for PC enforcers who can’t bear to entertain the possibility of differing IQ’s across national and ethnic groups).
--------------
Many Indians like to see themselves as equal competitors to China, and are encouraged in their endeavour by gushing Western editorials and Tom Friedman drones who praise their few islands of programming prowess – in reality, much of which is actually pretty low-level stuff – and widespread knowledge of the English language (which makes India a good destination for call centers but not much else), while ignoring the various aspects of Indian life – the caste system, malnutrition, stupendously bad schools – that are holding them back. The low quality of Indians human capital reveals the “demographic dividend” that India is supposed to enjoy in the coming decades as the wild fantasies of what Sailer rightly calls ”Davos Man craziness at its craziest.” A large cohort of young people is worse than useless when most of them are functionally illiterate and innumerate; instead of fostering well-compensated jobs that drive productivity forwards, they will form reservoirs of poverty and potential instability.Instead of buying into their own rhetoric of a “India shining”, Indians would be better served by focusing on the nitty gritty of bringing childhood malnutrition DOWN to Sub-Saharan African levels, achieving the life expectancy of late Maoist China, and moving up at least to the level of a Mexico or Moldova in numeracy and science skills. Because as long as India’s human capital remains at the bottom of the global league tables so will the prosperity of its citizens....
http://www.sublimeoblivion.com/2012/02/04/china-superior-to-india/
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 16, 2012 at 9:11pm
-
Here's Times of India on Indian textbook distortions about Pakistan: Pakistan is a part of India and P V Narasimha Rao is the Prime Minister of the country, this is being taught to school students in some states, according to a member of Parliament.
AIADMK member S Semmalai highlighted this in Lok Sabha today while referring to the controversy over Ambedkar cartoon in CBSE textbooks during a discussion on Central Educational Institutions (Reservation in Admission) Amendment Bill, 2011.
"In the CBSE textbooks of Karnataka, it is mentioned even now that Pakistan is a part of India. It went on to state that American constitution is based on capitalism. Class-III students of Urdu medium in Andhra Pradesh are taught that P V Narasimha Rao is the Prime Minister of the country," Semmalai said, evoking laughter all around the House.
Finding further faults with the textbooks, he said, "In the CBSE textbooks, a forest is defined as a group of trees and heavy industry is defined as one where heavy type of raw materials are used."
The member said that only 15 per cent of graduates are suitable for employment and it is a sorry state of affairs. It reflects the poor quality of education at all levels, from primary to higher levels.
He lamented, "If this is the quality and stuff that we provide to our students, one can imagine what will be the standard of our students.
"Unless we make concerted efforts to allocate six per cent of the GDP to education, our goal will remain unreachable," he added.
http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/School-textbooks-Pakistan-...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 11, 2012 at 4:45pm
-
Here's a Wharton School piece on India's low ranking on innovation index:
Just a few weeks ago, global credit rating agency Standard and Poor’s (S&P) released a study titled, “Will India be the first BRIC fallen angel?” The report suggests that India may become the first “BRIC” country (Brazil, Russia, India and China) to lose its investment grade rating. While it remains to be seen if India can escape this ignominy, the country has earned another dubious distinction: It ranks the lowest among the BRIC nations on the Global Innovation Index 2012.
This innovation index was released recently by the international business school INSEAD and the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) along with the Confederation of Indian Industries (CII), Alcatel-Lucent and Booz & Co. The index ranks 141 countries on the basis of their innovation capabilities and results. Brazil, Russia and China were ranked 58th, 51st and 34th respectively. India stands at the 64th position, two notches below where the country landed last year.
According to the study, “The innovation front in India continues to be penalized by deficits in human capital and research; infrastructure and business sophistication, where it comes last among BRICs, and in knowledge and technology outputs, where it comes in ahead of Brazil only.” The report also notes that the BRIC countries need to invest further in their innovation capabilities to live up to their expected potential.
Vijay Govindarajan, a professor of international business at Dartmouth College and the first professor-in-residence and chief innovation consultant at General Electric, points out that innovation is critical to India’s future. He suggests that the government must provide seed capital to strengthen applications research and create incentives for universities, research labs and industry to collaborate. “Much is at stake if India does not move up on the Global Innovation Index,” Govindarajan says. “Without business model innovations, India cannot solve the problems for 90% of Indians. Such innovations can then be used to launch global strategies. This is the essence of reverse innovation [innovations adopted first in the developing world] — where India can lead.”
As part of the same report, India is ranked second (behind China) in the global innovation efficiency index. (The innovation efficiency index is the ratio of innovation input and innovation output.) Chandrajit Banerjee, director-general of CII notes that innovation efficiency is “a ratio and not a direct measure …. [This implies that] while India can produce innovation output best in the world when equal amounts of input are fed into its innovation ecosystem, it also needs to strengthen certain innovation drivers that will improve the situation.”
Gopichand Katragadda, managing director of General Electric’s John F. Welch Technology Center in Bangalore adds: “The results of the study point to the fact that, in India, the innovation ecosystem (input) is poor while the knowledge/creative output under the constraints is good. One interpretation of this is that we need better government measures on regulations, education and infrastructure to tap the demonstrated potential of talented people.”
According to Katragadda, if India does not get its act together on the innovation front, the country could lose the opportunity “to make this a century of Indian innovation, tapping into the brilliant technical minds of the region.”
http://knowledgetoday.wharton.upenn.edu/2012/07/india-ranks-lowest-...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on October 8, 2012 at 10:43pm
-
India has decided to drop out of 2012 PISA, report Steve Sailor and Times of India:
I always try to keep up on China and India test score news, since the topic offers us important clues about the future of the world. From the Times of India:
After an earlier, embarrassing show, India has backed out of this year's Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), a global evaluation process by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Secretariat that gauges where schoolchildren stand alongside their peers from other countries.
This academic Olympics measures the performance of 15-year-olds in their reading, math and science abilities.
... In the last assessment, Tamil Nadu and Himachal Pradesh, showpieces of India's education and development, were put through the PISA evaluation and they performed miserably. The idea was that the entire country would participate in the next round of assessment. However, that plan was also dropped.
http://isteve.blogspot.co.uk/2012/08/india-drops-out-of-2012-pisa-t...
Here are some excuses for poor performance as reported in The Indian Express:
Just why did Indians perform so badly at the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) as to stand at the bottom of the ladder? The government thinks it is not a reflection on the country’s schooling. Advised by the NCERT, the HRD Ministry has concluded that India trailed in the international rankings because of the questions posed.
Terming these out of context, the government will take up the issue with organisers of PISA before deciding on full-scale participation in the test for 2012, with students from 10 of its states.
-----------
Incidentally, PISA results were reaffirmed by NGO Pratham’s annual ASER report on learning levels of schoolchildren.Why ATM, air Bag questions: officials
The NCERT in its report concluded that “non-exposure of students (especially in rural areas) towards the items tested in PISA” was a critical factor in the poor performance by Indian students. They cited questions relating to ATMs and use of air bags in cars.
http://www.indianexpress.com/news/poor-pisa-score-govt-blames--disc...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 21, 2013 at 10:28am
-
Here's Business Standard on declining reading skills among Indian students:
Five out of 10 school students of class V in rural India cannot solve simple arithmetic problems, says a nationwide survey on education.
Putting a question mark on the quality of education imparted, the findings of the Annual Status of Education Report (ASAR) said while in 2010 more than half of class V students were able to read class II level texts, the proportion came down to 46.8 per cent in 2012.
"The decline in reading levels is more visible among children in government schools as compared to those in private schools... It has fallen from 50.7 per cent in 2010 to 41.7 per cent in 2010," the report prepared by Pratham, a voluntary organisation, said.
HRD Minister M M Pallam, who released the report, expressed his "dismay" over some of the findings even as he dismissed suggestion that the decline was due to introduction of contentious and comprehensive evaluation (CCE) process in classrooms.
"... I will certainly not attribute it to the factor of CCE," he said after president of Pratham Education Foundation Madhav Chavan sought to highlight CCE for some of the negative indicators.
Raju also appeared to play down the findings of the report, saying it is a "dipstick survey".
He said the ministry has its own NCERT survey conducted every three years though he acknowledged that the survey underscores that "it is important we all work together".
The report was based on a survey carried out in rural schools across 567 districts and covering about six lakh children in the age of 3-16.
Highlighting the declining reading level, the report said that while seven out of 10 children (70.9 per cent) in class 5 were able to solve simple two-digit subtraction problem, it declined to five out of 10 (53.5 per cent) in 2012.
http://www.business-standard.com/generalnews/news/sharp-decline-in-...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 4, 2013 at 9:22am
-
Here are a few excerpts of a recent NY Times Op Ed by Rakesh Mani on sad state of education in India:
It is now almost four years since I first walked through a series of winding by-lanes in a Mumbai slum toward my new job as a teacher at a low-income school. I was forced to confront India’s educational inequities squarely in the eye. Students filed into a dilapidated old school building, and my own musty classroom, crammed with cupboards, barely left any room to move.
What was more jarring than my physical surroundings, however, was the magnitude of my students’ achievement gap. Only a handful of my third-grade students could read first-grade books, and almost all struggled with elementary arithmetic. Despite this being an English-language school, few teachers – and fewer students – could speak the language at all. Indeed, most of my students were unable to recognize basic alphabets or perform simple addition.
This was compounded by the sobering fact that families in my slum scrounged to send their kids – boys and girls – to the very best schools they could afford. Why? Because they recognized that education was their only weapon against penury and struggle. They dreamed of their children going on to build livelihoods in a burgeoning economy and pulling them out of the slums.
Rubina, a fourth grade student at the Umedbhai Patel School in Mumbai, Maharashtra, in this Aug., 2010 photo.Courtesy of Rakesh Mani Rubina, a fourth grade student at the Umedbhai Patel School in Mumbai, Maharashtra, in this Aug., 2010 photo.Unfortunately, the poor quality of instruction (and high levels of teacher absenteeism) across the proliferation of shoddy schools ensures that they will hardly be able to compete – whether for university admissions or for jobs – with students who can afford expensive, high-quality schooling. Moreover, according to the National Family Health Survey, India now has the highest rate of child malnourishment on the planet – almost twice that of sub-Saharan Africa.
------------
The situation across the rest of the country is not much different – according to recent figures, 4 percent of Indian children never start school, 57 percent don’t complete primary school and almost 90 percent — around 172 million — will not complete secondary school. These numbers should deeply anger Indians and force them to question society’s priorities and values.
---------
In just a few more decades, the implications of India’s apathy will have profound implications – not just within the country, but around the world as well.http://india.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/03/25/what-are-you-doing-to-fix...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 6, 2013 at 7:10pm
-
Here's a piece by Thane Richard, a Brown University student who did a semester abroad at St. Stephens College in India:
“Wait, what?! You are studying here for three years just so you can go do it again for four more years?” I could not grasp the logic of this. What changed my understanding was when I started taking classes at St. Stephen’s College. Except for one, they were horrible.
This was not an isolated incident — all my fellow exchange students concurred that the academics were a joke compared to what we were used to back home. In one economic history class the professor would enter the room, take attendance, open his notebook, and begin reading. He would read his notes word for word while we, his students, copied these notes word for word until the bell sounded. Next class he would find the spot where the bell had interrupted him, like a storyteller reading to children and trying to recall where he had last put down the story. He would even pause slightly at the end of a long sentence to give us enough time to finish writing before he moved on. And this was only when he decided to show up — many times I arrived on campus to find class abruptly cancelled. Classmates exchanged cell phone numbers and created phone trees just to circulate word of a cancelled class. I got a text almost daily about one of my classes. My foreigner peers had many similar experiences.
---------------
To pause for a moment, here is the problem with me talking about this topic: right now many Indians reading this are starting to feel defensive. “Nationalist” is a term I have heard as a self-description as they defend Mother India from the bigoted, criticising foreigner. They focus on me rather than the problem. I have had people unfriend me on Facebook and walk out on meals because I politely expressed an opinion on politics or history that went against the publicly consented “Indian opinion.” For a nation that prides itself on the 17 languages printed on its currency, I am greeted with remarkable intolerance. Even after living in India for close to three years, attending an Indian college, working for an Indian company, founding an Indian company, paying taxes in India, and making India my home, I am not Indian enough to speak my mind. But in a nation that rivals all others in the breadth of its human diversity, who is Indian enough? Because if loyalty and a feeling of patriotism were the barometers for “Indianness,” rather than skin colour or a government document, then I would easily be a dual U.S.-Indian citizen. This Indian defensiveness is false nationalism. It is not a stance that cares about India, it is one that cares about what others think of India, which is not nationalism. That is narcissism.
My voice should be drowned out by the millions around me who are disappointed with how they have been short-changed by the Indian government — their government. Education is one of the most poignant examples of this and serves as great dinner conversation amongst the elite:
“The Indian education system is lost in the past and failing India.” Everyone at the table nods, mumbles their concurrence, and cites the most recent Economist article or Pricewaterhouse Cooper study on the matter in order to masquerade as informed....http://www.thehindu.com/features/education/college-and-university/a...
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Pakistani Student Enrollment in US Universities Hits All Time High
Pakistani student enrollment in America's institutions of higher learning rose 16% last year, outpacing the record 12% growth in the number of international students hosted by the country. This puts Pakistan among eight sources in the top 20 countries with the largest increases in US enrollment. India saw the biggest increase at 35%, followed by Ghana 32%, Bangladesh and…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on April 1, 2024 at 5:00pm
Agriculture, Caste, Religion and Happiness in South Asia
Pakistan's agriculture sector GDP grew at a rate of 5.2% in the October-December 2023 quarter, according to the government figures. This is a rare bright spot in the overall national economy that showed just 1% growth during the quarter. Strong performance of the farm sector gives the much needed boost for about …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on March 29, 2024 at 8:00pm
© 2024 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()

You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network